High-temperature-resistant cement hexavalent chromium reducing agent
A technology of hexavalent chromium and high temperature resistance, which is applied in the field of building materials, and can solve the problems of affecting the setting time and strength of cement, being difficult to be oxidized, and using a large amount of reducing agent.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
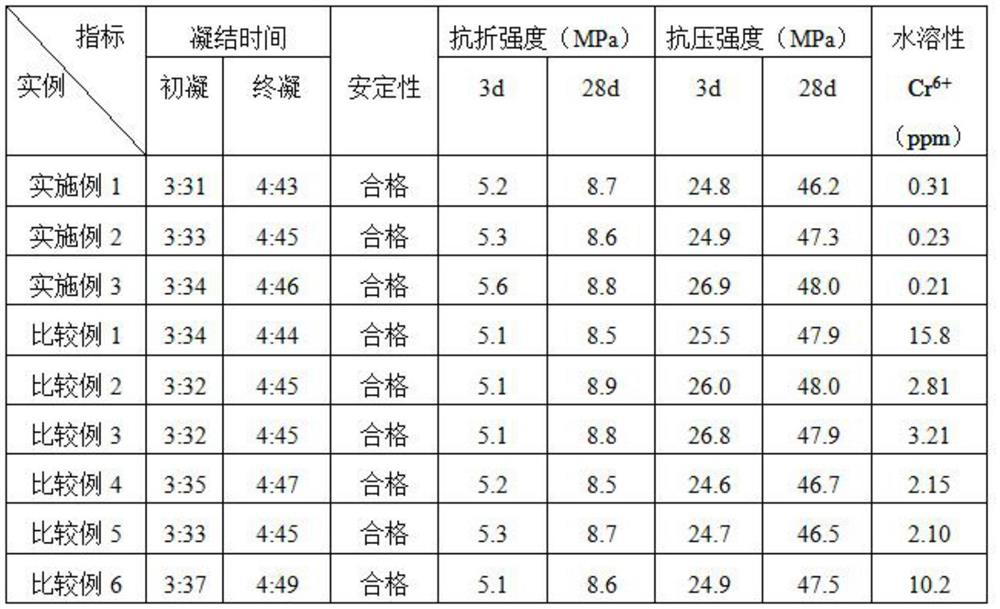
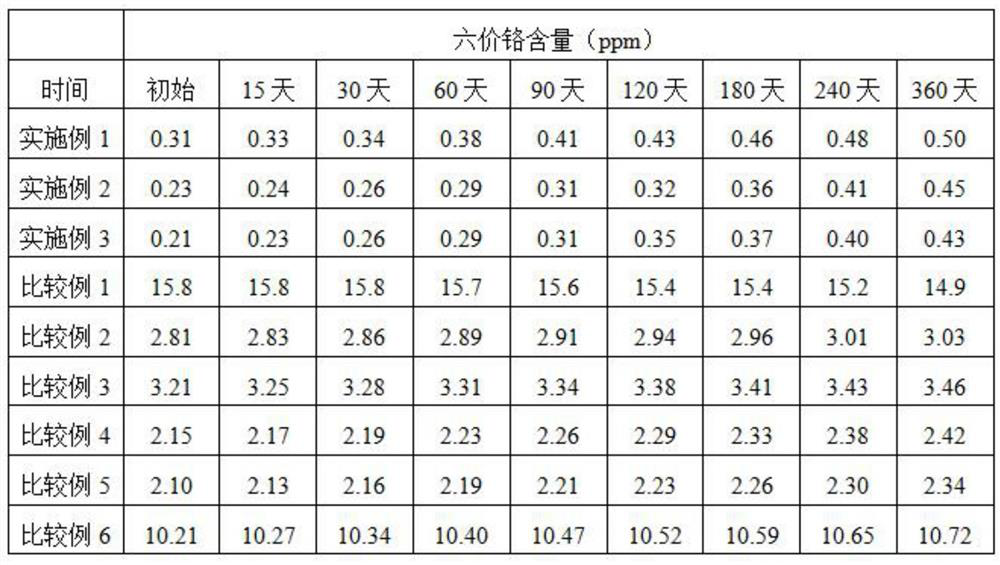
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] 2 parts of stannous sulfate, 20 parts of ferrous sulfate, 3 parts of montmorillonite, 4 parts of bentonite, 3 parts of magnesium fluoride, 5 parts of humic acid.
[0029] Prepare as follows:
[0030] (a) Dissolve 8 parts of ferrous sulfate in water of equal weight and stir evenly, then add montmorillonite, evaporate free water under reduced pressure at room temperature, then dry at 105°C for 2 hours in a nitrogen atmosphere to obtain baked Making montmorillonite;
[0031] (b) Mix and grind the baked montmorillonite, the remaining ferrous sulfate, stannous sulfate, bentonite, magnesium fluoride, and humic acid to 300 mesh, and pack it for later use.
[0032] Mix conventional 42.5 grade cement raw materials to form cement batch, mix and grind the cement batch with the hexavalent chromium reducing agent prepared in this example, and prepare cement according to the 42.5 grade cement preparation process (during 150-160 ℃ high temperature). Among them, 150 grams of hexaval...
Embodiment 2
[0034] 4 parts of stannous sulfate, 25 parts of ferrous sulfate, 5 parts of montmorillonite, 2 parts of bentonite, 5 parts of magnesium fluoride, 3 parts of humic acid.
[0035] Prepare as follows:
[0036] (a) Dissolve 10 parts of ferrous sulfate in water of equal weight and stir evenly, then add montmorillonite, evaporate free water under reduced pressure at room temperature, and then dry at 110°C for 1 hour in a nitrogen atmosphere to obtain baked Making montmorillonite;
[0037] (b) Mix and grind the baked montmorillonite, the remaining ferrous sulfate, stannous sulfate, bentonite, magnesium fluoride, and humic acid to 500 mesh, and pack it for later use.
[0038] Mix conventional 42.5 grade cement raw materials to form cement batch, mix and grind the cement batch with the hexavalent chromium reducing agent prepared in this example, and prepare cement according to the 42.5 grade cement preparation process (during 150-160 ℃ high temperature). Among them, 150 grams of hex...
Embodiment 3
[0040] 3 parts of stannous sulfate, 22 parts of ferrous sulfate, 4 parts of montmorillonite, 3 parts of bentonite, 4 parts of magnesium fluoride, 4 parts of humic acid.
[0041] Prepare as follows:
[0042] (a) Dissolve 9 parts of ferrous sulfate in water of equal weight and stir evenly, then add montmorillonite, evaporate free water under reduced pressure at room temperature, then dry at 107°C for 1.5 hours in a nitrogen atmosphere to obtain baked Making montmorillonite;
[0043] (b) Mix and grind the baked montmorillonite, the remaining ferrous sulfate, stannous sulfate, bentonite, magnesium fluoride, and humic acid to 400 mesh, and pack it for later use.
[0044] Mix conventional 42.5 grade cement raw materials to form cement batch, mix and grind the cement batch with the hexavalent chromium reducing agent prepared in this example, and prepare cement according to the 42.5 grade cement preparation process (during 150-160 ℃ high temperature). Among them, 150 grams of hexav...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com