Method of precipitating phytase
A phytase and polyanion technology, applied in the field of concentration and compositions containing phytase, can solve the problem of low availability of non-ruminants, and achieve the effect of changing specific activity or yield, improving purity and simplifying production
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0089] Example 1 - Phytase Materials and Analytical Methods
[0090] The enzyme materials used for polyelectrolyte precipitation were different sources of phytase, namely E. coli phytase, Aspergillus phytase and Buttiauxella phytase. All these phytases are expressed in the Trichoderma reesei fungus. Precipitation of E. coli phytase or Aspergillus phytase was started using clarified spent broth from several different fermentations of phytase protein or their concentrates, which contained preservatives to prevent microbial contamination. The spent broth was clarified by filtration and concentrated using a 10 kDa ultrafiltration membrane to increase protein concentration. Precipitation of Buttiauxella phytase was performed using purified enzyme liquid from dried granules as starting material. The enzymatic activity of the protein was measured as the release of inorganic phosphate (FTU activity) from sodium phytate (0.98% (w / v) phytate) within 60 min at 37°C in 250 mM sodium a...
Embodiment 2
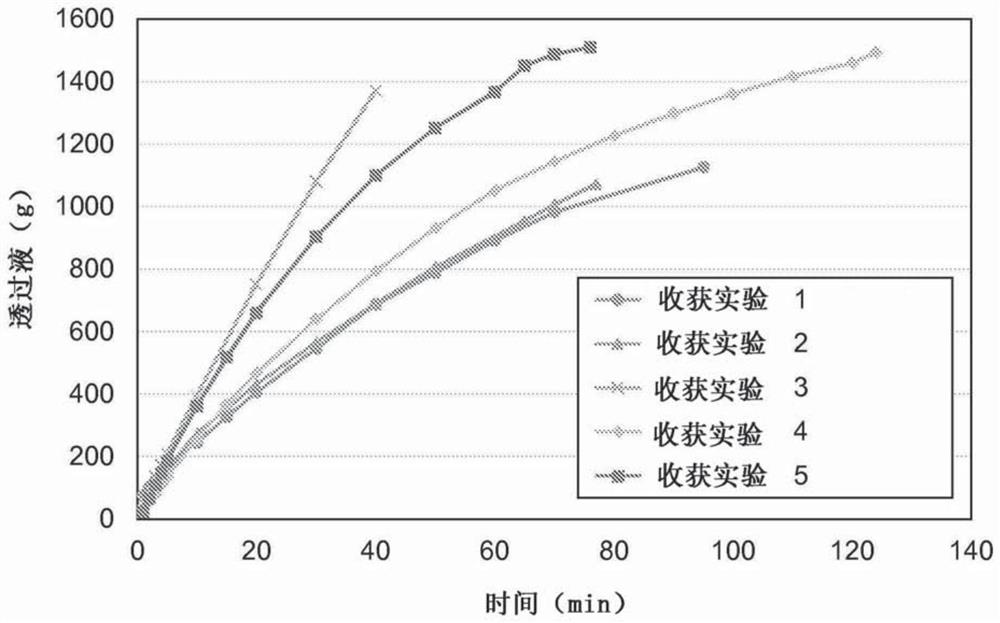
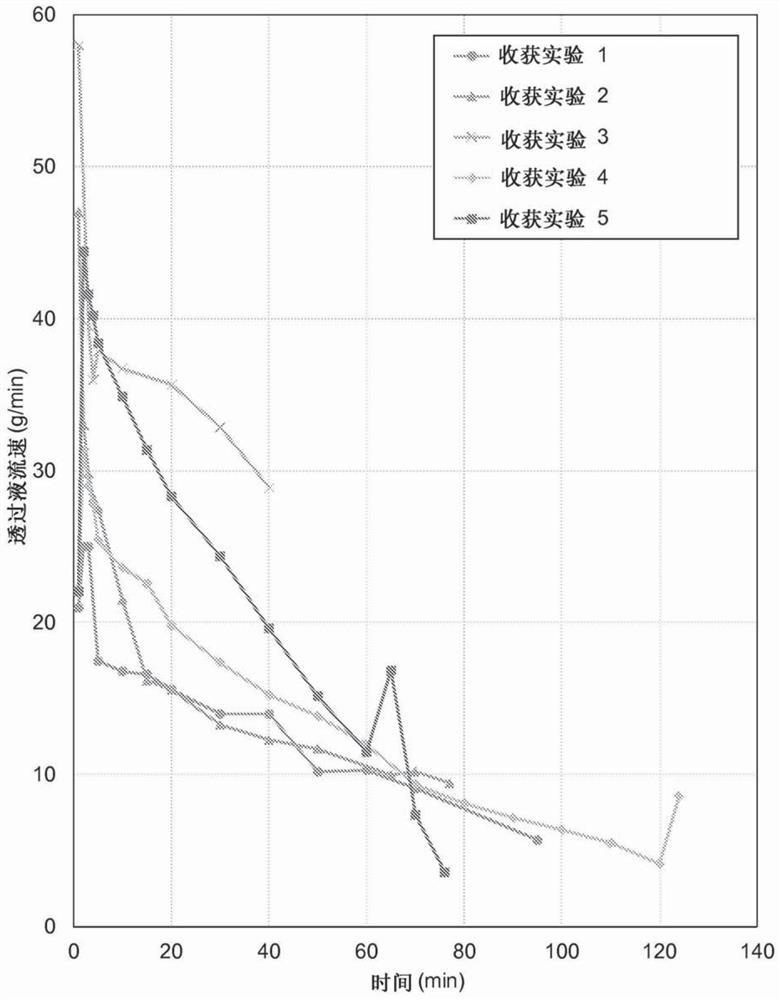
[0091] Example 2 - Reversible phytase-alginate complex formation by polyelectrolyte precipitation in a batch process
