Method for reducing curing reaction temperature and toughening thermosetting resin in situ
A curing reaction and thermosetting technology, applied in the direction of coating, etc., can solve the problems of loss of thermal and mechanical properties of thermosetting resins, damage to material processability, thermal properties and strength, etc., to achieve good mechanical properties, good thermal stability, and mechanical properties good performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
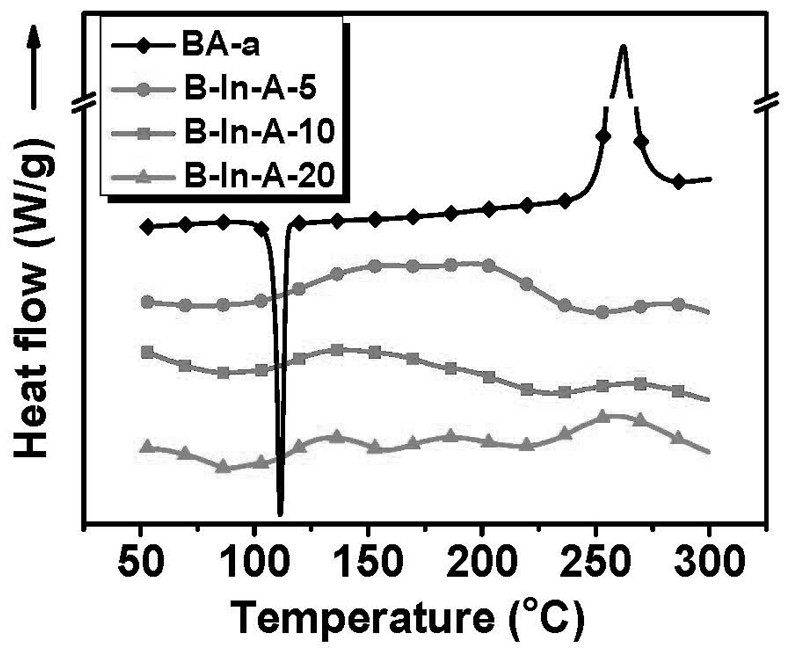
[0027] A solution was prepared by dissolving indium nitrate and acetylacetone with a molar ratio of 1:2 in an appropriate amount of ethanol, and ultrasonically mixing for 5 min to prepare a solution; dissolving bisphenol A benzoxazine in an appropriate amount of acetone and ultrasonically for 5 min to prepare a solution. The two solutions were mixed by ultrasonication for 0.5 h to obtain a homogeneous solution. The molar ratio of the indium nitrate to bisphenol A benzoxazine is 1:20. The concentration of the transition metal nitrate is 0.03g / mL, and the concentration of the thermosetting resin solution is 0.3g / mL.
[0028] 1. Use a spray gun to evenly coat the above solution on the pre-treated substrate, and then vacuumize the solvent in an oven at 50°C / 1h and 70°C / 1h.
[0029] 2. Use the following steps to cure the sprayed substrate: 140°C / 1h, 160°C / 1h, 180°C / 1h and 200°C / 1h.
