Chemical magnesium removal method for collophanite and free of tailings
A technology for chemical magnesium removal and collophosite, applied in the field of chemical magnesium removal, can solve the problems of high concentration energy consumption, high solubility of magnesium chloride, etc., achieve high resource utilization, avoid crystallization and separation difficulties, and solve the effect of occupying land resources
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
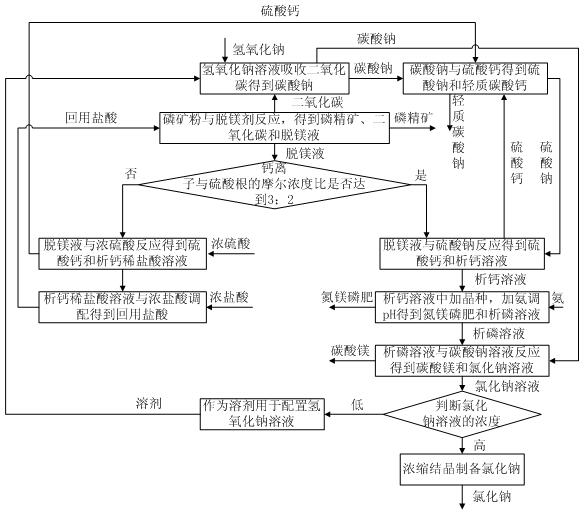
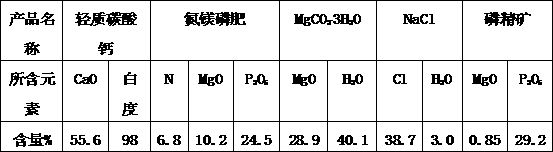
[0050] (1) Take 100g of collophosphine powder and place it in a 500mL three-necked flask, add 50mL of water to adjust the slurry, install a stirrer, a gas outlet pipe and a dropping funnel, configure NaOH into a solution with a concentration of 30wt%, and take 46g of the solution in the absorption in the bottle. Turn on the stirrer, drop 90g of 4mol / L dilute hydrochloric acid into the three-necked flask at a rate of 5-10mL / min, continue to react for 20min, filter, and wash with water 3 times. The solid concentrate was dried at 100°C, and the obtained phosphorous concentrate weighed 69.8g. Determination of Ca in Phosphate Rock Demagnesium Filtrate 2+ Concentration, PO 4 3- Concentration and Mg 2+ concentration. Reserve the sodium carbonate solution in the absorption bottle for later use. If Ca in the demagnesizing solution 2+ Ions and SO 4 2+ When the molar ratio of ions reaches 3:2, step (4) is performed; otherwise, step (3) is performed.
[0051] (2) Keep the temper...
Embodiment 2
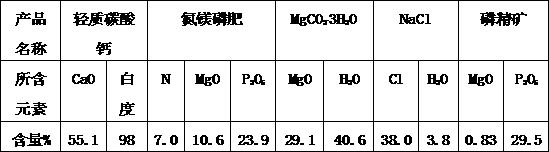
[0060] (1) Take 200g of collophosphine powder and place it in a 500mL three-neck flask, add 50mL of water to adjust the slurry, install a stirrer, a gas outlet pipe and a dropping funnel, and then take 92g of a 30wt% NaOH solution in the absorption bottle. Turn on the stirrer, drop 144g of 5mol / L dilute hydrochloric acid into the three-necked flask at a rate of 10-20mL / min, continue the reaction for 20min, filter, and wash with water 3 times. The solid concentrate was dried at 100°C, and the obtained phosphorous concentrate weighed 141g. Determination of Ca in filtrate 2+ Concentration, PO 4 3- Concentration and Mg 2+ concentration. Reserve the sodium carbonate solution in the absorption bottle for later use. If Ca in the demagnesizing solution 2+ Ions and SO 4 2+ When the molar ratio of ions reaches 3:2, step (4) is performed; otherwise, step (3) is performed.
[0061] (2) Keep the temperature of the solution in the absorption bottle at 25°C, turn on the stirrer and ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com