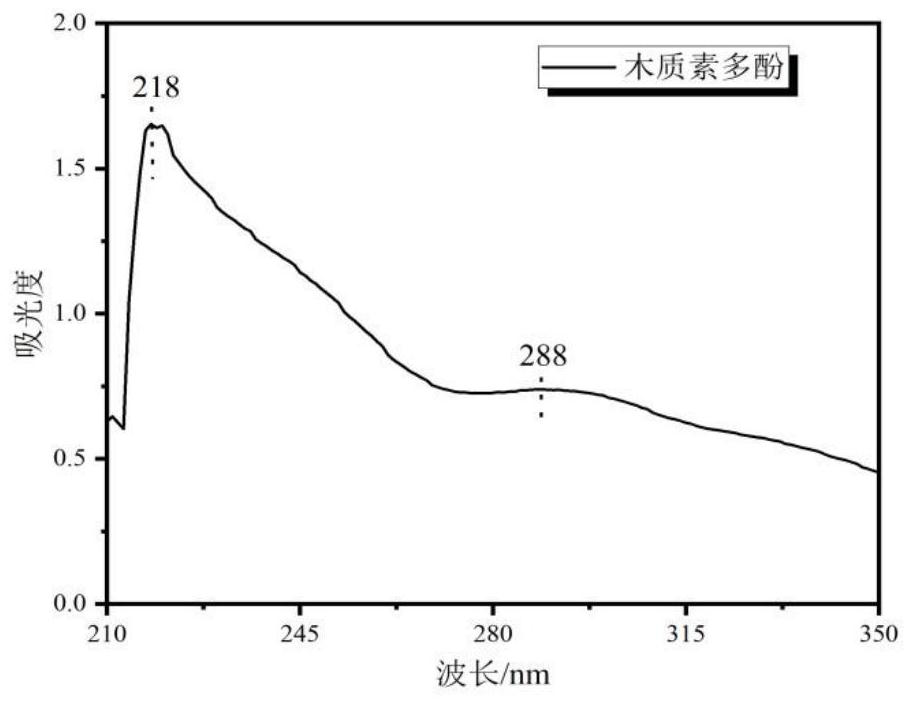
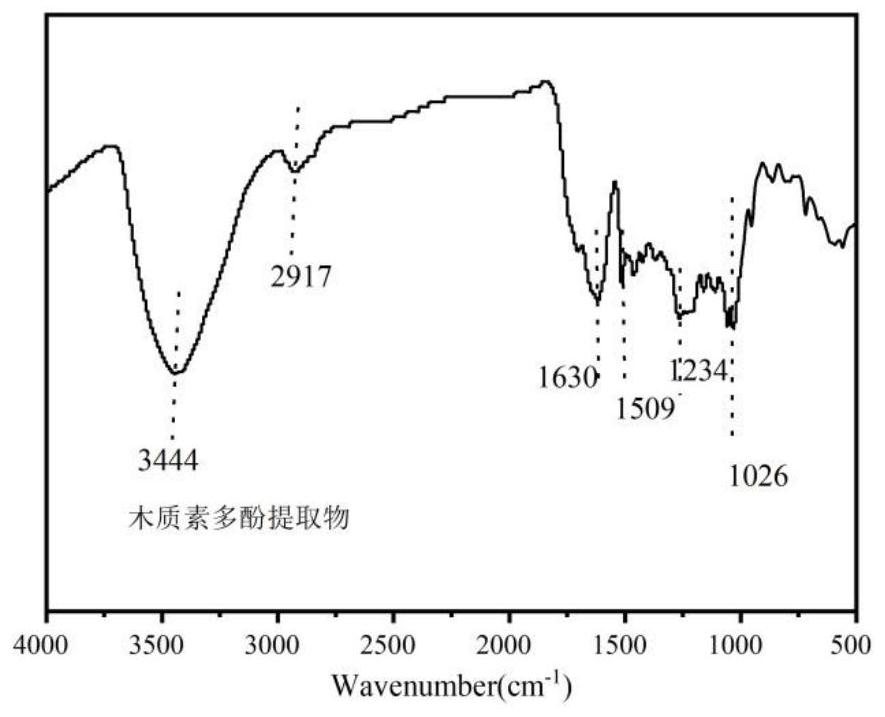
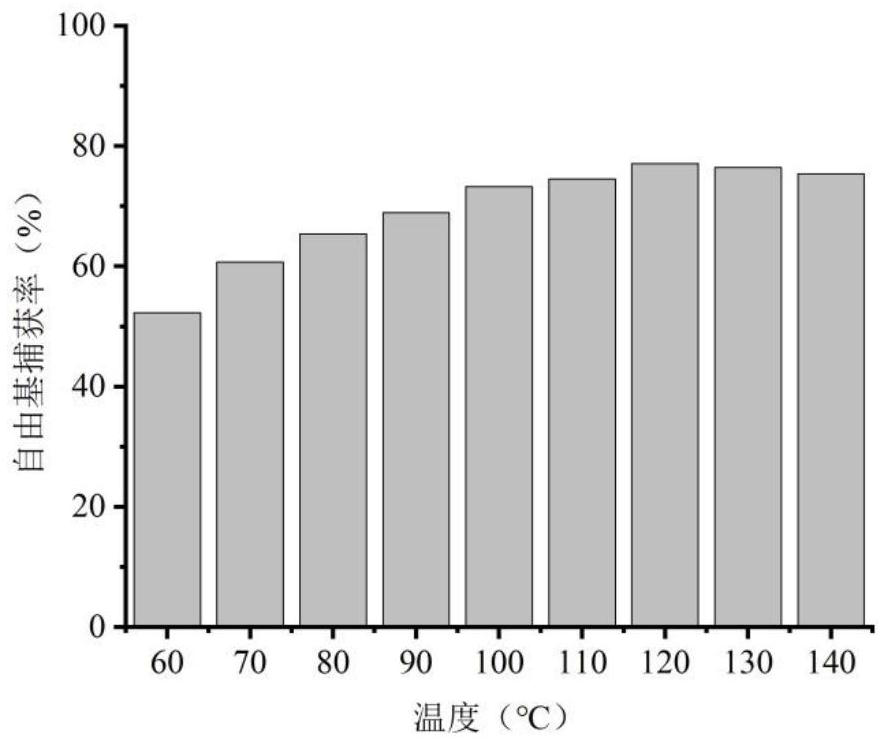
Method for extracting multifunctional active biological polyphenol from waste wood fiber, and application of multifunctional active biological polyphenol
A technology for lignocellulosic and lignocellulosic raw materials, which is applied in the directions of lignin derivatives, botanical equipment and methods, and chemicals for biological control, etc. problems, to achieve the effect of widening high-value applications, wide distribution of raw materials, and strong functionality
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] 1) Prepare the green extraction solution: configure the choline chloride-oxalic acid solution according to the molar ratio of 1:1, add 1wt% JGF penetrant and 1.5wt% FeCl catalyst to it, and mechanically stir at 100°C 1h, configure A solution;
[0034] 2) Dissolving biomass polyphenols: put lignocellulosic raw materials in solution A at a bath ratio of 10:1 (wood fiber: solution A, w / w), and dissolve at 100° C. for 8 hours. Then add ethanol solution (ethanol: A solution, w / w) in a ratio of 1:1 and shake fully, and filter through a 200-mesh polyester filter cloth to obtain the filtrate, which is B solution;
[0035] 3) Purification of biomass polyphenols: add pure water (pure water: B solution, v / v) to the B solution according to the volume ratio of 4:1, and let it stand for 24 hours until the biomass polyphenols are completely precipitated, and pass through the filtration method A precipitated solid was obtained. The obtained precipitated solid was shaken and washed wi...
Embodiment 2-5
[0036] Embodiment 2-5: oxalic acid in embodiment 1 is replaced with any one in citric acid, lactic acid, phytic acid, glycine and malic acid, and other conditions are the same as embodiment 1.
