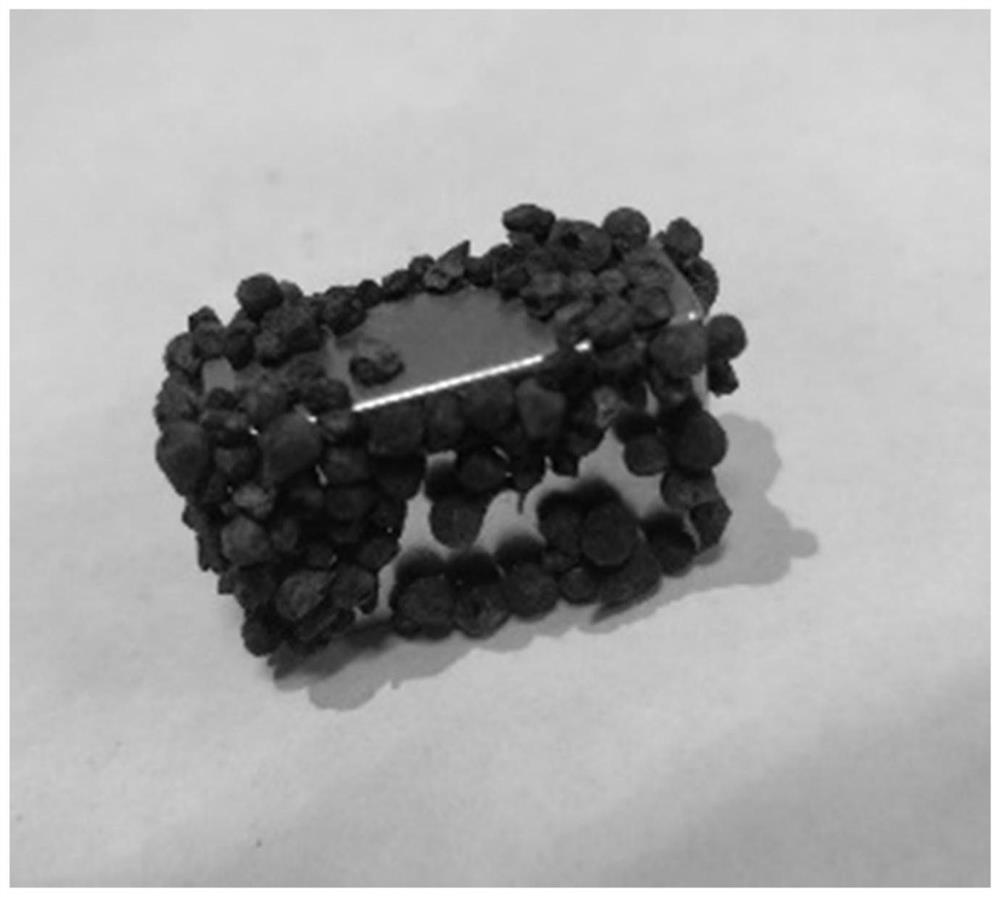
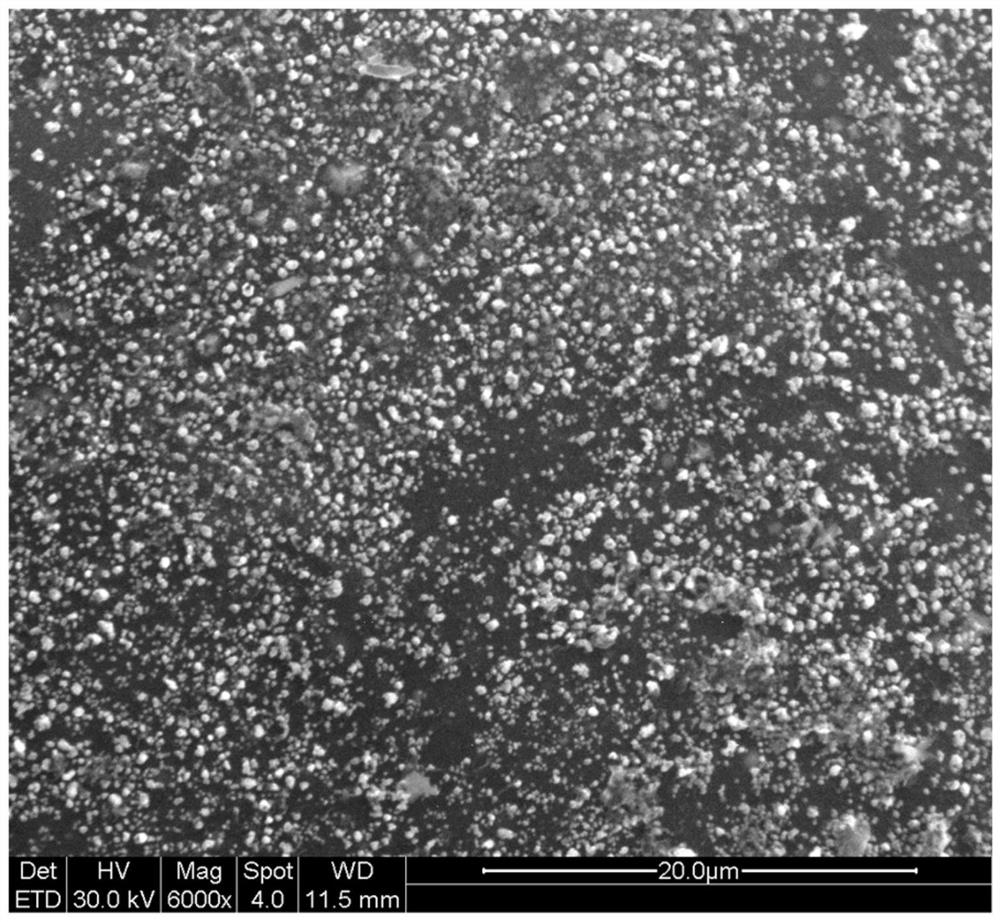
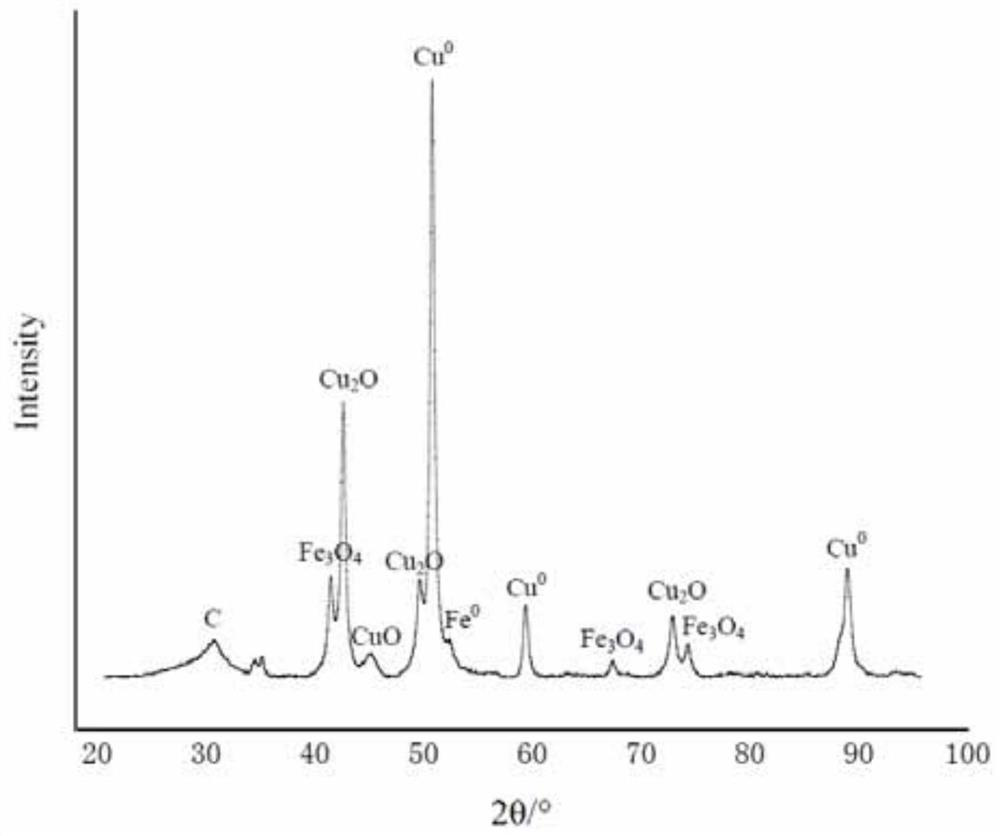
Preparation method of Cu-Fe bimetal complexing type magnetic chitosan carbon aerogel catalyst applied to wet oxidation
A bimetallic complex, wet oxidation technology, applied in metal/metal oxide/metal hydroxide catalysts, catalyst activation/preparation, physical/chemical process catalysts, etc., can solve the problem of poor catalyst stability and low catalyst metal loading. , the problem of easy loss of active components, etc., to achieve the effects of good stability, low dissolution, and stable COD removal rate in effluent
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0026] Example 1. Catalyst Preparation Specific Embodiment 1
[0027] Weigh 0.03mol copper nitrate trihydrate and 0.01mol ferrous chloride tetrahydrate respectively, and dissolve them in 960ml deionized water to form a solution. And weigh 30g of chitosan in the solution to form a suspension, add 40ml of acetic acid while stirring until a sol is formed. Cu in the formed sol 2+ Concentration is 0.03mol / L, Fe 2+ The concentration is 0.01mol / L. Vacuum for 12 hours to remove air bubbles. The sol was extracted with a syringe, and 1 L of a sodium hydroxide solution with a concentration of 