Method for amplifying nucleic acid in single cell
A single-cell, cell-based technology, applied in the field of amplifying nucleic acid in single cells and performing nucleic acid amplification on single cells, can solve the problems of genome fragment loss, high amplification deviation, etc., to increase concentration, compress reaction volume, and exclude Source nucleic acid contamination and effects of cross-contamination
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
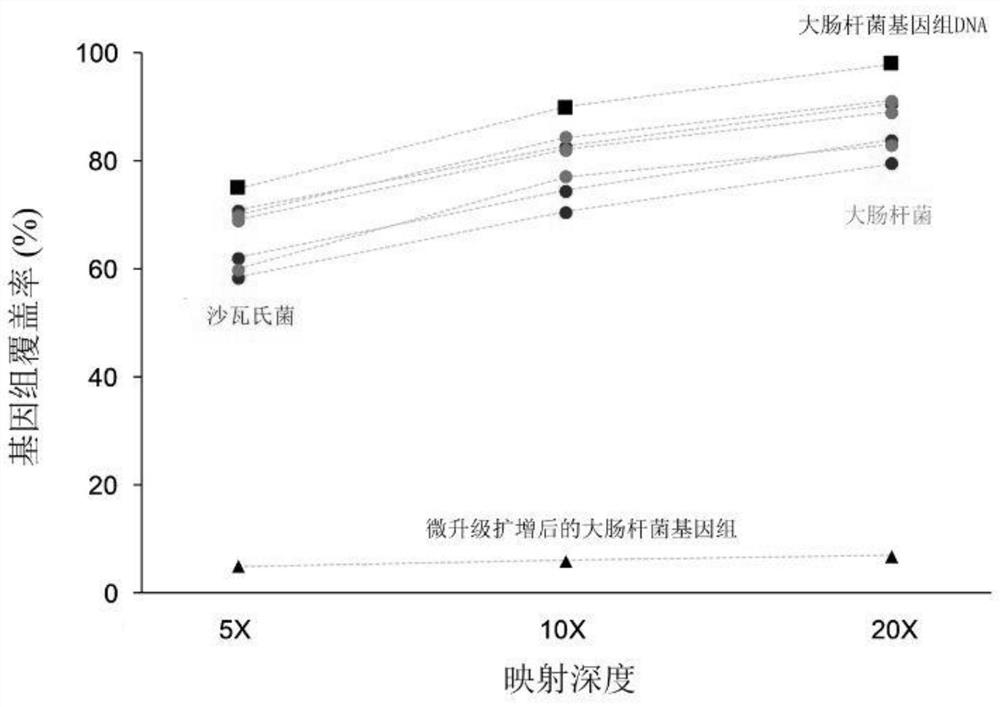
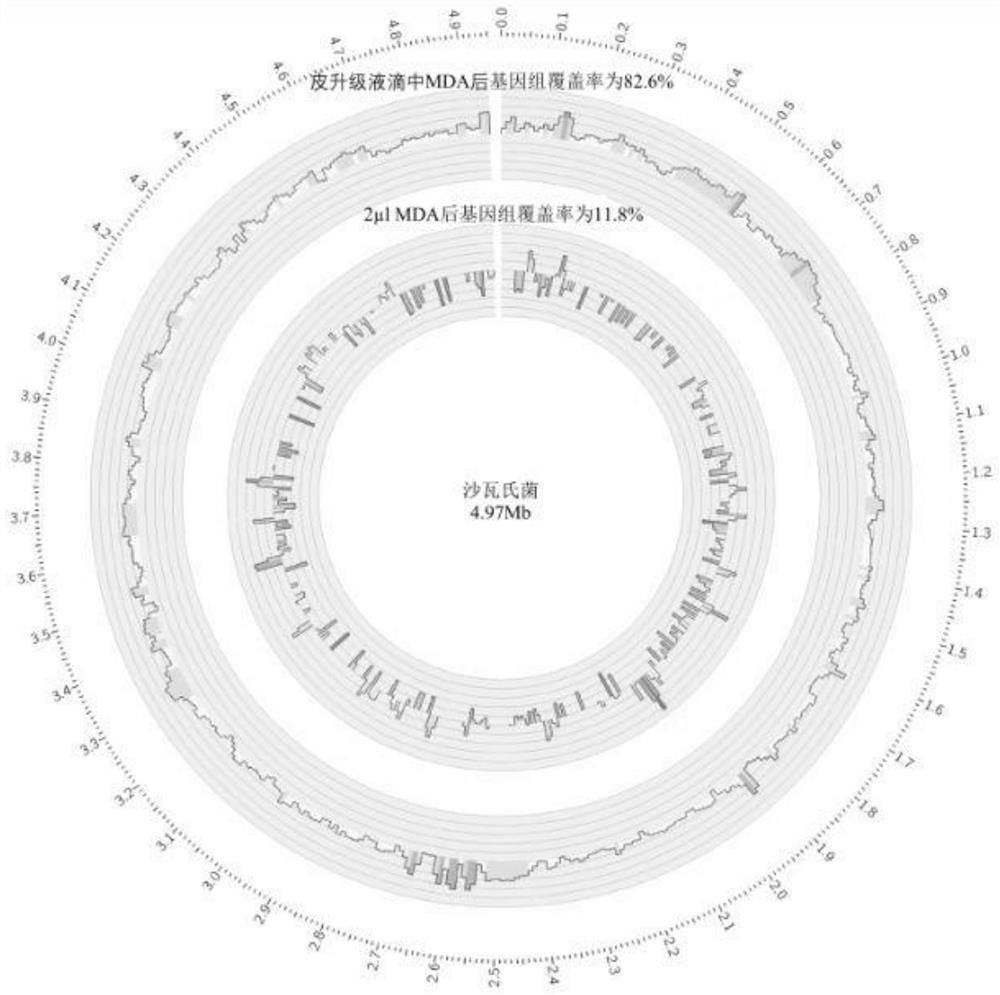
[0039] To validate the invention, the inventors have first tested the MDA response of single cells in microdroplets of 40 μm (diameter) size. In Figure 1, the genome identity in different cases is compared. in: Figure 1A Among them, the E. coli genome amplified by the micro-upgrading system (2μl) has very poor uniformity and low coverage, which cannot be applied to any downstream analysis; while putting the genome into the droplet for amplification can obtain better Uniformity and high genome coverage. The sequencing results prove that the whole genome amplified E. coli genome in the skin-upgraded droplets can achieve a response rate of 80%, while the E. coli genome amplified by micro-upgrading can only achieve a response rate of about 10%. It can be seen that Many genome fragment deletion regions ( Figure 1B ). Single-cell genomes can achieve a response rate of 80%, which is very beneficial for many applications, such as single-nucleotide variation analysis of cancer cel...
Embodiment 2
