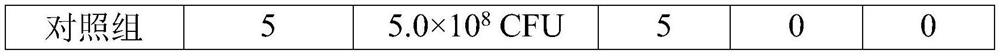Streptococcus suis and haemophilus parasuis bivalent inactivated vaccine and preparation method thereof
A technology for Haemophilus suis and Haemophilus suis disease, which is applied in the field of vaccines, can solve the problems of hazards in the pig industry, high morbidity and mortality, and high separation rates, and achieves antigen universality, good stability, and injectability. Good and safe effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] Embodiment 1 prepares quadrivalent inactivated vaccine
[0035] 1.1 Preparation of strains for Streptococcus suis production
[0036] 1.1.1 Breeding and identification of primary strains
[0037] Add 1.0 mL of sterile saline to dissolve the freeze-dried strains of Streptococcus suis (SS2-NT strain, SS9-CZ strain) respectively, streak and inoculate them on TSA plates containing 5% calf serum, and incubate at 37°C for 8h~ 16h, observe the colony morphology. Select 5 typical colonies and inoculate them on the TSA slant containing 5% calf serum, culture at 37°C for 8h-16h, and pass the pure inspection as the first-class strain.
[0038] 1.1.2 Secondary strain reproduction and identification
[0039] Inoculate the first-grade strains into TSB liquid medium containing 5% calf serum at a ratio of 1% to 2% (V / V), place them at 37°C for 8h-16h, and after passing the pure test, use them as the second grade strains. grade bacteria.
[0040] 1.2 Preparation of strains for prod...
Embodiment 2
[0076] Embodiment 2 finished product inspection
[0077] 2.1 Trait test
[0078] After the product is left standing, the upper layer is a colorless clear liquid, and the lower layer is an off-white precipitate; after shaking, it becomes a uniform suspension.
[0079] 2.2 Sterility test
[0080] According to the current "Chinese Veterinary Pharmacopoeia" appendix to test, aseptic growth is qualified.
[0081] 2.3 Safety inspection
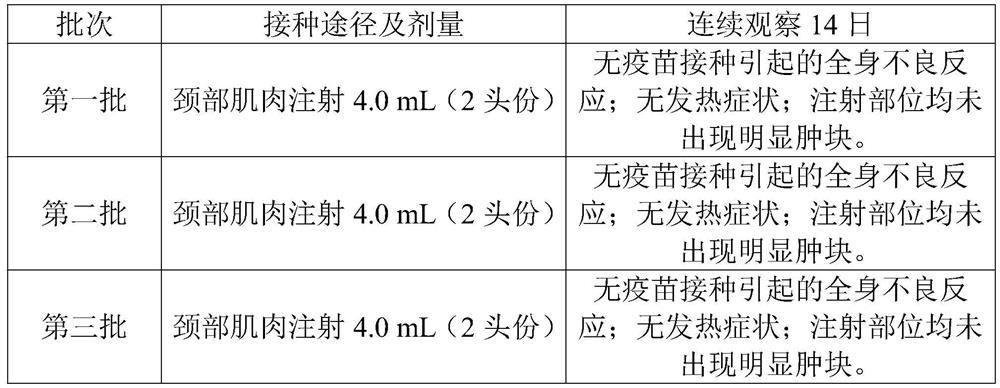
[0082] Five healthy susceptible pigs aged 2 to 3 weeks were injected intramuscularly with 4.0 mL of vaccine (2 pigs) in each neck, and observed continuously for 14 days. There should be no local or systemic adverse reactions caused by the vaccine.
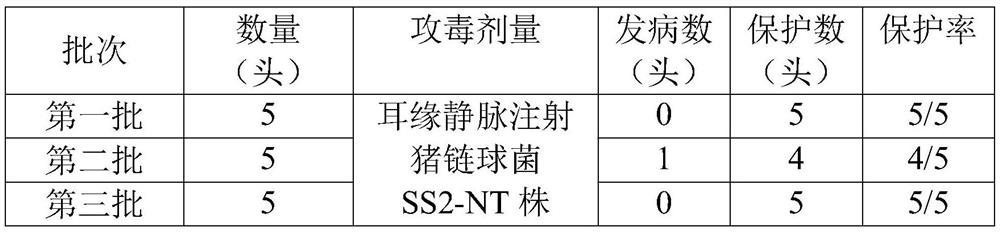
[0083] 2.4 Effectiveness test
[0084] Forty healthy susceptible pigs aged 2-3 weeks were randomly divided into 8 groups, 5 pigs in each group. Among them, 2.0mL of this vaccine was intramuscularly injected into the neck of each pig in groups I, II, III and IV (1 head); as negative controls, 2.0mL o...
Embodiment 3
[0085] Example 3 result
[0086] 3.1 Sterility test
[0087] 5 bottles of the 3 batches of vaccines were randomly selected, inoculated with TG medium, cultured at 37°C for 3 days, then inoculated with thioglycolate medium and casetone medium slant, cultured at 37°C and 25°C respectively, and cultured for 7 days. All (5 / 5) grew sterile (Table 1).
[0088] Table 1 Sterility test results of each batch of vaccines
[0089] batch Sterility test first batch 5 / 5 sterile growth second batch 5 / 5 sterile growth third batch 5 / 5 sterile growth
[0090] 3.2 Formaldehyde residue detection
[0091] 5 bottles were randomly selected from the 3 batches of vaccines, and tested for formaldehyde residues. After testing (Table 2), the formaldehyde residues of the first, second, and third batches of vaccines were 0.11%, 0.10%, and 0.13%, respectively.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com