1.25 mol / L was added dropwise to carry out deprotonation curing for 4 hours. Soak and wash with deionized water until the filtrate is neutral, and place it in a freezer at -12°C for 12 hours. The pellets were lyophilized in a lyophilizer for 72 hours without thawing. The freeze-dried airgel was calcined at 800 °C for 2 hours in a nitrogen atmosphere to complete the carbonization process (in th...
example 2
[0038] Example 2. Catalyst Preparation Specific Embodiment 2
[0039] Weigh 0.05 mol of copper nitrate trihydrate and 0.02 mol of ferrous chloride tetrahydrate respectively, and dissolve them in 950 ml of deionized water to form a solution. And weigh 36g of chitosan in the solution to form a suspension, add 50ml of acetic acid while stirring until a sol is formed. Cu in the formed sol 2+ Concentration is 0.05mol / L, Fe 2+ The concentration is 0.02mol / L. Vacuum for 12 hours to remove air bubbles. The sol was drawn out with a syringe, and 1 L of a sodium hydroxide solution with a concentration of 1.5 mol / L was added dropwise to carry out deprotonation curing for 4 hours. Soak and wash with deionized water until the filtrate is neutral, and place it in a freezer at -12°C for 12 hours. The pellets were lyophilized in a lyophilizer for 72 hours without thawing. The freeze-dried airgel was calcined at 820°C for 2 hours in a nitrogen atmosphere to complete the carbonization proc...
example 3
[0050] Example 3. Catalyst Preparation Specific Embodiment 3
[0051] Weigh 0.08mol copper nitrate trihydrate and 0.04mol ferrous chloride tetrahydrate respectively, and dissolve them in 920ml deionized water to form a solution. And weigh 42g of chitosan in the solution to form a suspension, add 80ml of acetic acid while stirring until forming a sol. Cu in the formed sol 2+ Concentration is 0.08mol / L, Fe 2+ The concentration is 0.04mol / L. Vacuum for 12 hours to remove air bubbles. The sol was extracted with a syringe, and 1 L of a sodium hydroxide solution with a concentration of 2 mol / L was added dropwise to carry out deprotonation curing for 4 hours. Soak and wash with deionized water until the filtrate is neutral, and place it in a freezer at -12°C for 12 hours. The pellets were lyophilized in a lyophilizer for 72 hours without thawing. The freeze-dried airgel was calcined at 850°C for 2.5 hours in a nitrogen atmosphere to complete the carbonization process (in the he...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| clearance rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| decolorization rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com