Carrier-free protein intracellular delivery prodrug as well as preparation method and application thereof
A technology for delivering prodrugs and proteins, applied in the field of protein modification and transport, to achieve the effect of reducing toxic and side effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Synthetic example
[0045] (1) 4-(Hydroxymethyl)phenylboronic acid pinacol ester (0.5 g, 2.1 mmol) was dissolved in 20 mL of anhydrous THF. Triethylamine (0.6 mL, 4.5 mmol) was added, followed by 4-nitrophenyl chloroformate (0.47 g, 2.3 mmol), followed by stirring at room temperature for 1 hour. The reaction mixture was diluted with ethyl acetate and washed with 1.0 M HCl followed by saturated NaHCO 3 Wash with aqueous solution. The organic layer was treated with MgSO 4 Drying, filtration and concentration, followed by purification on a silica gel column eluting with 5% ethyl acetate in hexanes gave a white solid as monomer N:
[0046]
[0047] pass 1 H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) characterization, δ = 8.25 (d, J = 9.2 Hz, 2H), 7.85(d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H), 7.43 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H), 7.36 ( d, J = 9.2 Hz, 2H), 5.31(s, 2H), 1.35 (s, 12H);
[0048] Monomer P is the structure shown in the following formula:
[0049]
[0050] Monomer N and monomer P are used in the following examples.
Embodiment 1
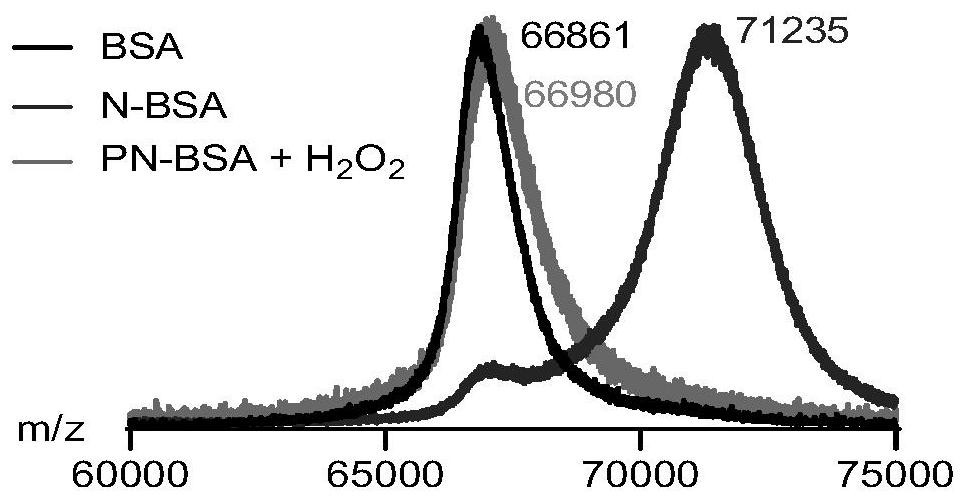
[0052] Dissolve monomer N in dimethyl sulfoxide solution to a final concentration of (32 mg / mL) to obtain monomer N solution; dissolve bovine serum protein (BSA) in NaHCO at a concentration of 0.1 M 3 aqueous solution (6 mg / mL) to obtain bovine serum protein solution; then mix the two solutions according to the molar ratio of monomer N and amino group of bovine serum protein as 2:1, stir at room temperature for 10 hours, and transfer the reaction solution into a dialysis bag (MWCO = 1 kDa), dialyzed with ultrapure water for 3 days, and freeze-dried to obtain N-modified protein monomer (N-BSA).
[0053] Dissolve monomer P and N-BSA in water respectively to obtain monomer P solution (1 mg / mL) and N-BSA solution (6 mg / mL). Mix the monomer P solution and the N-BSA solution in a molar ratio of 2:3 according to the molar ratio of the monomer P and the primary amino group of the protein BSA, stir at room temperature for 30 minutes, and then transfer the reaction solution to an ultraf...
