Method for artificially constructing chitin corpuscle multienzyme complex scoford-chiC-chiA-sg and application
A technology of scaford-chic-chia-sg and scaford-chbd is applied in the field of artificial construction of chitinosome multi-enzyme complexes, which can solve the problems of unfixed distance and intermediate product capture, so as to reduce production costs and achieve efficient degradation. , the effect of high monosaccharide yield
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] The following examples can enable those skilled in the art to understand the present invention more fully, but do not limit the present invention in any way.
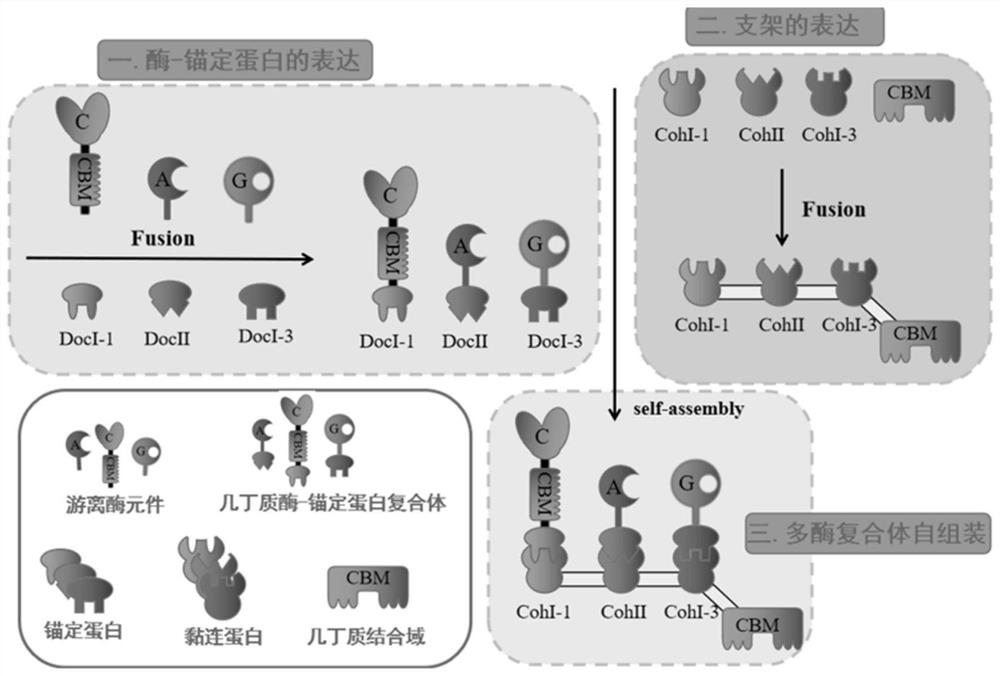
[0035] The construction of embodiment 1 protein scaffold scaford-ChBD
[0036] CohesinI-1, cohesinII, and cohesinI-3 were derived from the strain Clostridium cellulovorans (ATCC 35296 T ), Clostridium cellulolyticum, (ATCC 35319 T ) and Clostridium thermocellum (ATCC 27405 T ) genome. The chitin-binding domain gene ChBD comes from the strain Chitinolyticbacter meiyuanensis SYBC-H1 (ATCC BAA-2140 T ) genome. The genes cohesinI-1, cohesinII, and cohesinI-3 were obtained by total gene synthesis from General Biosystems (Anhui) Co., Ltd.
[0037] The plasmid construction of the protein scaffold scaford-ChBD adopts a one-step cloning method, designing homology arms in the upper and lower primers of the genes cohesinI-1, cohesinII, cohesinI-3 and ChBD, and using the linearized vector pETDuet in homologous recombina...
Embodiment 2
[0038] The construction of embodiment 2 chitinase-dockerins
[0039] The anchoring proteins dockerin-I-1, dockerin-II, and dockerin-I-3 were derived from the strain Clostridium cellulovorans (ATCC 35296 T ), Clostridium cellulolyticum, (ATCC35319 T ) and Clostridiumthermocellum (ATCC 27405 T ). The genes dockerin-I-1, dockerin-II, and dockerin-I-3 were obtained by total gene synthesis from General Biosystems (Anhui) Co., Ltd. Chitinase chiC and chitinase chiA were derived from the strain Serratia marcescens (ATCC 13880 T ), N-acetylglucosaminidase sg from laboratory preservation strain Chitinolyticbacter meiyuanensis SYBC-H1 (ATCC BAA-2140 T ) genome.
[0040] The plasmid construction of chiC-doc1 adopts a one-step cloning method, and a homology arm is designed and added to the upper and lower primers of the gene chiC and dockerin-I-1, and the plasmid is constructed with the linearized vector pET22b under the action of homologous recombination enzyme (Vazyme CE113) pET22...
