Influenza A virus PB1 protein T cell epitope polypeptide fragment and application thereof
A technology of influenza vaccine and medicinal salt, which is applied in the direction of viral peptides, viruses, antiviral agents, etc., can solve the problems of incompletely clear synergistic mechanism, inability to resist virus attack, etc., and achieve the effect of stimulating virus-specific T cell immune response
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
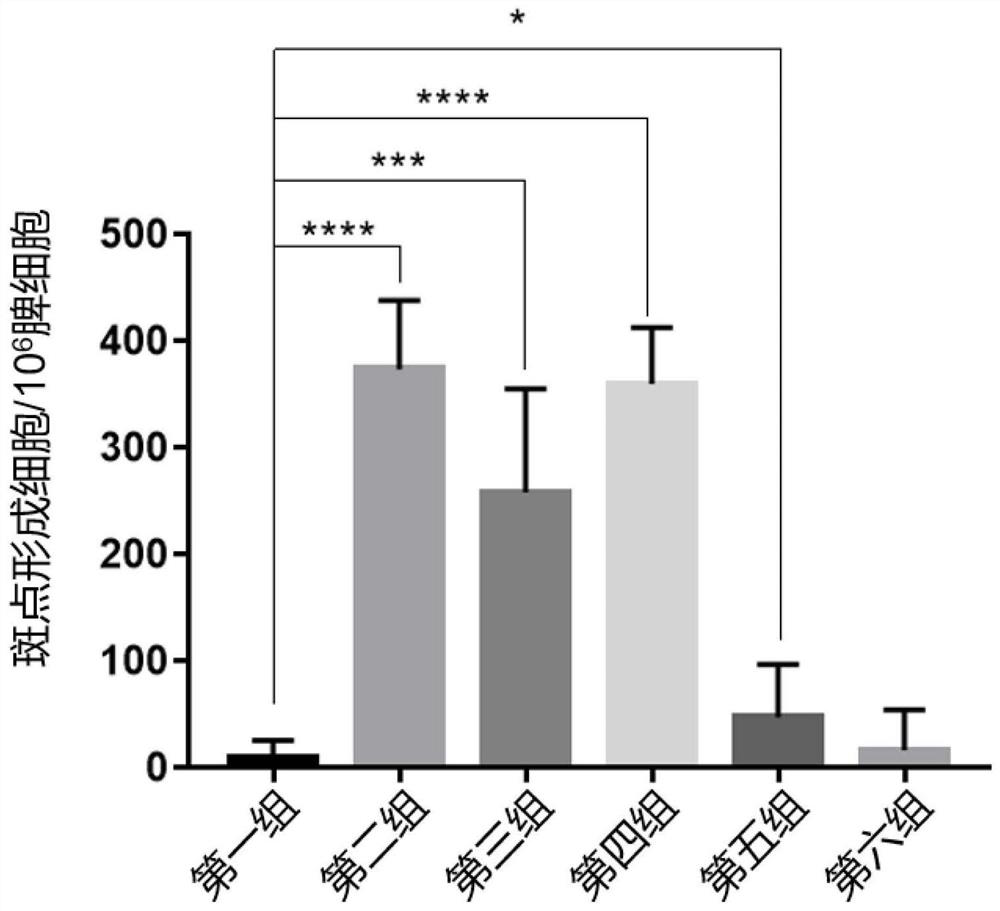
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0055] Embodiment 1, preparation of nonapeptide derived from PB1
[0056] The amino acid sequence of influenza A virus (PR8) PB1 is shown in SEQ ID NO.1, which is used as the sequence source of the synthetic polypeptide fragment PB1 81-89. Artificially synthesized polypeptide fragments PB1 81-89, randomly constructed point mutations (corresponding mutant polypeptide fragments a, b) except the anchor amino acids of PB1 81-89, and the negative control hepatitis B virus HBc82-90 peptide used in the experiment (abbreviated as polypeptide fragment HBc82 -90).
[0057] The amino acid sequences of these four polypeptides are as follows (from left to right from the nitrogen terminal to the carbon terminal direction):
[0058] Polypeptide fragment PB1 81-89 (SEQ ID NO.2): GYAQTDCVL
[0059] Polypeptide fragment HBc82-90 (SEQ ID NO.3): RELVVSYVN
[0060] Mutant polypeptide fragment a (SEQ ID NO.10): GYAQADCVL
[0061] Mutant polypeptide fragment b (SEQ ID NO.11): GYAQTDAVL
[0062]...
