Comprehensive utilization method for boron-extraction and iron-extraction tailings of ludwigite
A technology of mafic ore and iron tailings, which is applied in the field of comprehensive utilization of secondary resources, can solve problems such as environmental pollution and waste of resources, achieve high purity, realize zero discharge of solid waste, and simple process technology
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
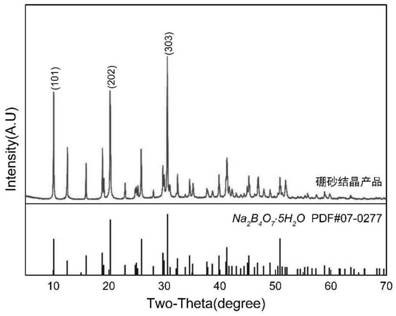
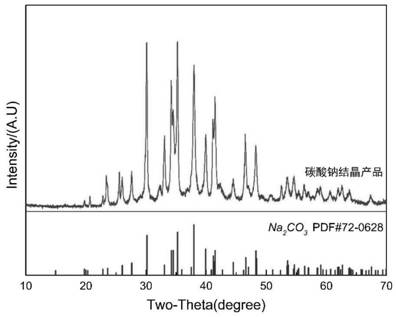
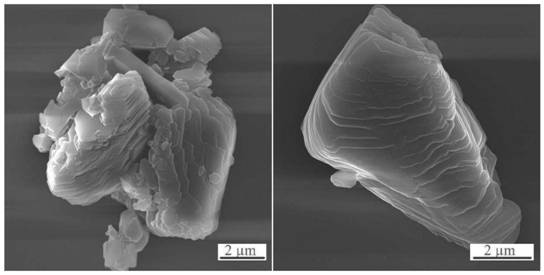
[0035] Example 1: Using the above tailings as raw materials, the liquid-solid mass ratio is 6:1, the water immersion temperature is 180° C., and the water immersion time is 6 hours. After leaching, the leachate and leach residue are obtained by filtration. Inject CO into the leaching solution 2The gas and leachate are concentrated by evaporation and crystallized step by step to separate borax and sodium carbonate crystals. The leached slag is pressed and formed under a pressure of 100-150 MPa, and dried; after treatment, it is roasted for 2-3 hours in an oxidizing atmosphere at 1300-1350 ° C to obtain a magnesia refractory material.
[0036] The leaching rates of boron and sodium during the leaching process in Example 1 were 95.69% and 95.41%, respectively. The refractoriness of the refractory material prepared by leaching slag is between 1600°C and 1650°C, and the bulk density and apparent porosity are 1.48g / cm3 respectively. 3 , 1.88%.
[0037] Inject CO into the leaching...
Embodiment 2
[0038] Example 2: Using the above tailings as raw materials, the liquid-solid mass ratio is 8:1, the water immersion temperature is 180° C., and the water immersion time is 6 hours. Inject CO into the leaching solution 2 The gas and leachate are concentrated by evaporation and crystallized step by step to separate borax and sodium carbonate crystals. The leached slag is pressed and formed under a pressure of 100-150 MPa, and dried; after treatment, it is roasted for 2-3 hours in an oxidizing atmosphere at 1300-1350 ° C to obtain a magnesia refractory material.
[0039] The leaching rates of boron and sodium during the leaching process in Example 2 were 96.47% and 95.94%. The refractoriness of the refractory material prepared by leaching slag is 1610℃~1670℃, and the bulk density and apparent porosity are 1.49g / cm3 respectively. 3 , 1.85%.
[0040] Inject CO into the leaching solution 2 Gas, convert the boron in the solution into borax, and convert the remaining sodium into ...
Embodiment 3
[0041] Example 3: Using the above tailings as raw materials, the liquid-solid mass ratio was 8:1, the water immersion temperature was 180° C., and the water immersion time was 5 hours. After leaching, the leaching solution and leaching residue were obtained by filtration. Inject CO into the leaching solution 2 The gas and leachate are concentrated by evaporation and crystallized step by step to separate borax and sodium carbonate crystals. The leached slag is pressed and formed under a pressure of 100-150 MPa, and dried; after treatment, it is roasted for 2-3 hours in an oxidizing atmosphere at 1300-1350 ° C to obtain a magnesia refractory material.
[0042] The leaching rates of boron and sodium during the leaching process in Example 3 were 96.69% and 96.41%. The refractoriness of the refractory material prepared by leaching slag is 1630℃~1680℃, and the bulk density and apparent porosity are 1.49g / cm3 respectively. 3 , 2.105%.
[0043] Inject CO into the leaching solution ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| flame retardant | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| porosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| flame retardant | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com