Mushroom rot-causing fungus bacteriophage and application thereof
A bacteriophage and bacterial liquid technology, applied in the field of microorganisms, can solve the problems of chemical reagents affecting the health of consumers, human deformities or cancer, etc., and achieve the effects of non-toxic side effects, inhibiting metabolism and reproduction, and reducing pollution.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
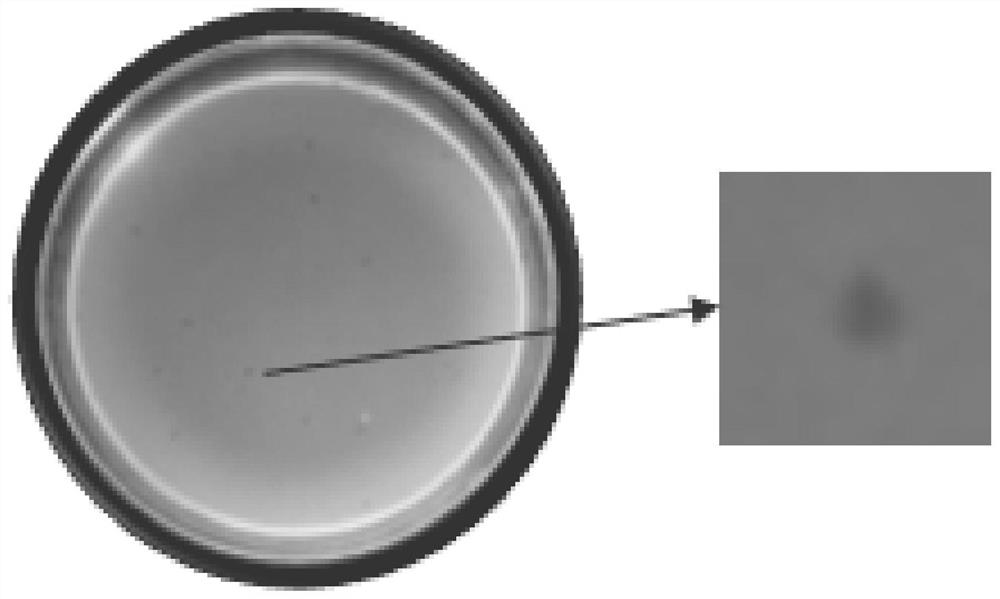
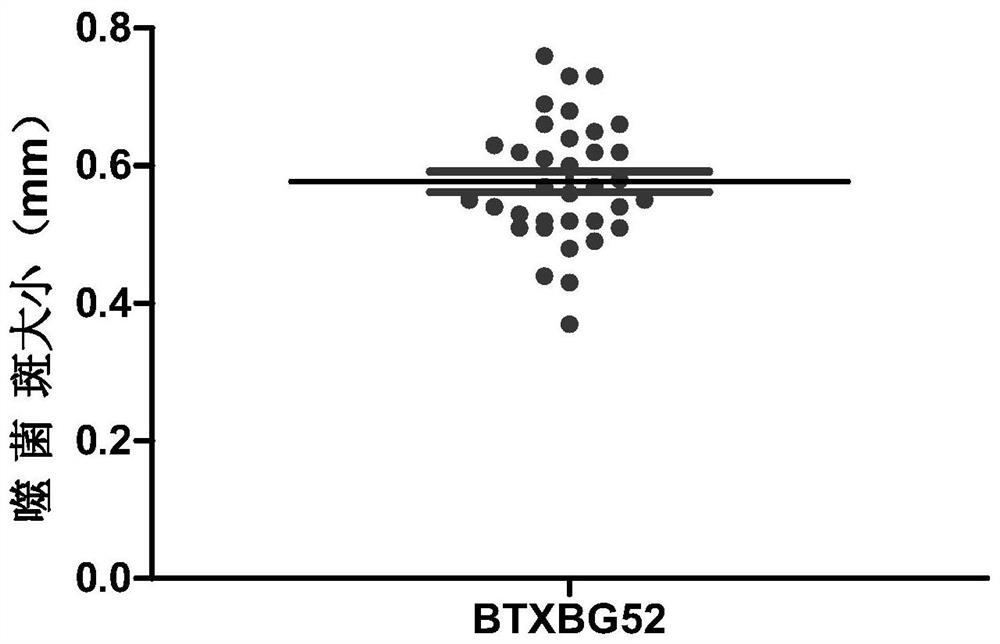
[0043] Example 1: Obtaining of bacteriophage BTXBG52
[0044] 1. Isolation and identification of spoilage bacteria XBG5 from edible fungi
[0045] (1) The edible fungi used in this stage are commercially available edible fungi, which are sealed and stored in sterile homogeneous bags, and placed in a constant temperature incubator at 37°C to accelerate corruption.
