Escherichia coli engineering bacterium for producing acetoin as well as construction method and application of escherichia coli engineering bacterium in whole-cell catalytic production of acetoin
A technology of Escherichia coli and construction method, applied in microorganism-based methods, applications, genetic engineering and other directions, can solve the problems of low yield, expensive substrate acetaldehyde, difficult to store, etc., and achieves lower production costs, mild reaction conditions, The effect of high product yield
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
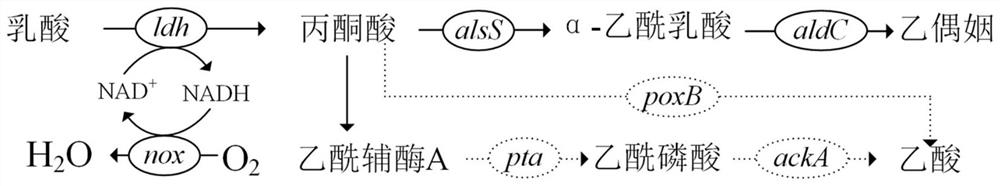
[0067] The NADH oxidase is derived from Lactococcus lactis subsp.lactisIO-1 Example 1: Knocking out the genes pta-ackA and poxB on the Escherichia coli genome using the λ-Red recombination method
[0068] With pta-ackA-U-F (SEQ ID NO.22) and pta-ackA-U-R (SEQ ID NO.23) as primers (Table 1),
[0069] Using the Escherichia coli genome as a template, pta-ackA-U (SEQ ID No.12) was obtained by PCR reaction;
[0070] With pta-ackA-tet-1 (SEQ ID NO.24) and pta-ackA-tet-2 (SEQ ID NO.25) as primers,
[0071] Using pTKS / CS as a template, pta-ackA-tet-U (SEQ ID No.13) was obtained by PCR reaction;
[0072] Using pta-ackA-tet-3 (SEQ ID NO.26) and pta-ackA-tet-4 (SEQ ID NO.27) as primers and pTKS / CS as template, pta-ackA-tet was obtained by PCR reaction -D (SEQ ID No. 14);
[0073] With pta-ackA-D-F (SEQ ID NO.28) and pta-ackA-D-R (SEQ ID NO.29) as primers, with Escherichia coli genome as template, by PCR reaction, obtain pta-ackA-D (SEQ ID No. .15).
[0074] Then using pta-ackA-U-F a...
Embodiment 2
[0084] Embodiment 2: Construction of expression vector pET28a-aldC-S2-alsS-ldh-nox and acetoin-producing Escherichia coli engineering bacteria
[0085] The amino acid sequence of the α-acetolactate synthase used in the present invention is shown in SEQ ID No.1, derived from Bacillus subtilis 168; the amino acid sequence of the α-acetolactate decarboxylase used is shown in SEQ ID No.2 Shown, derived from lactate dehydrogenase Bacillus subtilis 168; the amino acid sequence of lactate dehydrogenase used is SEQ ID No.3; derived from Bacillus coagulans 2-6, the amino acid sequence of NADH oxidase used is SEQ ID No.3 ID No.4, derived from Lactococcus lactissubsp.lactis IO-1.
[0086]Using the primer LDH-F (SEQ ID NO.38) as the upstream primer, the primer LDH-R (SEQ ID NO.39) as the downstream primer, and the vector pET28a-ldh (SEQ ID NO.10) as the template, by PCR, A fragment ldh-1 containing the gene ldh (SEQ ID NO. 8) encoding lactate dehydrogenase was prepared. Using NOX-F (SEQ...
