Preparation method of solid polymer electrolyte of zinc ion battery
A solid polymer, zinc ion battery technology, applied in the preparation of solid polymer electrolyte, polyacrylonitrile-polyethylene glycol diacrylate-based solid polymer electrolyte preparation field, can solve the problem of low electrical conductivity at room temperature, metal zinc The problems of uneven deposition of negative electrode and dissolution of positive active material can achieve high ionic conductivity, improve cycle stability, and reduce polarization.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
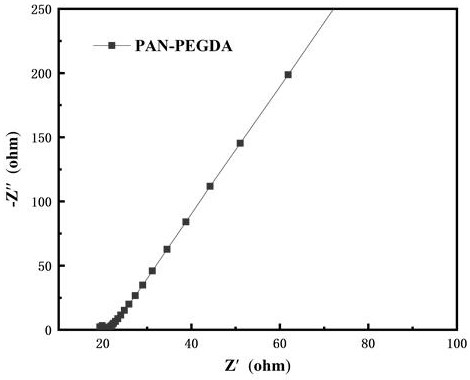
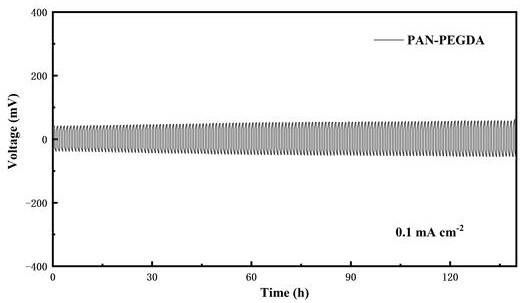
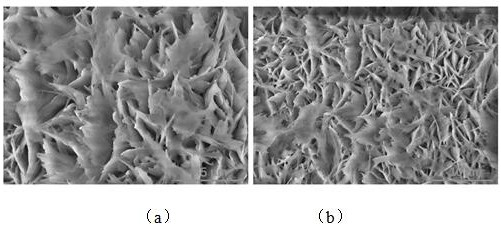
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] Step 1: Take 0.3g polyethylene glycol acrylate (PEGDA), heat and melt at 80°C to obtain a colorless transparent viscous liquid;
[0023] Step 2: Take benzoin dimethyl ether (DMPA) photoinitiator with a mass fraction of 2%, add it to PEGDA, and keep stirring at 80°C for 5 minutes to form a uniform colorless transparent viscous liquid;
[0024] Step 3: Place the liquid obtained in Step 2 under a xenon lamp with a power of 1.125W and irradiate at a constant temperature of 60°C for 10 minutes. At this time, PEGDA is partially polymerized under the irradiation of a photoinitiator and ultraviolet light, and is still a colorless transparent viscous liquid, which is ready for use;
[0025] Step 4: Take 0.83g Zn(OAc) 2 2H 2 O and 0.2g of polyacrylonitrile (PAN) were added to 10ml of N-methylpyrrolidone (NMP) solvent in turn, and the mixed solution was heated and stirred in a water bath at 80°C for 50min to form a light yellow liquid;
[0026] Step 5: Slowly pour the light yell...
Embodiment 2
[0029] Step 1: Take 0.3g polyethylene glycol acrylate (PEGDA), heat and melt at 80°C to obtain a colorless transparent viscous liquid;
[0030] Step 2: Take benzoin dimethyl ether (DMPA) photoinitiator with a mass fraction of 2%, add it to PEGDA, and keep stirring at 80°C for 5 minutes to form a uniform colorless transparent viscous liquid;
[0031] Step 3: Place the liquid obtained in Step 2 under a xenon lamp with a power of 1.125W and irradiate at a constant temperature of 60°C for 8 minutes. At this time, PEGDA is partially polymerized under the irradiation of a photoinitiator and ultraviolet light, and is still a colorless transparent viscous liquid, which is ready for use;
[0032] Step 4: Take 0.83g Zn(OAc) 2 2H 2 O and 0.2g of polyacrylonitrile (PAN) were added to 10ml of N-methylpyrrolidone (NMP) solvent in turn, and the mixed solution was heated and stirred in a water bath at 80°C for 50min to form a light yellow liquid;
[0033] Step 5: Slowly pour the light yello...
Embodiment 3
[0040]Step 1: Take 0.3g polyethylene glycol acrylate (PEGDA), heat and melt at 80°C to obtain a colorless transparent viscous liquid;
[0041] Step 2: Take benzoin dimethyl ether (DMPA) photoinitiator with a mass fraction of 2%, add it to PEGDA, and keep stirring at 80°C for 5 minutes to form a uniform colorless transparent viscous liquid;
[0042] Step 3: Place the liquid obtained in Step 2 under a xenon lamp with a power of 1.125W and irradiate at a constant temperature of 60°C for 5 minutes. At this time, PEGDA is partially polymerized under the irradiation of a photoinitiator and ultraviolet light, and is still a colorless transparent viscous liquid, which is ready for use;
[0043] Step 4: Take 0.83g Zn(OAc) 2 2H 2 O and 0.2g polyacrylonitrile (PAN) were added to 10ml N-methylpyrrolidone (NMP) solvent in turn, and the mixed solution was heated and stirred in a water bath at 80°C for 50min to form a light yellow liquid;
[0044] Step 5: Slowly pour the light yellow liqui...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Impedance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Conductivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com