Embodiment 2
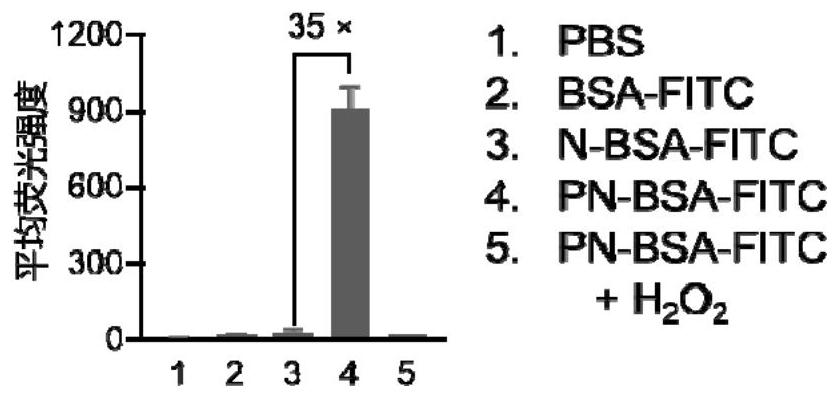
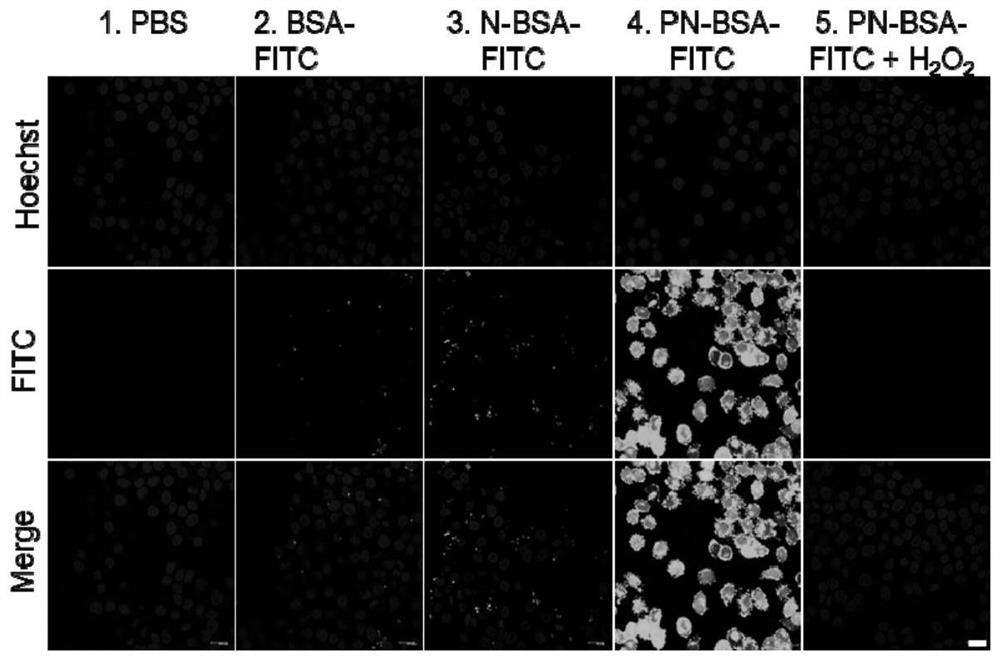
[0056] BSA was labeled with fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC) in 0.1 M NaHCO 3 According to protein: FITC = 1:4 (mass ratio) in the buffer solution, react overnight under dark conditions, and then use ultrapure water dialysis (MWCO = 3.5kDa) for two days to remove unreacted FITC molecules and obtain FITC-labeled protein , and then use the method in Example 1 to modify the protein to obtain PN-BSA-FITC. Then human cervical cancer cells (HeLa) were divided into 5×10 cells per well 4 Inoculated into 24-well plates and cultured in DMEM medium containing 10% FBS for 24 hours. After the cells were completely attached to the wall, different modifications were made according to the concentration of 4 μg / mL and the final concentration of 100 μM H 2 o 2 Protein samples processed 12 hours in advance were added to the wells at 37 °C and 5% CO 2 Incubate under conditions for 12 hours. After washing twice with PBS, incubate with trypan blue solution for 3 minutes, continue to wash thr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com