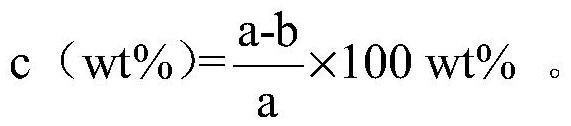Method for preparing electrochromic fibers without additional electrodes by coaxial microfluid spinning method
An electrochromic, liquid crystal fiber technology, applied in the fields of fine chemical industry and material science, can solve the problems such as the inability to meet the breathable and flexible wearing requirements of textiles, the coloring of liquid crystals, and the inability to get rid of the application limitations of external electrodes, and achieve controllable optical appearance, driving The effect of low voltage and easy large-scale production
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0053] A method for preparing electrochromic liquid crystal fibers by a coaxial microfluidic spinning method, comprising the steps of:
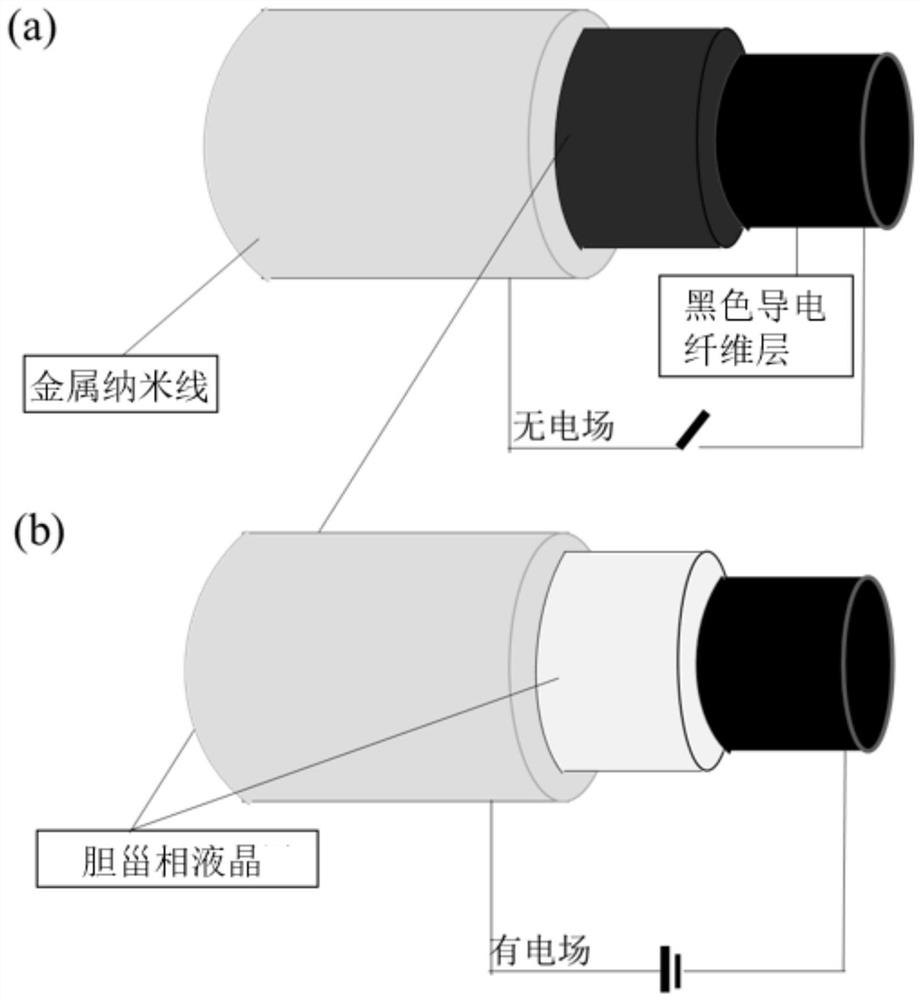
[0054] (1) Preparation of transparent conductive outer layer injection 1: Disperse 0.05g sodium alginate powder, 0.5g glucose powder, 1.5g silver nanowire (length, diameter 10μm, 60nm) (Sigma company) in 10mL water with magnetic stirring 10min, and prepare uniform injection 1, wherein the mass fraction of silver nanowires relative to water is 0.15wt%;
[0055] (2) Preparation of black conductive inner layer injection 2: 0.05g sodium alginate powder, 0.5g glucose powder, 0.15g poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene)-poly(styrenesulfonic acid)( Sinopharm Shanghai Test Company) was dispersed in 10mL water with magnetic stirring for 10min, and prepared into uniform injection 2, wherein the mass fraction of poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene)-poly(styrenesulfonic acid) relative to water was 0.015wt%;
[0056] (3) Preparation of electrochromic liquid cryst...
Embodiment 2
[0062] Adjust the red cholesteric liquid crystal of 90wt% in the injection 3 of embodiment 1 to the blue cholesteric liquid crystal of 80wt% (U10-006G-480, Shijiazhuang Chengzhi Yonghua Company), the metal nanowire in the injection 1 Copper nanowires are used, wherein the mass fraction of copper nanowires is 0.3 wt %; other steps are the same as in Example 1 to prepare electrochromic liquid crystal microfibers.
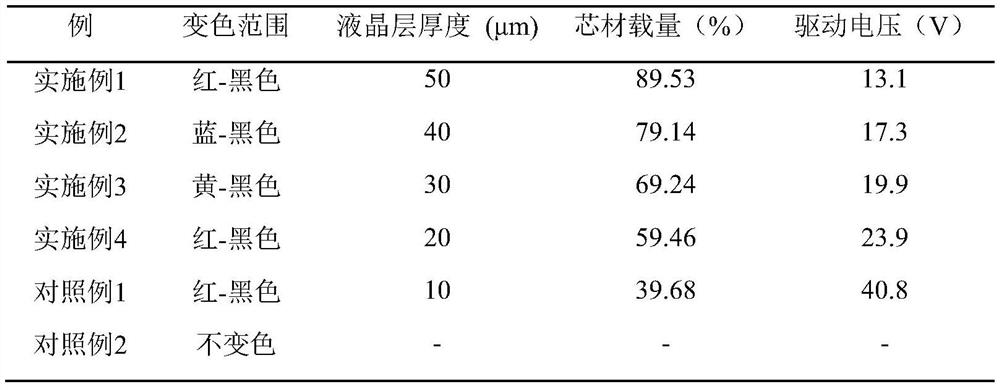
[0063] The photoelectric performance test (see Table 1) and the water and solvent resistance performance test (see Table 2) of the electrochromic liquid crystal fiber prepared above were carried out. As can be seen from the test results: for the electrochromic liquid crystal fiber obtained in Comparative Example 1, as the concentration of the cholesteric liquid crystal decreases, the thickness of the liquid crystal layer also becomes thinner, and the required electrochromic driving voltage also increases thereupon. .
Embodiment 3
[0065] Adjust the red cholesteric liquid crystal of 90wt% in the injection 3 of embodiment 1 to the yellow cholesteric liquid crystal of 70wt% (U10-006G-580, Shijiazhuang Chengzhi Yonghua Company), and others are prepared according to the same method of embodiment 1 The steps are to prepare electrochromic liquid crystal microfibers.
[0066] The photoelectric performance test (see Table 1) and the water and solvent resistance performance test (see Table 2) were carried out on the electrochromic liquid crystal fiber prepared above. It can be seen from the test results that for the electrochromic liquid crystal fiber obtained in Comparative Example 1, as the concentration of the cholesteric liquid crystal continues to decrease, the thickness of the liquid crystal layer continues to become thinner, and the required electrochromic driving voltage also continues to increase.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile stress | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com