Ginseng PgJAZ1 gene, method for improving protopanaxatriol saponin based on gene and application
A ginseng and gene technology, applied in the fields of application, genetic engineering, plant gene improvement, etc., can solve the problems of JAZ gene cloning and functional research that have not been reported
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
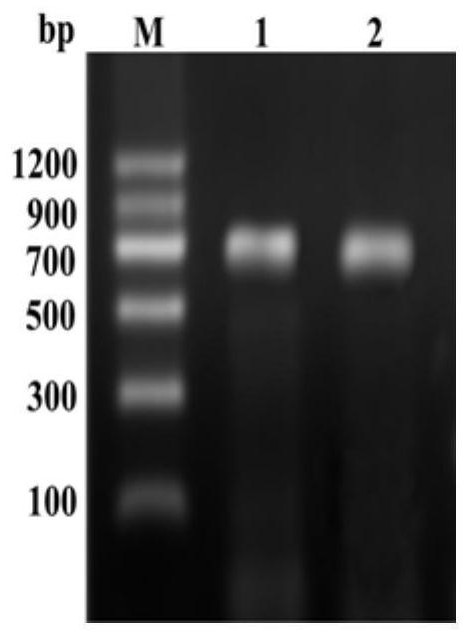
[0030] Acquisition of the PgJAZ1 gene
[0031] 1. Ginseng RNA extraction and reverse transcription
[0032] After culturing the hairy roots of ginseng at 25°C for 3 weeks, add 100 μmol / L MeJA to the culture medium, culture at 120 rpm, 25°C for 24 hours in the dark, extract total RNA, and use oligod(T) 18 As a primer, the first strand of cDNA was synthesized by reverse transcription with reverse transcriptase, and the synthesized cDNA was stored at -20°C for future use.
[0033] 2. PgJAZ1 gene amplification
[0034] According to the MeJA-induced ginseng transcriptome sequencing results, primers were designed for PCR amplification. PgJAZ1 gene PCR amplification primers are as follows.
[0035] PgJAZ1-F: 5'-ATGTTTCTTCAACGGCCGGAAAT-3'; (SEQ ID NO.4)
[0036] PgJAZ1-R: 5'-CTATAAGTTGAGATCAAACTG-3'; (SEQ ID N0.5)
[0037] The PCR amplification conditions were: pre-denaturation at 94°C for 3 min; denaturation at 94°C for 30 s, annealing at 50°C for 20 s, extension at 72°C for 30 ...
Embodiment 2
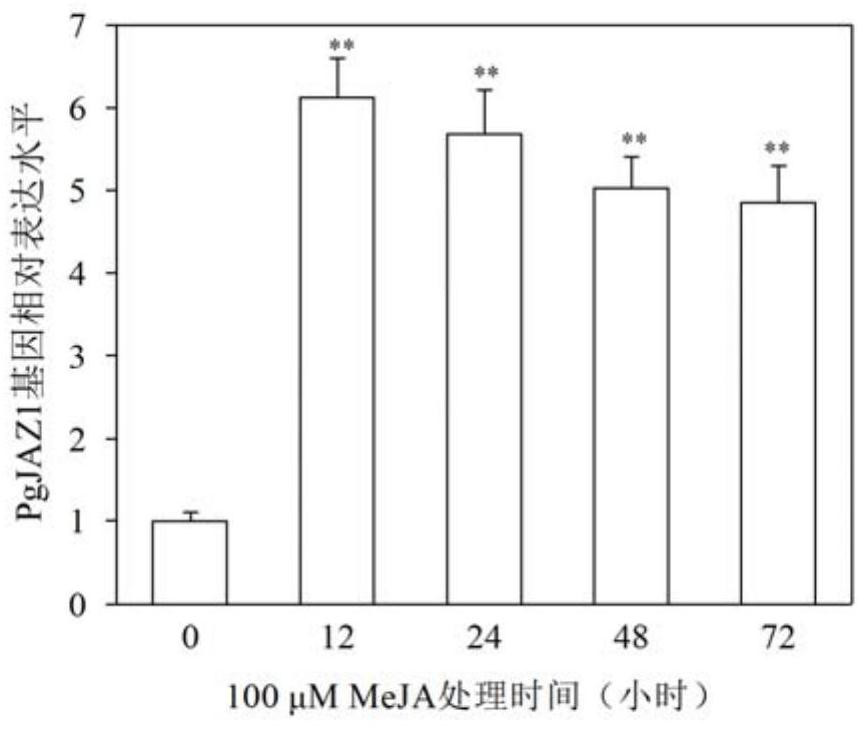
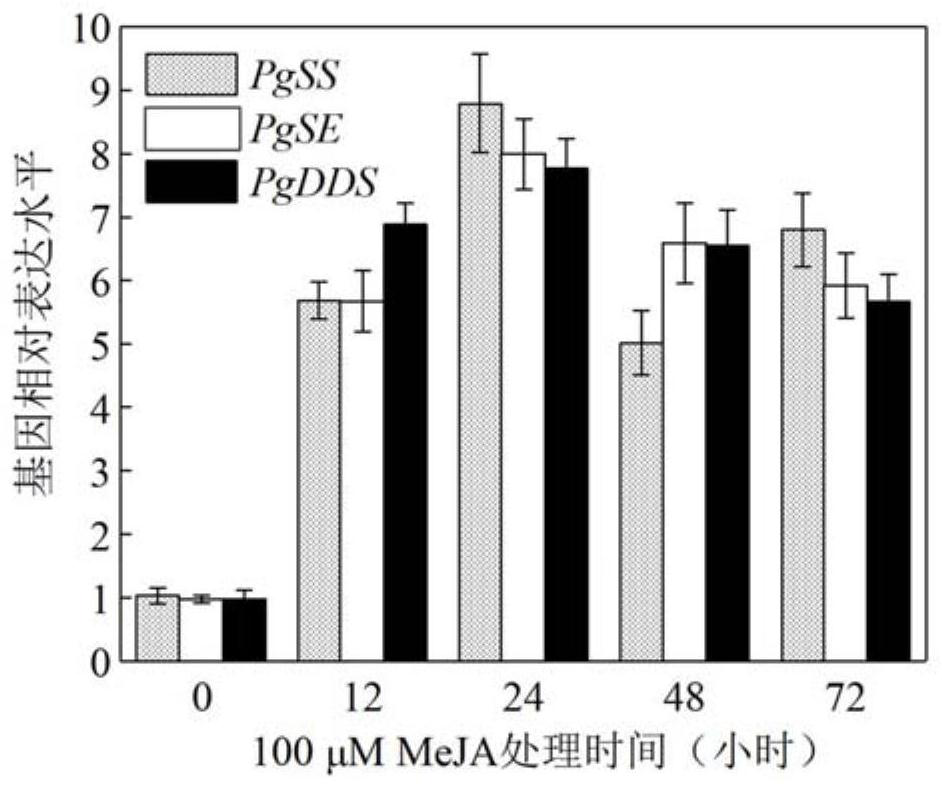
[0039] Relative quantitative analysis of PgJAZ1 gene expression
[0040] 1. RNA extraction and reverse transcription