Embodiment 2
[0063] Example 2, PB1 81-89 polypeptide fragment and H-2K D Molecular binding force
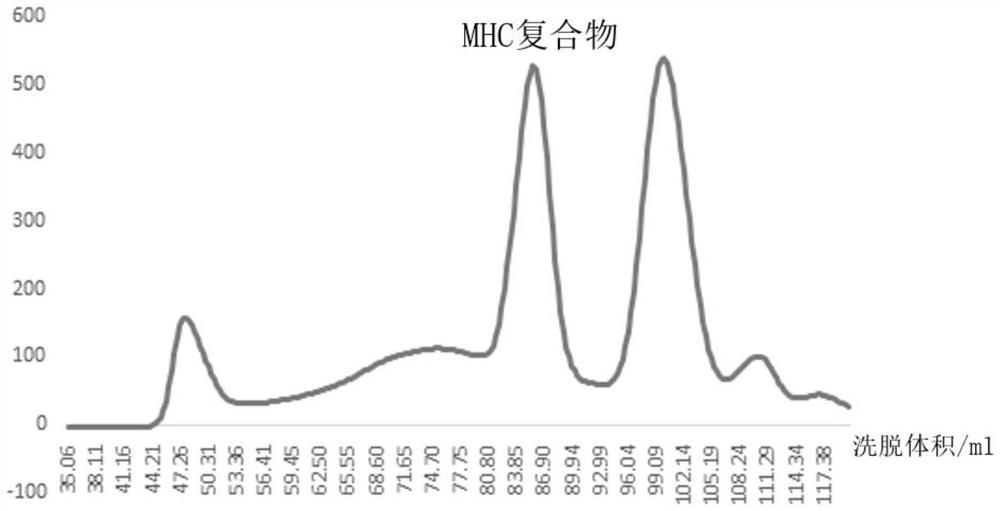
[0064] 1. In vitro refolding (refolding) test to detect peptide and H-2K D molecular binding capacity
[0065] In the in vitro refolding experiment, if the polypeptide can bind with H-2K D Molecular binding, then peptide, H-2K D And β2 microglobulin (β2m) can form a stable polypeptide-H-2K D -β2m ternary complex, polypeptide-H-2K appears in the molecular sieve chromatogram D - β2m complex protein peak. H-2K D The molecule is composed of a heavy chain and a light chain, the coding sequence of the heavy chain is shown in SEQ ID NO.4, and its amino acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.5; the coding sequence of the light chain is shown in SEQ ID NO.6, and its The amino acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.7.
[0066] (1) H-2K D Construction of heavy chain extracellular region expression plasmid
[0067]will code H-2K D The DNA of the extracellular region of the heavy chain (Genbank No. K...
Embodiment 3
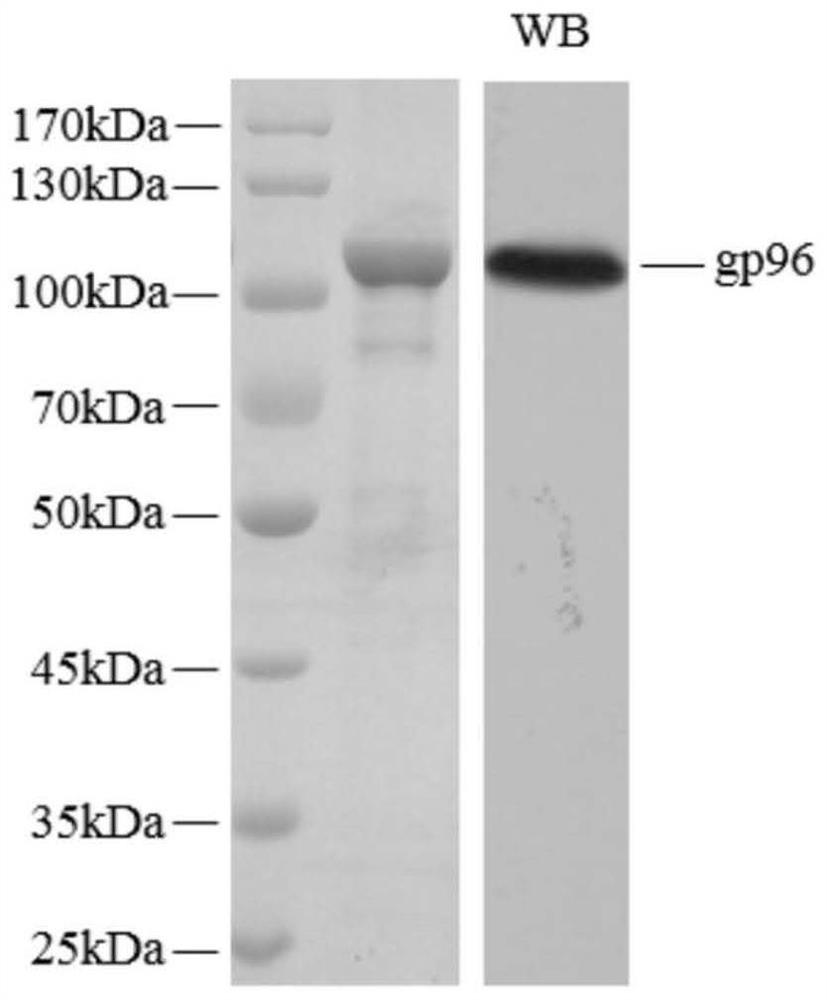
[0084] Example 3, Insect Baculovirus Expression System Expressing Heat Shock Protein gp96
[0085] 1. pFastBac TM 1- Construction of gp96 plasmid
[0086] 1. Design and synthesis of gp96 primers: according to the sequence of the human gp96 gene in GenBank (the sequence number is NM_003299, its gene sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.8, and its encoded amino acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.9) as a template , an EcoRI restriction site was added to the 5' end of the gp96 gene, and an XbaI restriction site was added to the 3' end. The forward primer sequence is: 5'-G GAATTC ATGGGCAGCAGCCATCAT-3' (the underline is the EcoRI restriction site); the reverse primer sequence is: 5'-GC TCTAGA CTATTACAATTCATCTTTTTC-3' (the underline is the XbaI restriction site), commissioned Shanghai Sangon Bioengineering Technology Service Company to synthesize the primer, and sequenced to verify that the sequence of the primer was correct.
[0087] 2. Extract the mRNA of human liver cancer cell H...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com