Composite vegetable protein foaming agent and preparation method thereof
A plant protein and foaming agent technology, applied in the field of concrete foaming agent, can solve the problems of affecting the strength of foam concrete, long foam stabilization time, serious retardation, etc., achieve good foaming ratio, good foaming effect, Effect of small water rate and settling distance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
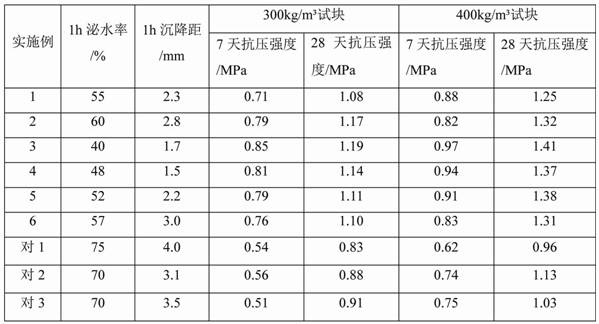
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] A compound vegetable protein foaming agent, made of the following raw materials in parts by weight: 5 parts of tea saponin, 5 parts of coconut oil fatty acid diethanolamide, 15 parts of fatty alcohol polyoxyethylene ether sodium sulfate, cocamide propane 10 parts of betaine, 0.5 parts of hydroxypropyl methylcellulose, 5 parts of magnesium chloride, 10 parts of n-butanol and 70 parts of water.
[0035] The preparation method of above-mentioned compound vegetable protein whipping agent, comprises the following steps:
[0036] (1) Add water into the reaction kettle and set aside;
[0037] (2) Slowly add fatty alcohol polyoxyethylene ether sodium sulfate and cocamidopropyl betaine to the water in step (1), and stir for 2 hours;
[0038] (3) Add hydroxypropyl methylcellulose to the mixture obtained in step (2), and stir for 30 minutes;
[0039] (4) Mix tea saponin and coconut oil fatty acid diethanolamide evenly, then add to the mixture obtained in step (3), and stir for 1...
Embodiment 2
[0042] A compound vegetable protein foaming agent, made of the following raw materials in parts by weight: 8 parts of tea saponin, 10 parts of coconut oil fatty acid diethanolamide, 10 parts of sodium fatty acid methyl ester sulfonate, lauryl ethoxylate 12 parts of sulfobetaine, 1 part of foam stabilizer, 5 parts of sodium chloride, 10 parts of sec-butanol and 55 parts of water.
[0043] The foam stabilizer is hydroxypropyl methylcellulose, polyacrylamide and polyvinyl alcohol in a weight ratio of 5:2:3.
[0044] The preparation method of above-mentioned compound vegetable protein whipping agent, comprises the following steps:
[0045] (1) Add water into the reaction kettle and set aside;
[0046] (2) Slowly add sodium fatty acid methyl ester sulfonate and dodecyl ethoxy sulfobetaine to the water in step (1), and stir for 3 hours;
[0047] (3) Add a foam stabilizer to the mixture obtained in step (2), and stir for 60 minutes;
[0048] (4) Mix tea saponin and coconut oil fat...
Embodiment 3
[0051] A compound vegetable protein foaming agent, made of the following raw materials in parts by weight: 5 parts of tea saponin, 10 parts of coconut oil fatty acid diethanolamide, 10 parts of fatty alcohol polyoxyethylene ether sodium sulfate, fatty acid methyl ester sulfonate 5 parts of sodium bicarbonate, 5 parts of cocamidopropyl betaine, 1.2 parts of foam stabilizer, 14 parts of magnesium chloride, 10 parts of sec-butanol and 60 parts of water.
[0052] The foam stabilizer is hydroxypropyl methylcellulose, polyacrylamide and polyvinyl alcohol in a weight ratio of 5:2:3.
[0053] The preparation method of above-mentioned compound vegetable protein whipping agent, comprises the following steps:
[0054] (1) Add water into the reaction kettle and set aside;
[0055] (2) Add sodium fatty alcohol polyoxyethylene ether sulfate, sodium fatty acid methyl ester sulfonate, and cocamidopropyl betaine slowly into the water in step (1), and stir for 4 hours;
[0056] (3) Add a foam...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com