Application of plant extract in preparation of cosmetics with bacteriostatic and acarus killing functions
A technology of plant extracts and cosmetics, applied in cosmetics, cosmetic preparations, plant/algae/fungus/moss components, etc., can solve the problems of uncontrollable product quality and complicated preparation process, and achieve better mite removal effect and preparation The method is simple, and the effect of strong mite removal effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0055] Embodiment 1 plant extract and preparation method thereof
[0056] Plant Extract #1:
[0057] Take 16kg of licorice roots, 18kg of eucalyptus leaves, 20kg of solitary roots, and 22kg of perilla leaves, mix them, grind them, and pass through a 40-mesh sieve; use 40% ethanol to extract in an extraction tank to obtain a preliminary extract; carry out ultrafiltration on the preliminary extract Membrane concentration and separation to obtain a concentrated extract; dry the concentrated extract to obtain a plant extract, and dissolve the plant extract in 500 kg of water to obtain plant extract #1.
[0058] Plant Extract #2:
[0059] Get 16kg of licorice roots, 18kg of eucalyptus leaves, 20kg of solitary roots, and 22kg of perilla leaves, respectively crush them and pass through a 40-mesh sieve; use 40% ethanol to extract respectively in the extraction tank to obtain four preliminary extracts; The liquid was concentrated and separated by ultrafiltration membrane to obtain fo...
Embodiment 2
[0072] Antibacterial experiment of embodiment 2 plant extract
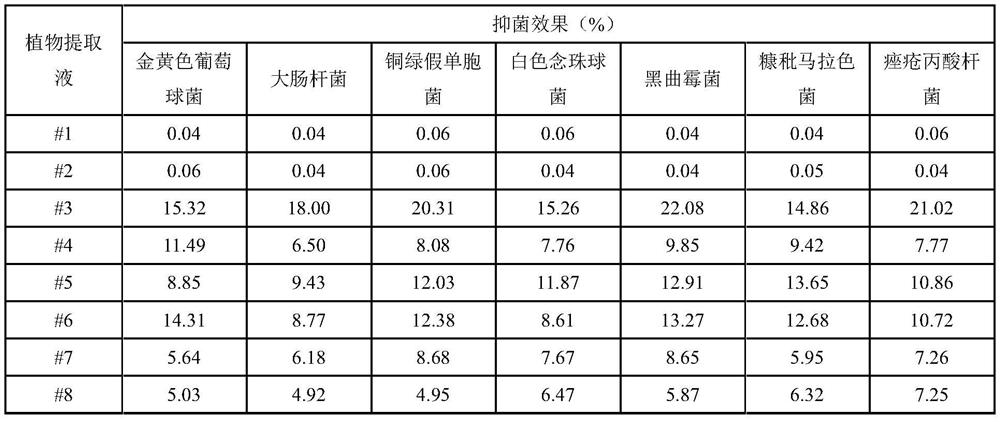
[0073] The minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC value) was used to measure the antibacterial effect of the plant extract (ie stock solution) prepared in Example 1 on common pathogenic bacteria.
[0074] The tested strains were Staphylococcus aureus (ATCC6538), Escherichia coli (ATCC 8739), Pseudomonas aeruginosa (ATCC 16404), Candida albicans (ATCC 10231), Aspergillus niger (ATCC 16404), Malassezia furfur (ATCC44344), Propionibacterium acnes (ATCC6919);
[0075] (1) The minimum inhibitory concentration for inhibiting Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Candida albicans adopts the microplate method.
[0076] Add 100 μL of Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Candida albicans bacteria liquid and 100 μL of plant extract (any one of the extracts prepared in Example 1 is concentrated in equal proportions according to the MIC method or Dilution), simultaneo...
Embodiment 3
[0085] The mite removal experiment of embodiment 3 plant extract
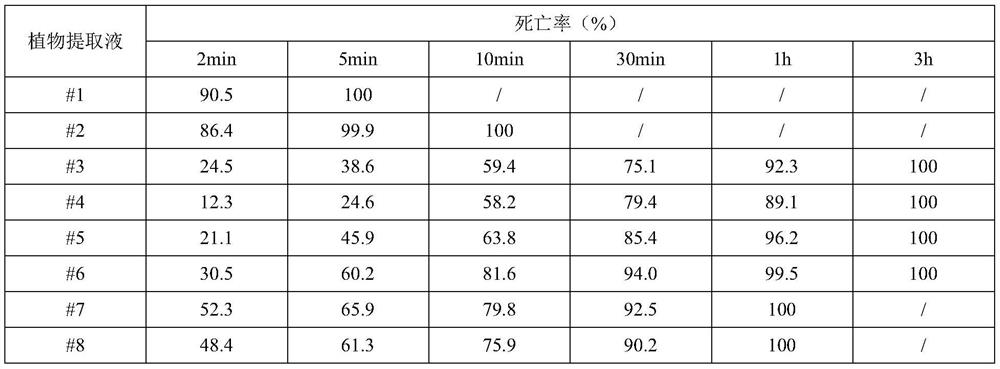
[0086] The male and female adults and nymphs of Dermatophagoides farinage were used as the tested mite species. Each plant extract prepared in Example 1 after dilution was used as the test agent respectively, and each plant extract was used to act on 500 mites, and the mite mortality was observed for 2min, 5min, 10min, 30min, 1h, and 3h. The results are shown in Table 2:
[0087] Table 2 Plant Extract Ability Test for Mite Removal
[0088]
[0089] It can be seen from Table 2 that plant extract #1 has the best lethal effect on mites, and the lethality rate can reach 90.5% after 2 minutes of action, and all mites can be killed within 5 minutes. The lethal effect of plant extract #2 on mites is second, the lethality rate reaches 86.4 in 2 minutes, 99.9 in 5 minutes, and all can be killed in 10 minutes. The lethal effect of plant extract #3, plant extract #4, plant extract #5 and plant extract #6 on mites is...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com