[0041] The hairy roots of ginseng were cultured in 1 / 2MS liquid medium at 25°C and 110r / min in the dark for 21 days, and were treated with MeJA (100 μmol / L) respectively. T) 18 As a primer, the first strand of cDNA was synthesized by reverse transcription with reverse transcriptase. Primers for qRT-PCR analysis of PgJAZ1, β-actin, PgSS, PgSE and PgDDS genes are as follows:
[0042] PgJAZ1 fluorescent quantitative primer F: 5'-GAGAGACCTGCTGCAATGGA-3'; (SEQ ID NO.6)
[0043] PgJAZ1 fluorescent quantitative primer R: 5'-GGGGGCATGTTGAGGAAAGA-3'; (SEQ ID NO.7)
[0044] β-actin fluorescence quantitative primer F: 5'-TGCCCCAGAAGAGCACCCTGT-3'; (SEQ ID NO.8)
[0045] β-actin fluorescent quantitative primer R: 5'-AGCATACAGGGAAAGATCGGCTTGA-3'; (SEQ ID N0.9)
[0046] PgSS fluorescent quantitative primer F: 5'-ATCCCTCCGGAGCCACACTGG-3'; (SEQ ID NO.10)
[0047] PgSS f...
Embodiment 3
[0055] Ginsenoside Extraction and Content Determination
[0056] 1. Extraction of ginsenosides
[0057] Take fresh ginseng hair roots or tissues, wash them with tap water for 2 minutes, and then use ddH 2 O washed, dried at 60°C to constant weight. Grind it into a fine powder, leaching with 80% methanol at 60°C (1g:40mL), ultrasonic treatment 3 times, 15min each time; Saturated n-butanol extraction, and the n-butanol layer was collected. Evaporate n-butanol to dryness in a water bath at 60°C to obtain total ginsenosides, dissolve with an appropriate amount of methanol ultrasonically, set the volume to the mark, and pass through a 0.45 μm microporous membrane to obtain a sample solution.
[0058] 2. Determination of ginsenoside content
[0059] Ginsenoside content determination adopts HPLC method, and HPLC measuring condition is: LC-MS 8050 high performance liquid chromatography; Chromatographic column is ACQUITY UPLC BEH Shield RP18 column (1.7 μ m, 2.1mm * 50mm); Mobile p...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com