[0037] See Table 1 for the results of the extraction efficiency of biomass polyphenols in the process conditions of Examples 2-5.
[0038] Table 1 Effect of different organic acid systems on the extraction performance of biomass polyphenols
[0039]
[0040]
[0041] From the results in Table 1, it can be seen that the organic acid systems have a certain dissolution efficiency for biomass polyphenols. Since there are differences in performance indicators such as viscosity and acidity of the extracts compounded with different organic acids, their effects on biomass polyphenols are different. The extraction efficiency of polyphenols is different. Among them, the extraction system represented by lactic acid and oxalic acid has higher comprehensive performance, and the extracted biom...
Embodiment 6-10
[0042] Embodiment 6-10: FeCl in embodiment 1 3 Catalyst is changed into zinc chloride, zinc oxide, cupric chloride, aluminum chloride, cobalt oxide, and all the other conditions are with embodiment 1.
[0043] See Table 2 for the results of catalyst types on the extraction efficiency of biomass polyphenols in Examples 6-10.
[0044] Table 2 Effect of different catalysts on the extraction performance of biomass polyphenols
[0045]
[0046] It can be seen from Table 2 that the type of catalyst has an important influence on the performance of the extracted biomass polyphenols, which is specifically reflected in the large difference in the content of phenolic hydroxyl groups in the product, among which zinc chloride is the best, and the biomass extracted by different catalysts is more Phenols had little effect on the relative purity of the product.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com