Sialic acid derivative modified ibrutinib (IBR) nanocomposite and preparation method thereof
A technology of sialic acid derivatives and nanocomposites, which is applied in the field of medicine, can solve the problems of high clinical dosage and patients' inability to take drugs orally, and achieve the effect of suppressing growth
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0079] The synthesis of embodiment 1 sialic acid methyl ester derivative MT-18
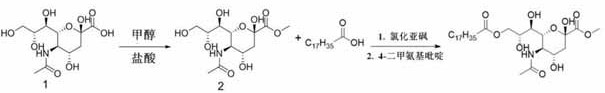
[0080] Accurately weigh 20 g of sialic acid, stir in 250 mL of methanol containing 3.68 M hydrochloric acid, and reflux at 50° C. for 2.5 h. The solvent was removed by vacuum drying and washed with cold methanol to give a residual mixture. The methylated sialic acid was obtained as a white solid after purification by recrystallization.
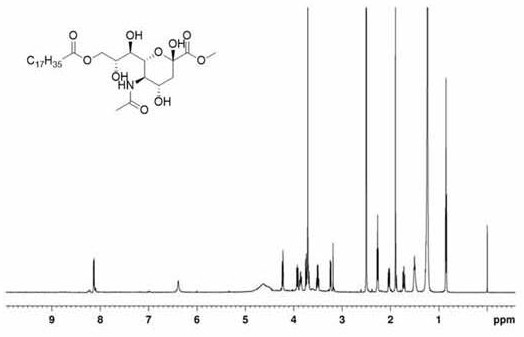
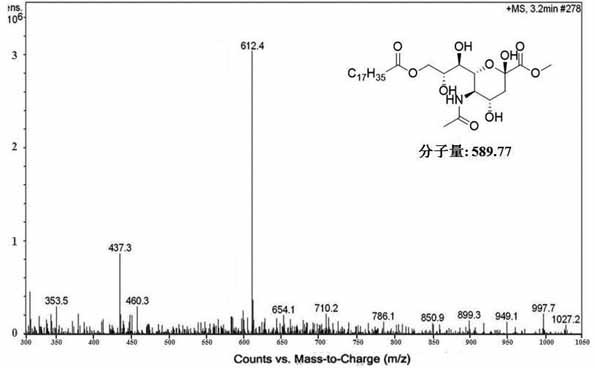
[0081] Accurately weigh 7.5 g of stearic acid and dissolve it in 0.233 mol of thionyl chloride with stirring for 1 h, and remove the residual solvent by evaporation under reduced pressure. Next, 3 g of methylated sialic acid and 0.1 g of 4-dimethylaminopyridine were dissolved in 30 mL of anhydrous pyridine. Subsequently, a dichloromethane solution containing 2.8 g of octadecyl chloride was added dropwise to the mixture at 0° C., and the reaction was stirred at the same temperature for 30 min. Afterwards, the temperature of the reactant was adjusted to room temp...
Embodiment 2
[0083] The synthesis of embodiment 2 sialic acid octadecanoic acid derivative SA-18
[0084] Accurately weigh 20 g of sialic acid, stir in 250 mL of methanol containing 3.68 M hydrochloric acid, and reflux at 50° C. for 2.5 h. The solvent was removed by vacuum drying and washed with cold methanol to give a residual mixture. The methylated sialic acid was obtained as a white solid after purification by recrystallization. Accurately weigh 7.5 g of stearic acid and dissolve it in 0.233 mol of thionyl chloride with stirring for 1 h, and remove the residual solvent by evaporation under reduced pressure. Next, 3 g of methylated sialic acid and 0.1 g of 4-dimethylaminopyridine were dissolved in 30 mL of anhydrous pyridine. Subsequently, a dichloromethane solution containing 2.8 g of octadecyl chloride was added dropwise to the mixture at 0° C., and the reaction was stirred at the same temperature for 30 min. Afterwards, the temperature of the reactant was adjusted to room temperat...
Embodiment 3
[0086] The synthesis of embodiment 3 ethyl sialic acid derivatives ET-18
[0087] Accurately weigh 20 g of sialic acid, stir in 250 mL of ethanol containing 3.68 M hydrochloric acid, and reflux at 50° C. for 2.5 h. The solvent was removed by vacuum drying and washed with cold methanol to give a residual mixture. Ethylated sialic acid was obtained as a white solid after purification by recrystallization.
[0088] Accurately weigh 7.5 g of stearic acid and dissolve it in 0.233 mol of thionyl chloride with stirring for 1 h, and remove the residual solvent by evaporation under reduced pressure. Next, 9.2 mmol of ethylated sialic acid and 0.1 g of 4-dimethylaminopyridine were dissolved in 30 mL of dry pyridine. Subsequently, a dichloromethane solution containing 2.8 g of octadecyl chloride was added dropwise to the mixture at 0° C., and the reaction was stirred at the same temperature for 30 min. Afterwards, the temperature of the reactant was adjusted to room temperature and th...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com