Method for delaying senescence of mesenchymal stem cells through FOXP1 gene editing and mutation
A kind of stem cell and gene editing technology, applied in the field of cell biology, can solve the problems of poor miRNA effect, off-target effect and gene mutation, risks brought by operators, etc., to improve the potential of disease treatment, promote proliferation, and improve organ repair Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
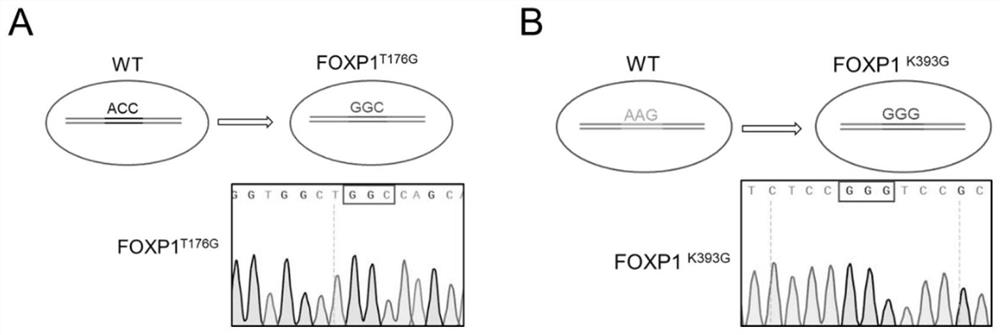
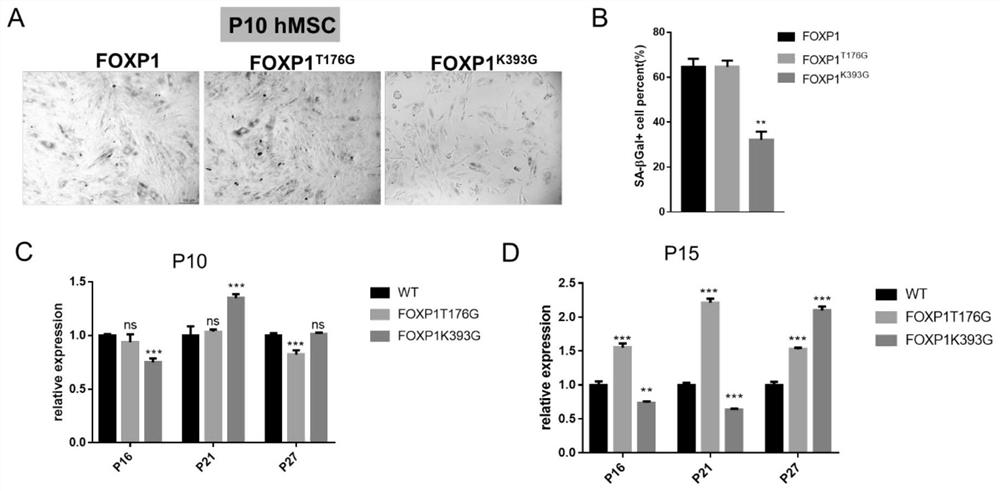
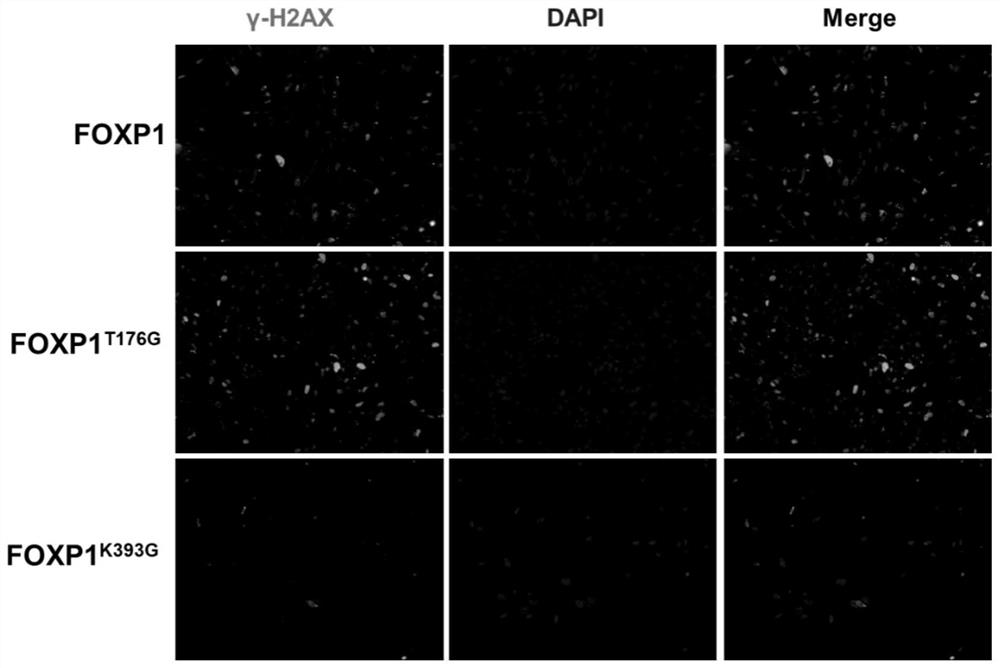
[0058] This embodiment relates to a method for delaying the aging of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) through FOXP1 gene editing. Using the artificial chromosome episomal-Cas9n vector, two reverse sgRNAs near the FOXP1 gene mutation site were inserted in series; meanwhile, donor DNA containing about 500 bp homology arms at the left and right sides of the mutation site was prepared by PCR. Episomal-Cas9n-FOXP1sgRNA and donor DNA were co-transfected into human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells, the cells were diluted and cultured to form single-cell clones, and after antibiotic screening, human-derived FOXP1 (T176G, T277G, K393G) point mutations were identified Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells.
[0059] The method comprises the steps of:
[0060] 1) Isolation and culture of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells
[0061] (1) Take out a 15cm dish (petri dish with a diameter of 15cm), cut up the fetal umbilical cord with scissors, suck up and disc...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com