[0046] (2) Weigh 5 g of the above spoilage edible fungus samples and put them in a sterile homogeneous bag filled with 45 mL of sterile saline, and homogenize for 1-2 min with a homogenizer, which is 10 -1 The homogeneous sample was serially diluted with sterile saline. Use a pipette to take 1mL of each gradient dilution solution into a 90mm sterile plate, pour about 15-20mL of nutrient agar medium that has been melted and cooled to about 46°C, and immediately rotate the plate to fully mix the bacterial solution with the medium. After the culture medium was completely solidified, the plate was turned upside down a...
Embodiment 2
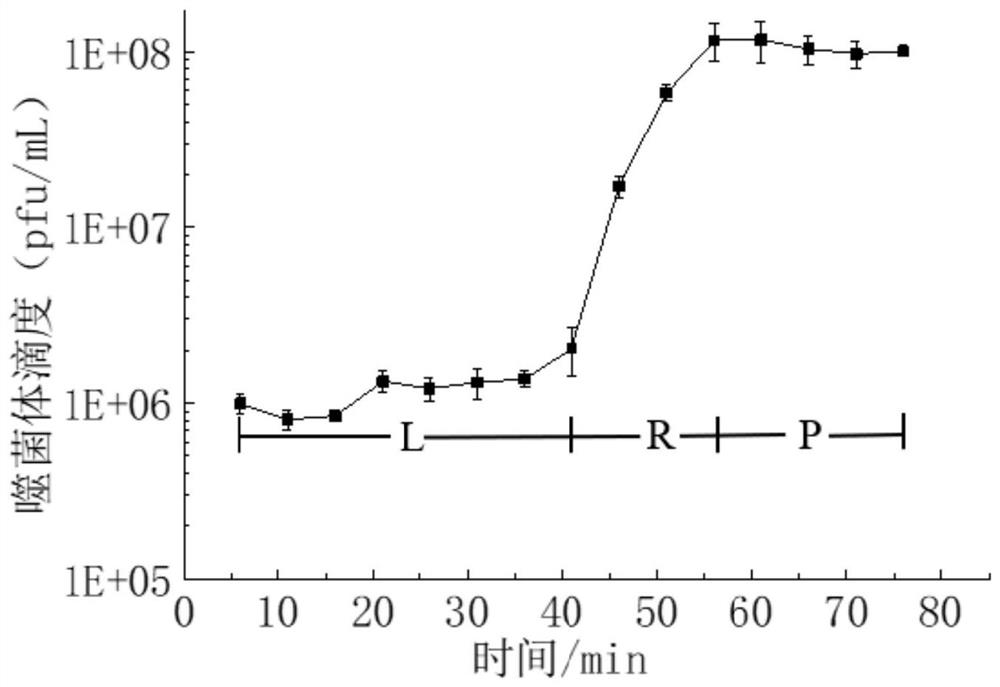
[0093] Embodiment 2: Drawing of one-step growth curve of phage BTXBG52
[0094] Take a ring of host bacteria cultured on a slant and inoculate it in a sterile LB liquid medium for 12-16 hours, then transfer it to a 100mL sterile LB liquid medium at a 3% inoculum size, at 37°C, 220r / h Min shaker culture to logarithmic growth phase (OD 600 ≈0.6), centrifuged at 4000r / min for 8min to collect the bacteria. Resuspend the bacteria in 500 μL of sterile liquid LB, add 500 μL of diluted phage particles to it to make MOI=10 -4 (MOI = phage titer / host bacterial concentration), after static adsorption for 1min, immediately centrifuge at 10000r / min for 1min and discard the supernatant to remove free phage particles. Immediately place it in a shaker at 37°C and 220r / min, take samples every 5 minutes, use the double-layer plate method to measure the titer of the phage in the process of 0-100 minutes, repeat three times at each time point to get the average titer, and draw a step growth cu...
Embodiment 3
[0097] Embodiment 3: Determination of bacteriophage BTXBG52 cracking ability
[0098] Pick a single colony of the host bacterium XBG5 on LB solid medium, inoculate it in 5mL sterile LB liquid medium, cultivate it on a shaker at 37°C and 220r / min for 12 hours, then serially dilute it 10 times, and measure it by plate coating method For the number of live bacteria, dilute the host bacteria liquid with sterile LB medium to make the bacterial concentration 10 7 cfu / mL. The purified phage lysate was amplified to a titer of 10 9 pfu / mL, the host bacterial liquid and phage lysate were mixed according to different MOI (MOI=phage titer / host bacterial colony number), and distributed in 96-well plates, and each MOI was set to 5 parallels. Place the 96-well plate at 37°C, 160r / min, shake and culture for 10h, and measure the OD of the culture solution with a microplate reader every 30min 600 , to OD 600 The average value is the ordinate, the time is the abscissa, and the antibacterial ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com