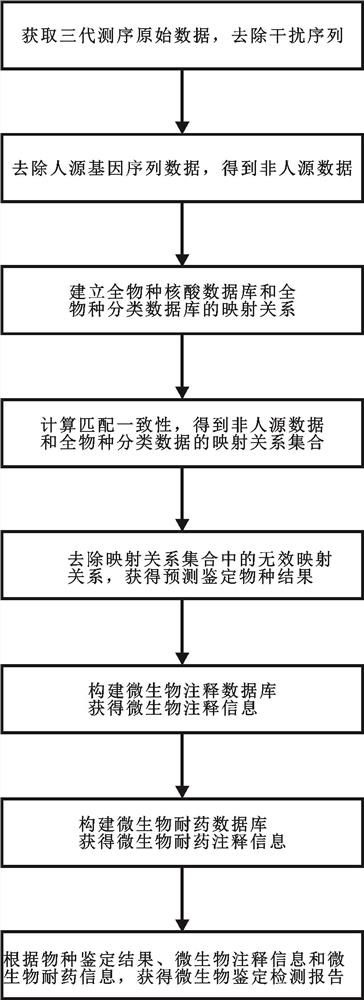
Pathogenic microorganism metagenome detection method based on third-generation sequencing
A pathogenic microorganism and metagenome technology, which is applied in the field of pathogenic microorganism metagenomic detection based on three-generation sequencing, can solve the problems of poor accuracy, retention, and low sequencing accuracy, and achieves the improvement of accuracy, accurate detection results, and improved detection accuracy. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
experiment example 1
[0123] The method of the present invention (referred to as MCP) was compared with the current mainstream microbial detection methods based on sequencing data, centrifuge and kraken2+bracken, and the corresponding comparison databases are relatively complete databases of species under the process of the method, respectively. NT and microbial-fatfree, where NT data is the NCBI all-species database, and the microbial-fatfree database mainly covers archaea, bacteria, fungi, protozoa, and viruses.
[0124] Because clinical samples are highly enriched with human data, and the 10-15% sequencing error in the third-generation sequencing will lead to unclean removal of human background data, and sometimes there are negative samples of autoimmune reactions similar to microbial infections , so first simulate and evaluate and compare the misclassification of species in a purely human background.
[0125] Human source data DNA comes from NCBI nucleic acid sequence CM000663.2, randomly gener...
experiment example 2
[0130] In order to evaluate the classification accuracy of microorganisms, the present invention randomly selected 10 common viruses, bacteria, and fungi, and randomly selected 500 sequences with a length of 300 bp from the nucleic acid sequences corresponding to each species as the starting sequence for analysis.
[0131] The nucleic acid sequence numbers involved in the simulation are:
[0132] Sequence 1: NC_006273.2; virus;
[0133] Sequence 2: NC_001798.2; virus;
[0134] Sequence 3: NC_002205.1; virus;
[0135] Sequence 4: NC_011071.1; Bacteria;
[0136] Sequence 5: NZ_CP014955.1; Bacteria;
[0137] Sequence 6: NC_007795.1; Bacteria;
[0138] SEQUENCE 7: NC_032089.1; Fungus;
[0139] SEQUENCE 8: NC_007445.1; Fungus;
[0140] Sequence 9: NC_013660.2; Fungus;
[0141] SEQ ID NO: CP022321.1; Fungus.
[0142] Detection method:
[0143] Method 1: MCP / ASD;
[0144] Method 2: centrifuge / NT;
[0145] Method 3: kraken2+bracken / microbial-fatfree.
[0146] Table 2: Expe...
experiment example 3
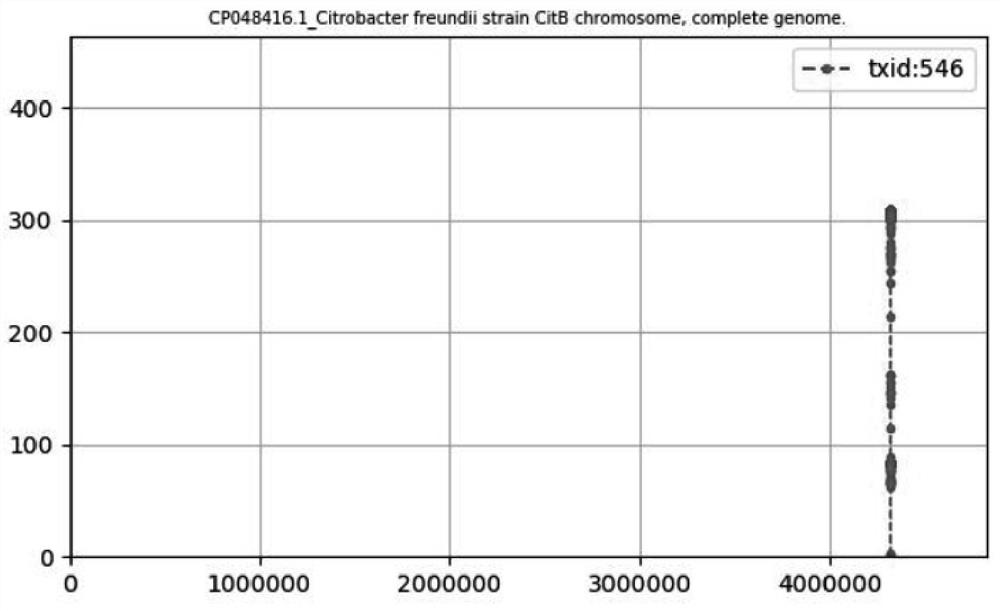
[0151] The whole process is demonstrated using the results of clinical blood samples with known drug-resistant types and microbial types. The clinical samples are Citrobacter freundii resistant to cephalosporins, and the initial sequencing data is PC001.fastq. Run the MCP program including preprocessing, mapping, classification, and drug resistance analysis modules under the Linux system:
[0152] MCP -i PC001.fastq -a preclean-mapping-ClassifyBlast-resistance -sPC001 -r y.
[0153] The whole block analysis took 7m36.839s. The result of the analysis of the drug resistance gene was the CMY beta-lactamase gene family, and the result of the detected microorganism was Citrobacter freundii, which was consistent with the results of clinical culture and drug resistance identification.
[0154] The results are displayed as follows:
[0155] 1) Raw sequence statistics
[0156] sample type of data Types of serial number number of bases shortest sequence Average seq...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com