[0049] First, using high-throughput microfluidic technology, a single Escherichia coli is captured in a single microdroplet (containing 3% w / v agarose hydrogel solution) (the microfluidic chip used for capture such as Figure 4 Shown: In the first input channel, the oil phase is input to the flow channel. The second input channel is used to input molten agarose hydrogel solution into the flow channel; in order to ensure that the agarose hydrogel is always in a molten state, the heating device is arranged near the second input channel. The third input channel is used to input Escherichia coli suspension into the flow channel. After the molten agarose hydrogel solution and the E. coli suspension are mixed, under the shear force of the oil phase, an agarose hydrogel micro-droplet containing a single E. coli is formed, and the micro-droplet can be passed through the fourth output channel. collected for subsequent experiments), and the collected micro-droplets were placed at 4°C t...
Embodiment 3
[0055] First, using high-throughput microfluidic technology, a single Escherichia coli was captured in a single droplet (containing 6% w / v acrylamide monomer and N, N'-methylenebisacrylamide, the mass ratio of the two 37.5:1; and 0.3% w / v ammonium persulfate solution) (capturing microfluidic chips such as Figure 4 shown), and the collected microdroplets were allowed to gel at room temperature. After gelation, the micro-droplets were de-emulsified to obtain polyacrylamide hydrogel microspheres (60 μm in diameter) encapsulating a single Escherichia coli. Secondly, the polyacrylamide hydrogel microspheres containing a single Escherichia coli were soaked in the lysate, so that the Escherichia coli was fully lysed, and its genome was fully exposed and stored in the polyacrylamide hydrogel microspheres. Again, after confirming that E. coli was completely lysed, the polyacrylamide hydrogel microspheres containing a single E. coli genome were washed 3 times with 200 microliters of n...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com