Food antibacterial additive and application thereof
An antimicrobial additive and food technology, applied in the field of food additives, can solve problems such as unsatisfactory effect and narrow antibacterial spectrum, and achieve stable antibacterial effect, good antibacterial effect, and excellent antibacterial effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0046] The preparation of the fermented product of the coronoid saccharomyces coronoides of embodiment one
[0047] 1. Preparation of S. coronoidis strain
[0048] Inoculate P. coronoidis on PDA medium, and culture in a constant temperature incubator at 25-30°C for 3-5 days until P. coronis produces a large number of golden-yellow amenocystic spores. Scrape off the spores with sterilized water , transferred to a centrifuge tube, added glass beads, shaken for 10-20min, and filtered with sterilized absorbent cotton. Measure the OD600 value with a spectrophotometer, adjust the OD600 value to 1.8-2.0 (1ⅹ108 spores / mL), and the spore suspension of S. coronoidis was obtained.
[0049] 2. Solid fermentation
[0050] Select fresh black tea leaves, remove impurities, fix the tea leaves at 180°C, knead them for 30 minutes to 45 minutes, add water, and make the tea water ratio (black tea fresh tea leaves: water weight ratio) 1:2 to 1:5, and then mix the tea leaves Push away the thickn...
Embodiment 2
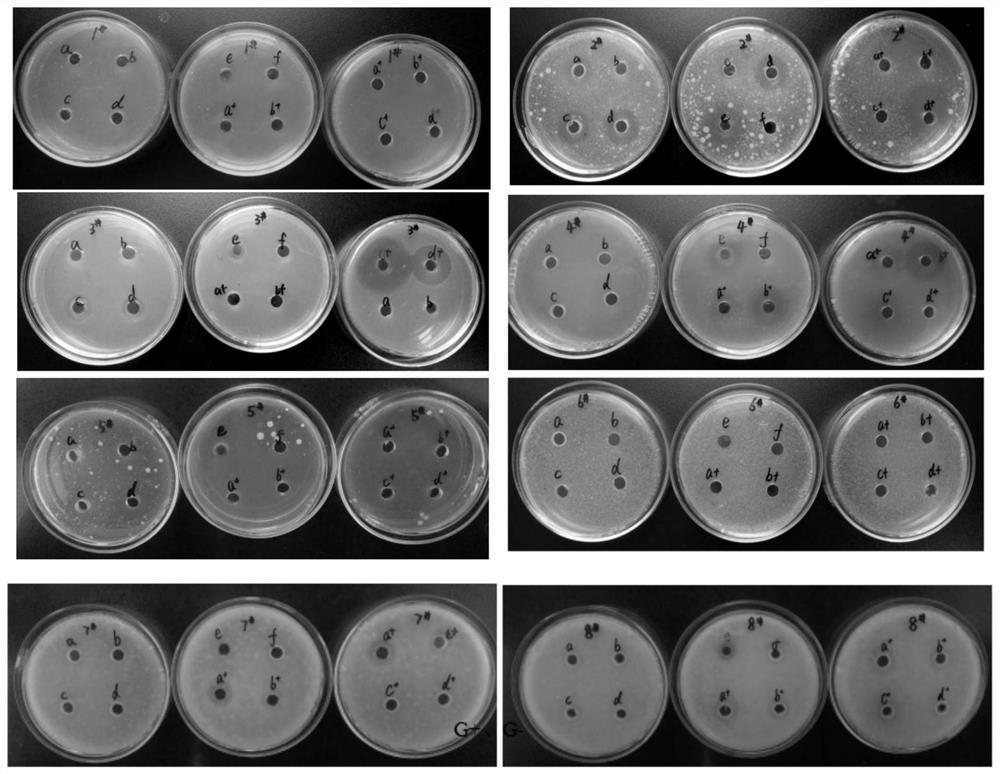
[0053] Example 2 Evaluation of antibacterial effect of fermented product solution of Saccharomyces coronarii in black tea (Oxford cup method)
[0054] 1. Preparation of fermented solution of Saccharomyces coronoidis
[0055] See the solution obtained by dissolving the dry matter of the liquid fermentation extract of Example 1 with 25 times the weight of water; following all implementation cases, unless otherwise stated, the fermented product solution used is the solution.
[0056] 2. Activation of bacteria
[0057] Under aseptic operation conditions, transfer the tested bacteria into the corresponding test tube slant culture medium, cultivate the bacteria in a constant temperature incubator at 30-37 °C, cultivate yeast and mold at 25-30 °C, and then place them at 0-30 °C. Refrigerate at 4°C for later use. Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas fluorescens, Bacillus subtilis, Bacillus cereus, Staphylococcus aureus, Aspergillus flavus, Aspergillus niger, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, all o...
Embodiment 3
[0071] The minimum inhibitory concentration MIC of the fermented product solution of the black tea coronoid sacrum of embodiment three
[0072] 1. Preparation of bacterial suspension
[0073] Bacteria and yeast suspension: use the combination of plate colony counting method and spectrophotometry, and use normal saline to prepare the initial bacterial solution with a concentration of 10 7 cfu / mL bacterial suspension.
[0074] Spore suspension: use sterile saline to wash a large number of spores produced by the mold from the slope, transfer to a centrifuge tube, add glass beads, shake for 10-20min, filter with sterilized absorbent cotton, plate colony counting method and spectrophotometry method combined with physiological saline to make the filtrate into a concentration of 10 7 cfu / mL of spore suspension.
[0075] 2. Preparation of bacterial liquid culture medium
[0076] Take the configured concentration as 1×10 7 Add the cfu / mL bacterial suspension into the broth liquid ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com