Neuronal intranuclear inclusion disease NOTCH2NLC gene GGC repeat amplification detection kit
A kit and neuron technology are applied in the field of detection of GGC repeat expansion of NOTCH2NLC gene in neuron nuclear inclusion body disease, which can solve the problems of easy misdiagnosis or missed diagnosis, difficulty in amplification of high GC sequences, and difficult detection, etc. The effect of small amount, overcoming the limitation of amplification length, and low price
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] Example 1: Preparation of NOTCH2NLC gene GGC repeat rapid screening kit
[0027] 1. Primer design
[0028] A pair of PCR system I specific upstream primer NOTCH2NLC-F and downstream primer NOTCH2NLC-R were designed within 200 bp of the upstream 5' end and downstream 3' end of the GGC repeat sequence of the NOTCH2NLC gene to amplify the target genome including the GGC repeat region, 5' flanking region and 3' flanking region. The 5' flanking region is 80bp, the 3' flanking region is 158bp, and the length of the amplified fragment is (238+3xn)bp, where n represents the number of GGC repeats. The formula for calculating the GGC repeat number in the normal range is: GGC repeat number=(PCR product length-238) / 3. When the length of the PCR product is 358bp, it is the upper limit of the normal value (40 repeats). When the number of repeats exceeds 100 GGCs, the resolution of capillary electrophoresis will continue to decrease, so the number of repeats needs to be corrected b...
Embodiment 2
[0037] Example 2: PCR system 1 screening of abnormally amplified GGC samples
[0038]Use a commercially available genomic DNA extraction kit to extract genomic DNA from the peripheral blood of female samples with a concentration of at least 50ng / μL, 260 / 230 value greater than 2.0, and 260 / 280 value greater than 1.8.
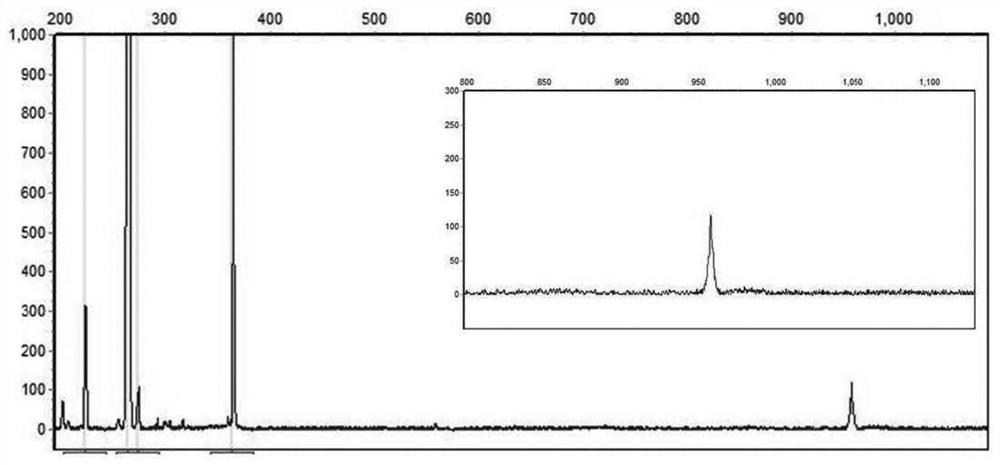
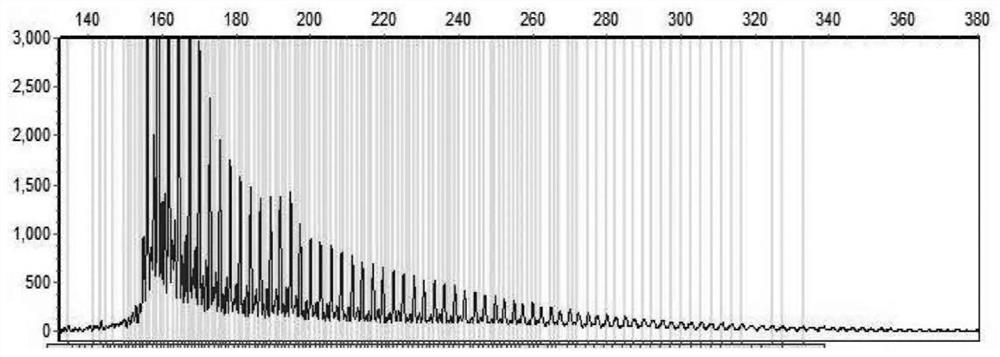
[0039] PCR system I reaction system prepared using the kit of Example 1: prepare 25 μL PCR system in a 200 μL PCR thin-walled tube. The sequences of primers NOTCH2NLC-F and NOTCH2NLC-R are: SEQ ID NO:1 and SEQ ID NO:2, respectively. PCR amplification program: pre-denaturation at 98°C for 10 minutes; 30 cycles of 97°C for 35 seconds→65°C for 35 seconds→68°C for 5 minutes; extension at 72°C for 10 minutes. After the reaction, 1 μL PCR product was taken, mixed with 10 μL deionized formamide and 1 μL DNA internal standard ROX1000, denatured at 95°C for 5 minutes, and cooled on ice. The mixture was subjected to capillary electrophoresis with ABI 3730, the injection ...
Embodiment 3
[0040] Example 3: PCR system 2 to screen abnormally amplified samples of GGC
[0041] Use the kit of Example 1 to prepare PCR system 2 reaction system: prepare 25 μL PCR system in a 200 μL PCR thin-walled tube.
[0042] The sequence of primer NOTCH2NLC-R is SEQ ID NO:2, the sequence of NOTCH2NLC-T is SEQ ID NO:3; the sequence of NOTCH2NLC-GGC4 is SEQ ID NO:4. PCR amplification program: pre-denaturation at 98°C for 10 minutes; 98°C for 45 seconds → 64°C for 45 seconds → 68°C for 6 minutes, 10 cycles; 98°C for 45 seconds → 68°C for 5 minutes, 20 cycles; extension at 72°C for 10 minutes . After the reaction, 1 μL of PCR product was taken, mixed with 10 μL of deionized formamide and 1 μL of DNA internal standard ROX1000, denatured at 95° C. for 5 minutes, and cooled on ice. The mixture was subjected to capillary electrophoresis with ABI 3730, the injection voltage was 2.5 kV, 20 seconds, and the electrophoresis time was 4000 seconds. The capillary electrophoresis diagram of PCR...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com