Method for fluoride-free extraction of valuable components from ilmenorutile
A technology of rutile and ferroniobium, applied in chemical instruments and methods, inorganic chemistry, process efficiency improvement, etc., can solve problems such as hazardous waste gas, and achieve high economic value, high-efficiency extraction, full and rapid release
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
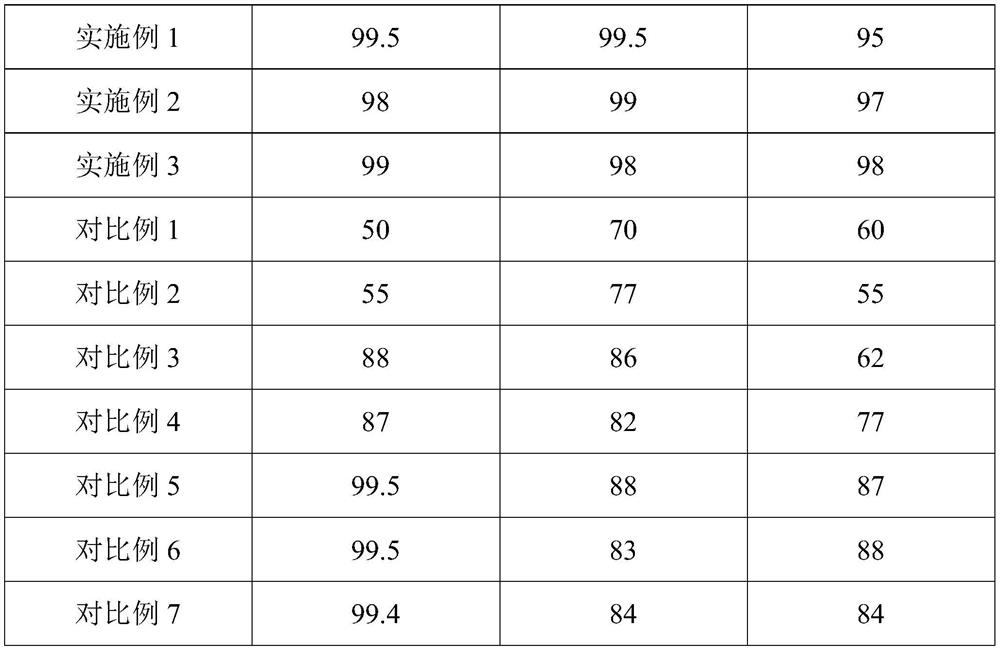
[0052] This embodiment provides a method for extracting valuable components without fluorine from ferro-niobium rutile, said method comprising the following steps:
[0053] (1) Carry out the first roasting and the second roasting successively to ferro-niobium rutile to obtain the roasted material; the auxiliary agent in the first roasting includes triethanolamine; the addition amount of the auxiliary agent in the first roasting is the ferroniobium 15% of rutile; the temperature of the first roasting is 300°C; the time of the first roasting is 80min; the auxiliary agent in the second roasting is salt, sodium carbonate; the auxiliary agent in the second roasting The mass ratio of the added amount to the niobium-iron rutile is 1.2:1; the temperature of the second calcination is 700°C; the time of the second calcination is 4h;
[0054] (2) The roasted material obtained in step (1) is subjected to water treatment and acid treatment successively to obtain an acid treatment liquid, a...
Embodiment 2
[0057] This embodiment provides a method for extracting valuable components without fluorine from ferro-niobium rutile, said method comprising the following steps:
[0058] (1) Carry out the first roasting and the second roasting successively to ferro-niobium rutile to obtain the roasted material; the auxiliary agent in the first roasting includes triethanolamine; the addition amount of the auxiliary agent in the first roasting is the ferroniobium 12% of rutile; the temperature of the first roasting is 250°C; the time of the first roasting is 70min; the auxiliary agent in the second roasting is alkali, potassium hydroxide and; the auxiliary agent in the second roasting The mass ratio of the additive amount of the agent to the niobium iron rutile is 1:1; the temperature of the second calcination is 600°C; the time of the second calcination is 2h;
[0059] (2) The roasted material obtained in step (1) is subjected to water treatment and acid treatment successively to obtain an a...
Embodiment 3
[0062] This embodiment provides a method for extracting valuable components without fluorine from ferro-niobium rutile, said method comprising the following steps:
[0063] (1) Carry out the first roasting and the second roasting successively to ferro-niobium rutile to obtain the roasted material; the auxiliary agent in the first roasting includes triethanolamine; the addition amount of the auxiliary agent in the first roasting is the ferroniobium 10% of rutile; the temperature of the first roasting is 200°C; the time of the first roasting is 60min; the auxiliary agent in the second roasting is alkali; the alkali is sodium hydroxide; the second The mass ratio of the amount of additives added during calcination to the niobium-iron rutile is 0.6:1; the temperature of the second calcination is 500°C; the time of the second calcination is 1h;
[0064] (2) The roasted material obtained in step (1) is subjected to water treatment and acid treatment successively to obtain an acid tre...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com