Method for efficiently separating vanadium and chromium based on pH regulation and control
A vanadium-chromium, high-efficiency technology, applied in the field of waste water resource utilization, can solve the problems of cumbersome separation steps, etc., and achieve the effect of high separation efficiency, simple operation process and guaranteed product purity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
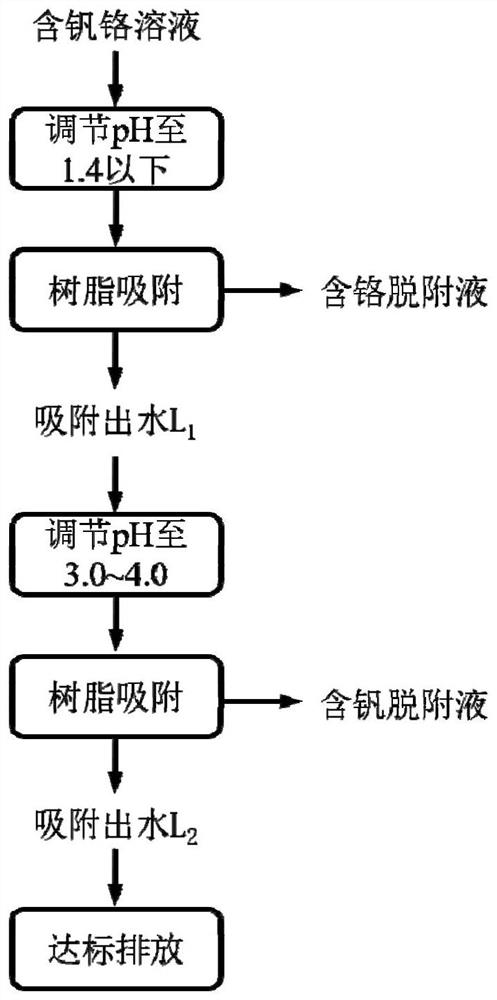
[0056] 1) Take 500mL of a mixed solution containing pentavalent vanadium (50mg / L) and hexavalent chromium (50mg / L), and adjust the pH of the solution to 1.0 with concentrated sulfuric acid;
[0057] 2) Add 0.3 g of IRA-900 strongly basic anion exchange resin after pickling with 10% sulfuric acid solution to the solution, and the resin concentration is 0.6 g / L. Using magnetic stirring, the mixture was stirred at room temperature for 10 h at a speed of 300 rpm. During this process, the curve of the concentration of vanadium chromium in the solution is as follows Figure 4 As shown, the concentration of chromium gradually decreases, and the concentration of vanadium remains almost constant. It can be seen that chromium is continuously extracted by resin exchange in the form of negatively charged chromate or dichromate, while vanadium exists in the form of positively charged vanadyl cations. Without being exchanged and extracted by anion exchange resin. The main ion exchange rea...
Embodiment 2
[0075] 1) Take 500mL of a mixed solution containing pentavalent vanadium (1000mg / L) and hexavalent chromium (500mg / L), and adjust the pH of the solution to 1.0 with concentrated sulfuric acid;
[0076] 2) Add 2 g of IRA-900 strongly basic anion exchange resin after pickling with 10% sulfuric acid solution to the solution, and the resin concentration is 4 g / L. Using magnetic stirring, the mixture was stirred at room temperature for 10 h at a speed of 300 rpm. During this process, chromium in the solution is continuously extracted by resin exchange in the form of negatively charged chromate or dichromate, while vanadium is not exchanged and extracted by anion exchange resin because it exists in the form of positively charged vanadyl cation. The main ion exchange reactions that occur are as follows:
[0077] R-SO 4 +2HCrO 4 - →R-(HCrO 4 ) 2 +SO 4 2-
[0078] R-SO 4 +Cr 2 o 7 2- →R-Cr 2 o 7 +SO 4 2-
[0079] 3) separating the resin from the solution by filtering,...