[0092] Four batches of precipitation were performed using a concentrate of E. coli phytase as the enzyme feedstock. Three of these batches were repeated batch precipitations in which buffered reagent solutions containing polyanions were prepared by adding 1 M sodium acetate buffer (nominal pH 3.6) and dry sodium alginate to tap water. In a batch precipitation, sodium citrate was used instead of sodium acetate as buffer. The dried alginate powder was dissolved and the reagent solution was stored overnight in a cold room. The next day, the phytase concentrate was added to the reagent solution at room temperature with proper stirring with a magnetic stirrer, following which the phytase-alginate complex formed rapidly. This was observed as a heavy, slightly fibrous and almost white precipitate formed during the phytase addition. Allow precipitation to continu...
Embodiment 3
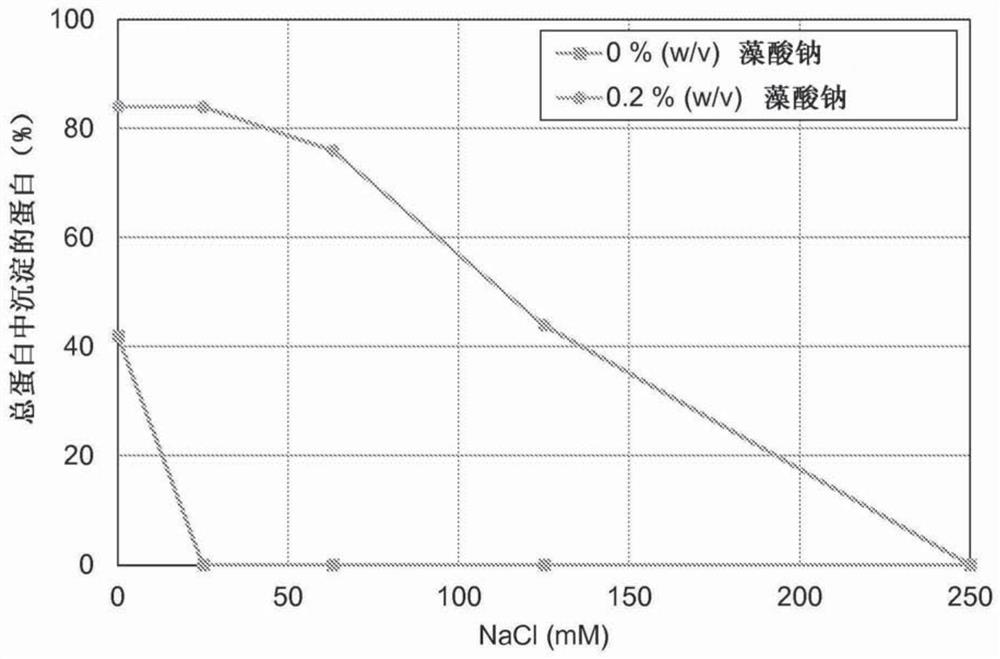
[0096] Example 3 - Effect of Ionic Strength on Yield of Precipitated Phytase
[0097] The experiment was carried out using a concentrate of Escherichia coli phytase as the enzyme starting material. In order to study the effect of ionic strength and sodium alginate on the precipitation yield, a series of precipitation experiments were carried out at room temperature. The experiments were carried out in 15 ml test tubes and the total volume of the experiments was 10 ml. Reagent solutions were prepared by mixing 5M sodium chloride, 0.4% (w / w) sodium alginate and tap water in a test tube. Half of the experiments were performed with sodium alginate and the other half without sodium alginate. Add 2ml of phytase concentrate to the tube and mix immediately to allow complex formation. Experiments were performed without pH adjustment. The measured pH ranged from 4.3 to 4.7. Determine the resulting soluble and total protein concentrations. The final precipitation conditions and y...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com