Embodiment 3
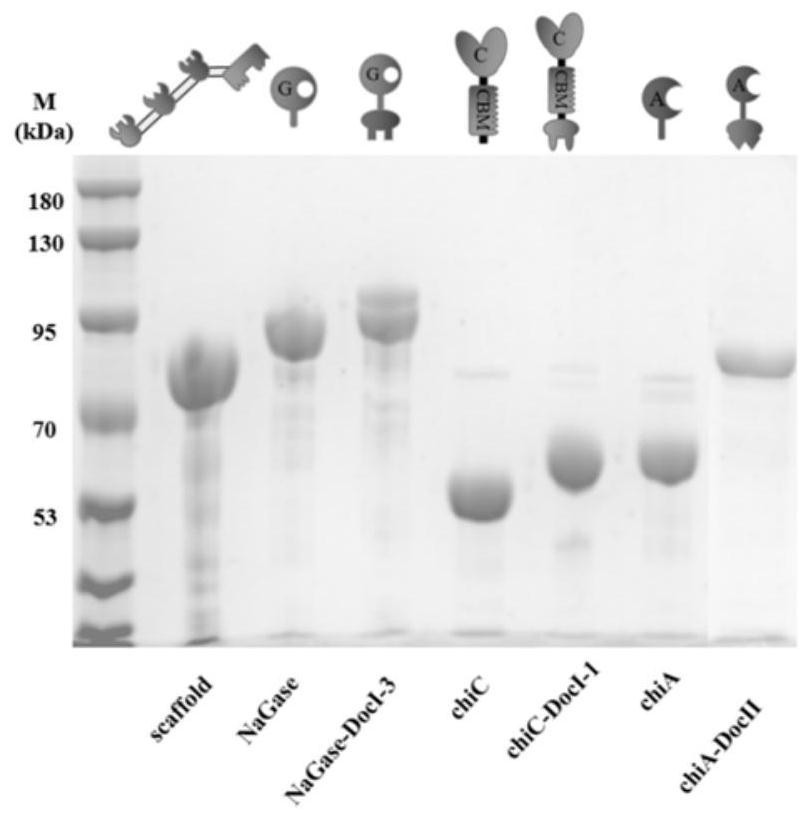
[0044] SDS-PAGE analysis of each enzyme element in the chitin body of embodiment 3
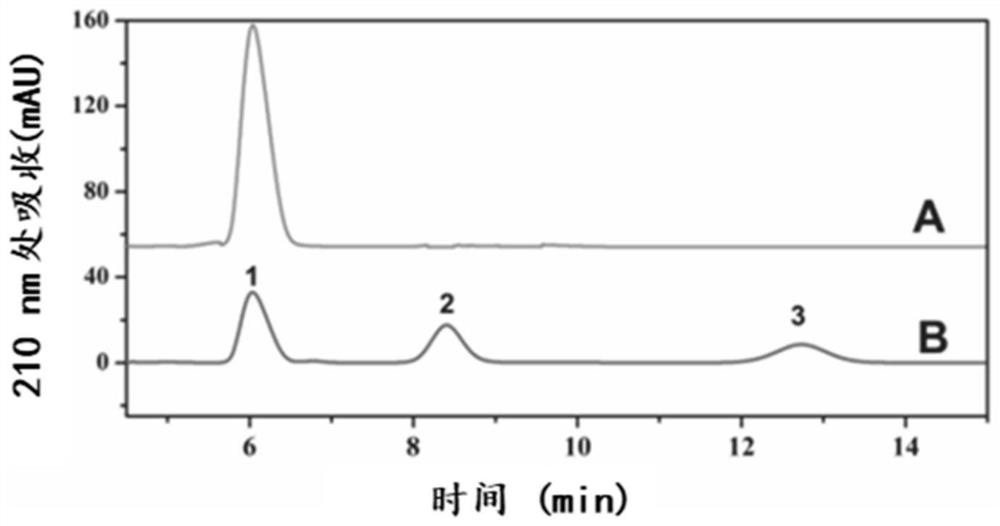
[0045] Preparation of the constructed protein scaffold scaford-ChBD, exonuclease chiC-doc1, endonuclease chiA-doc2, N-acetylglucosaminidase sg-doc3 and chitinase (chiC, chiA, sg) not connected to dockerins The seed liquid is LB medium, cultivated at 37°C and 200rpm for 6-7h, inoculated the seed liquid with a volume fraction of 2% in the fermentation medium containing 100ml LB, and cultivated to OD at 37°C and 200rpm was 0.6, and the inducer IPTG was added in an amount of 1‰, induced at 18°C and 200rpm for 20h, and then the fermentation was terminated to collect the fermentation broth. The fermentation broth was centrifuged at 8000g to collect the bacteria, washed twice with distilled water, resuspended in 25mL TBS (50mM pH7.0), ultrasonically broken and centrifuged at 8000g, and the supernatant collected was the crude enzyme solution of each enzyme component , stored at 4°C for later use. ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com