Embodiment 3
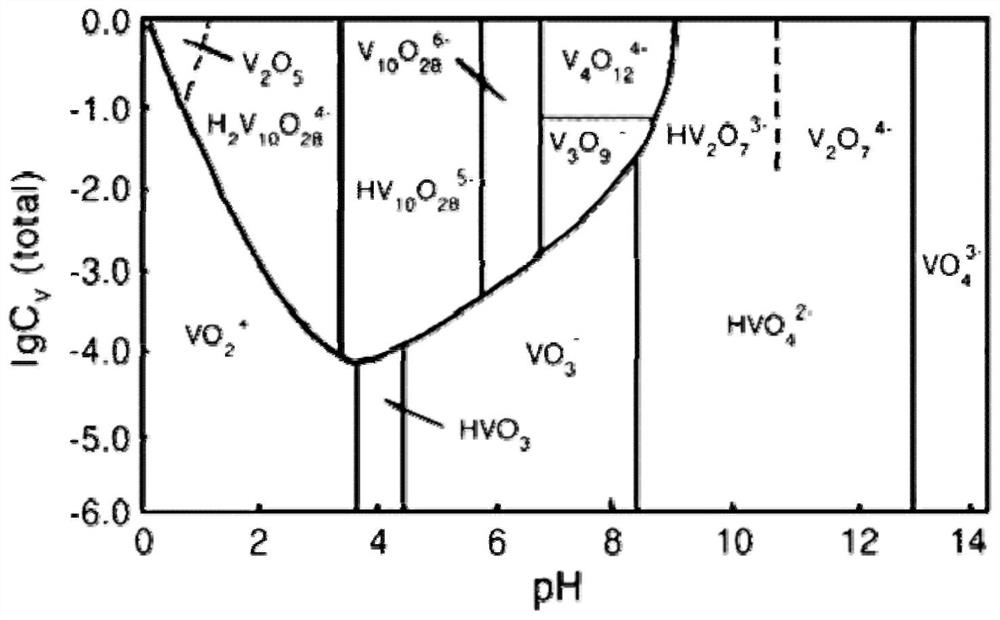
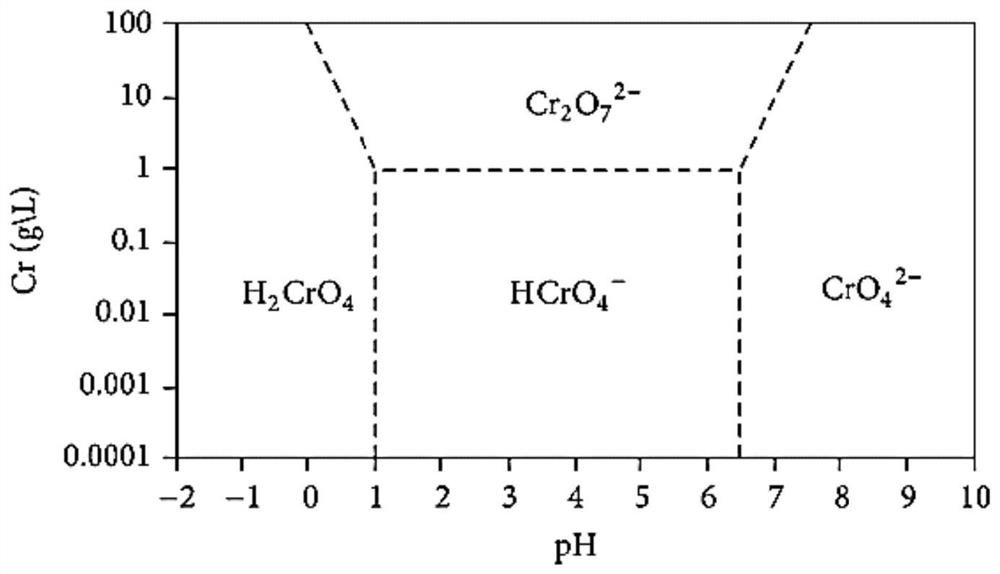
[0086] This example is basically the same as Example 2, except that the pH of the mixed solution is adjusted to 1.4 with concentrated sulfuric acid for the first time, and the pH of the solution is adjusted to 4.0 with 10% sodium hydroxide solution for the second time. After extracting with strong basic anion exchange resin for the first time, the chromium in the solution is basically completely removed, and the concentration of vanadium basically does not change; after the second extraction with strong basic anion exchange resin, the concentration of vanadium in the final solution is reduced to 0.9mg / L or so, the chromium concentration is reduced to about 0.6mg / L. The effective separation of vanadium and chromium is achieved and a high recovery rate is achieved.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com