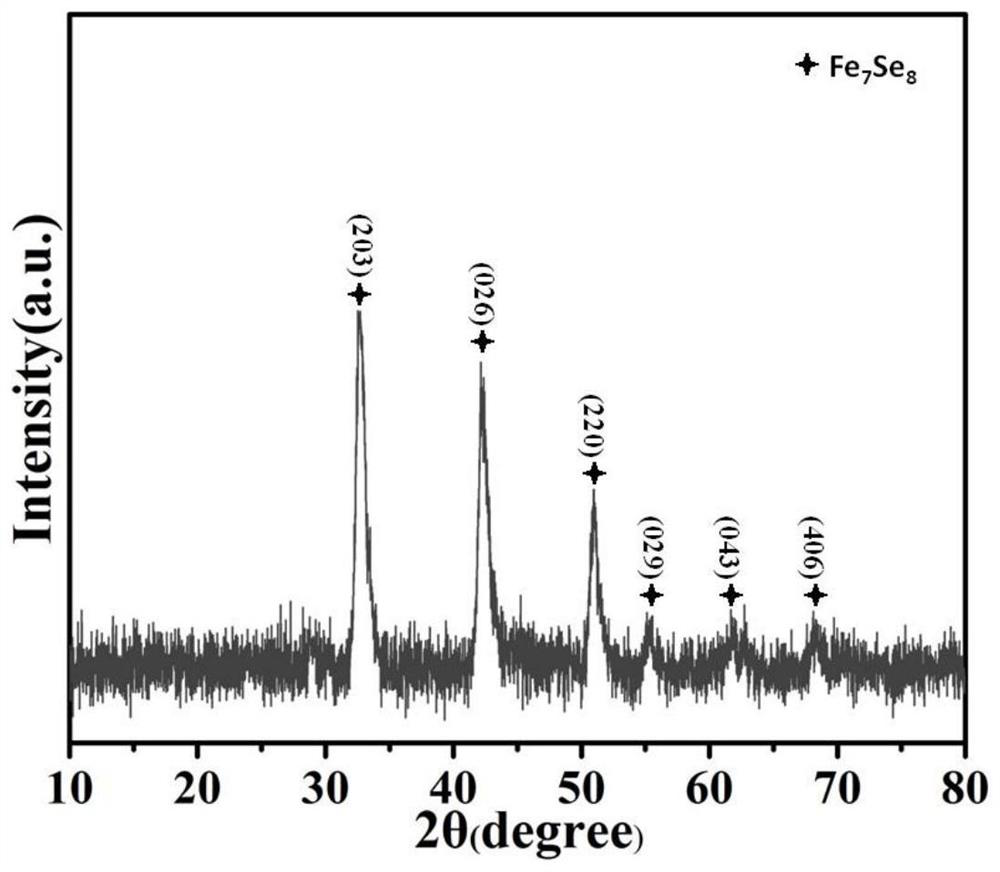
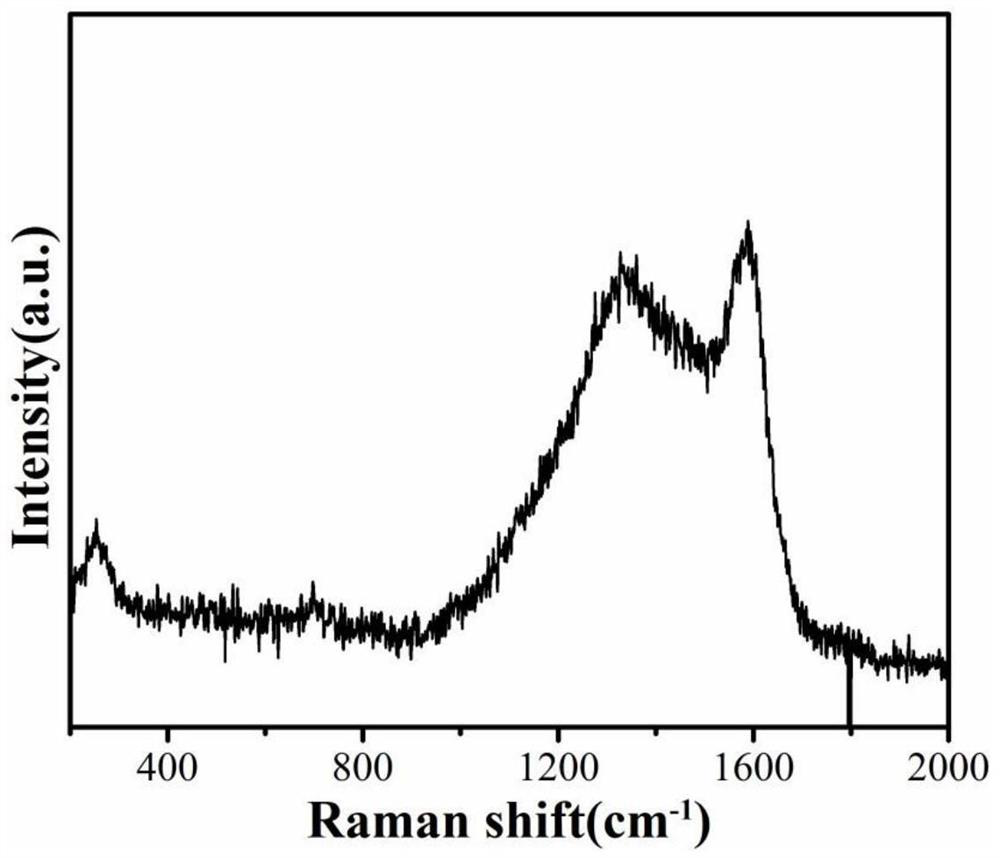
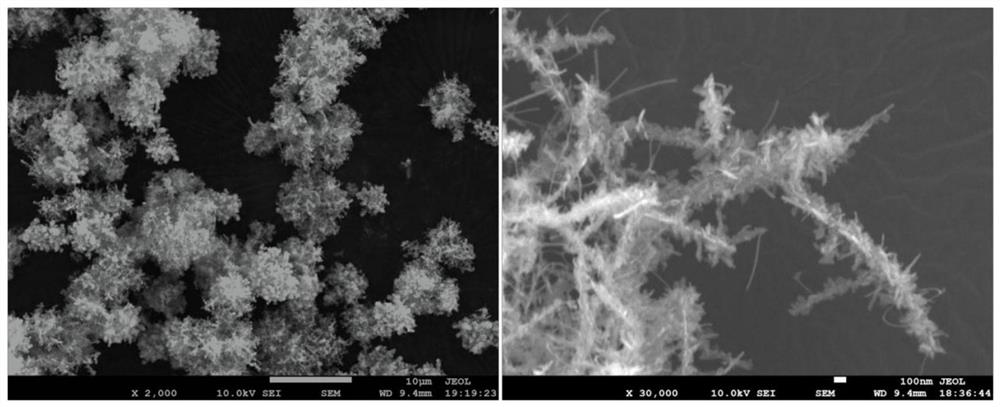
High-rate composite negative electrode material of sodium ion battery and preparation method thereof
A technology of sodium ion battery and negative electrode material, applied in battery electrodes, negative electrodes, secondary batteries and other directions, can solve the problems of cumbersome preparation process, difficult to scale up, serious pollution, etc., and achieves simple operation process, low equipment requirements, The effect of high sodium storage capacity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] A preparation method of a high-rate composite negative electrode material for a sodium ion battery, comprising the following steps:
[0028] In the first step, ferrocene and selenium powder with a particle size of 300 microns are used as raw materials, weighed and mixed uniformly according to a mass ratio of 2.5:1, and placed in a closed reaction kettle protected by argon for heating. The heating mechanism is as follows: the temperature is raised to 350°C at a rate of 2°C / min, and the temperature is kept for 1 hour to fully mix the ferrocene and selenium in the form of vapor. Then continue to heat up to 550°C at a rate of 5°C / min, keep the temperature for 4 hours and then cool down to room temperature naturally.
[0029] The second step is to take out the reaction product in the reaction kettle, place it in a tube furnace, and raise the temperature to 700°C at a rate of 5°C / min under an argon atmosphere. The final product obtained after constant temperature for 3 hours ...
Embodiment 2
[0038] A preparation method of a high-rate composite negative electrode material for a sodium ion battery, comprising the following steps:
[0039] In the first step, ferrocene and selenium powder with a particle size of 250 microns are used as raw materials, weighed and mixed uniformly according to a mass ratio of 5:1, and then placed in a closed reaction kettle protected by nitrogen for heating. The heating mechanism is as follows: the temperature is raised to 320°C at a rate of 1°C / min, and the temperature is kept for 2 hours to fully mix the ferrocene and selenium in the form of vapor. Then continue to heat up to 550°C at a rate of 3°C / min, keep the temperature for 1 hour, and cool down to room temperature naturally.
[0040] The second step is to take out the reaction product in the reaction kettle, place it in a tube furnace, and raise the temperature to 500°C at a rate of 2°C / min under a nitrogen atmosphere, and the final product obtained after constant temperature for ...
Embodiment 3
[0042] In the first step, ferrocene and selenium powder with a particle size of 50 microns are used as raw materials, weighed and mixed uniformly according to a mass ratio of 1:1, and placed in a closed reaction kettle protected by helium for heating. The heating mechanism is as follows: the temperature is raised to 400°C at a rate of 3°C / min, and the temperature is kept for 0.5h to fully mix the ferrocene and selenium in the form of vapor. Then continue to heat up to 450°C at a rate of 6°C / min, keep the temperature for 3 hours and then cool down to room temperature naturally.
[0043] The second step is to take out the reaction product in the reaction kettle, place it in a tube furnace, and raise the temperature to 850°C at a rate of 10°C / min under an argon atmosphere, and the final product obtained after constant temperature for 1 hour is the high-magnification composite Negative material. The sodium ion battery was assembled using the method described in Example 1. The te...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com