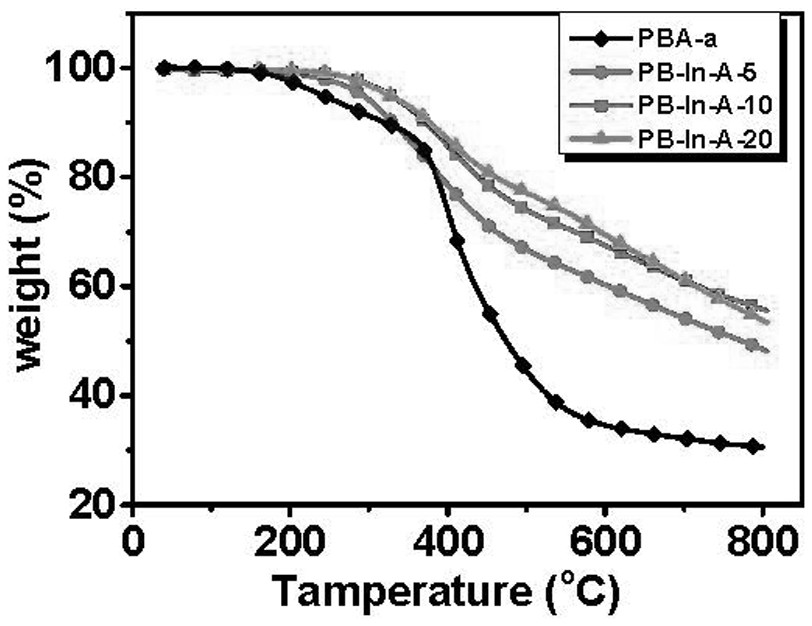
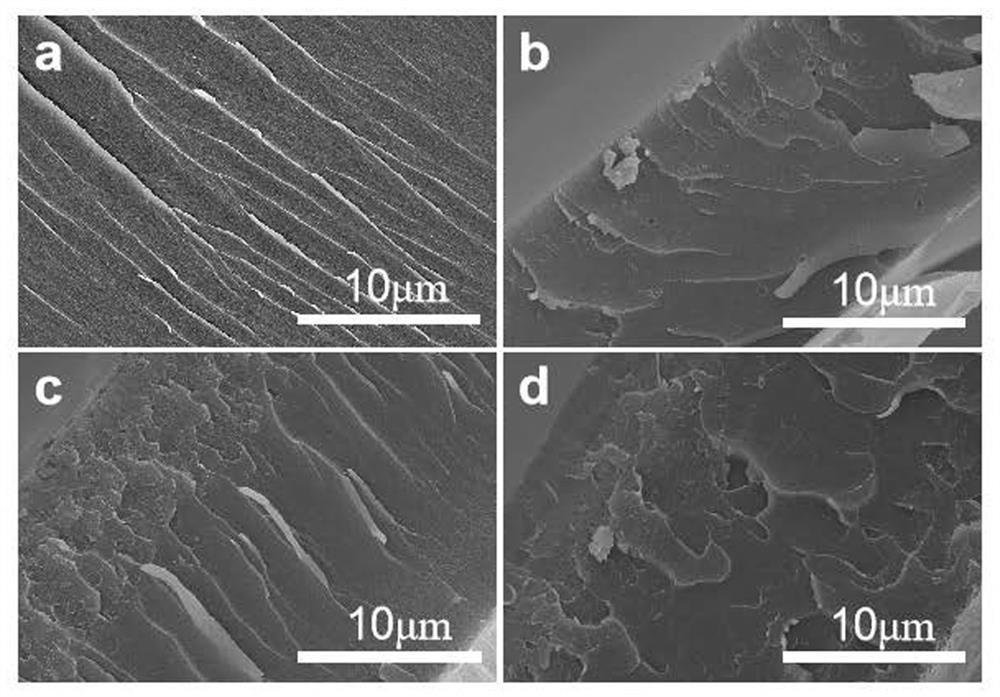
[0030] Finally, the polybenzoxazine coating (recorded as PB-In-A-5) has a carbon residue rate of ...
Embodiment 2
[0032] The difference between this example and Example 1 is that the molar ratio of indium nitrate and bisphenol A benzoxazine described in Step 1 is 1:10. Other steps and parameters are the same as in Example 1. Finally, the carbon residue rate of polybenzoxazine coating (recorded as PB-In-A-10) is 55.6%, T 5% The decomposition temperature is 328.4 o c. The impact resistance, hardness and surface adhesion are 7J, 6H and 5B respectively.
Embodiment 3
[0034] The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that the molar ratio of indium nitrate and bisphenol A benzoxazine described in Step 1 is 1:5. Other steps and parameters are the same as in Example 1. Finally, the carbon residue rate of polybenzoxazine coating (recorded as PB-In-A-20) is 53.4%, T 5% The decomposition temperature is 327.6 o c. Impact resistance, hardness and surface adhesion are 4J, 5H and 4B respectively.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com