Embodiment 3
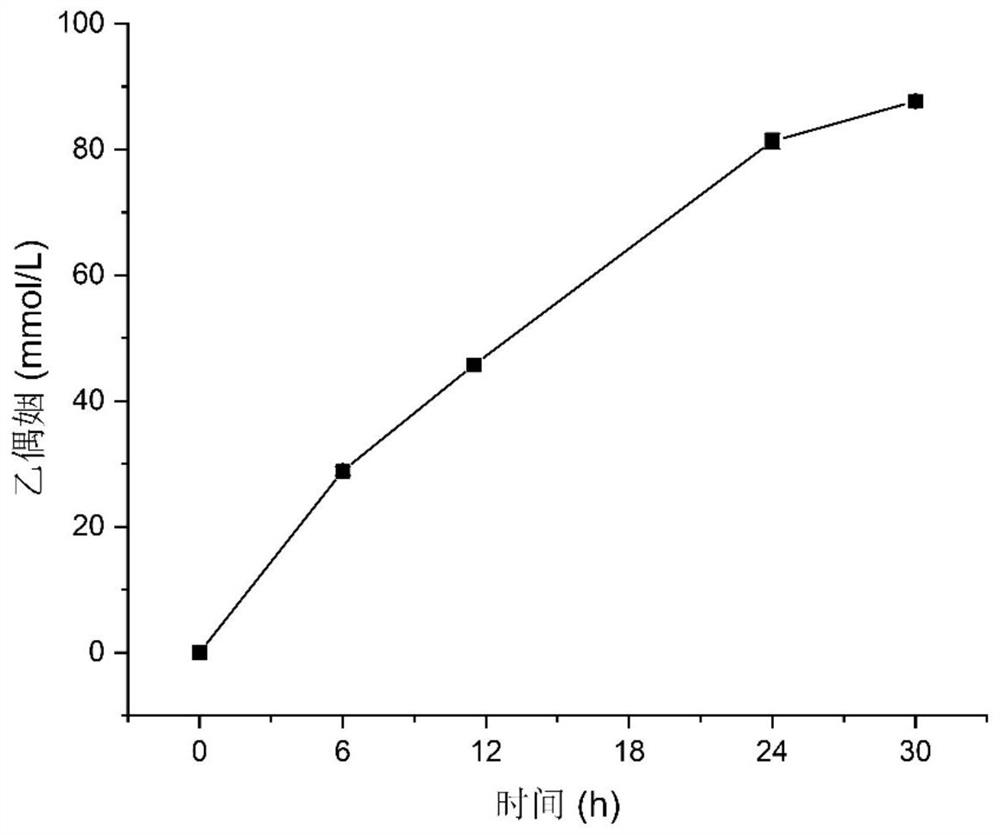
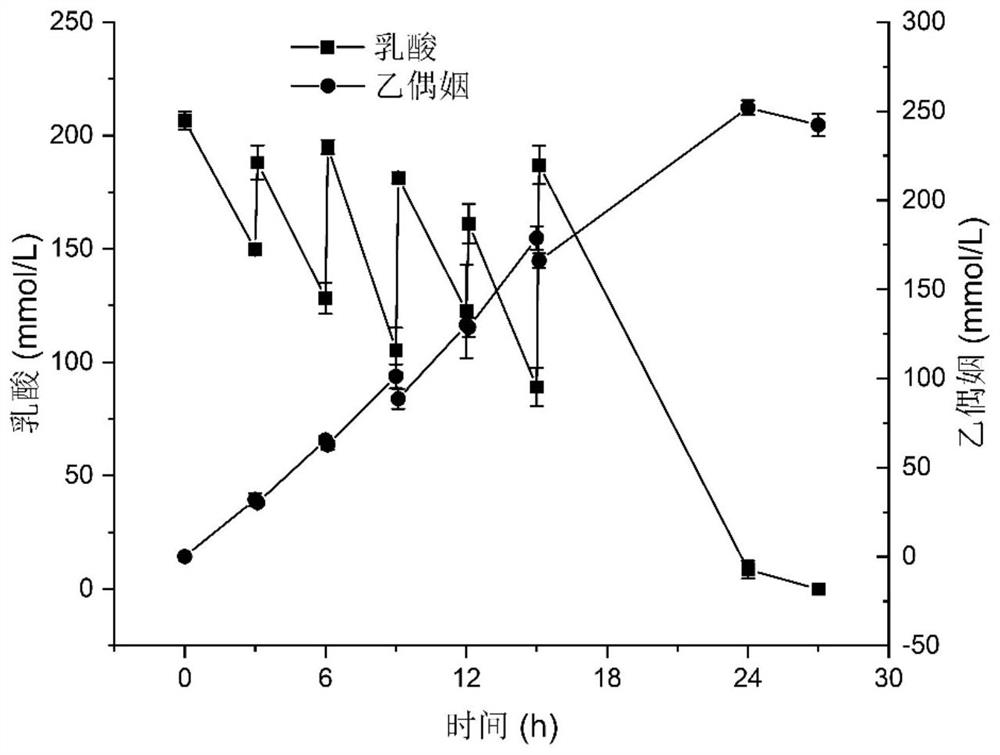
[0091] Embodiment 3: the application of acetoin-producing Escherichia coli engineered bacteria in whole-cell catalytic production of acetoin comprises the following steps:
[0092] 1) With the acetoin-producing Escherichia coli engineering bacteria BL-3 in Example 2, a single colony was picked from the plate, inoculated into 5mL LB medium, cultivated for 10h, and transferred to 200mL LB with 1% inoculum size culture medium at 37°C, 220rpm to OD 600 0.6-0.8, add IPTG (isopropyl β-D-1-thiogalactopyranoside) with a final concentration of 0.5mM, induce at 25°C for 12h, collect the bacteria at 4°C, 4500rpm, and use phosphate buffer solution (pH=6.0) to resuspend and wash the bacteria once, then centrifuge the bacteria at 4500 rpm at 4°C, and finally resuspend the bacteria with a small amount of phosphate buffer (pH=6.0);
[0093] 2) Suspend the thalline obtained in step 1) in the transformation solution containing lactic acid, so that the OD 600 =15, the concentration of lactic a...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com