Method for preparing monodisperse photoactive polymer microspheres
A photoactive polymer, monodisperse technology, applied in the field of preparing monodisperse photoactive polymer microspheres, can solve the problems of microsphere function limitation, influence effect, complicated operation, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0059] Example 1 Preparation of a small molecule RAFT agent (BMS-DDMAT) containing a benzophenone derivative photoinitiator at one end and a RAFT active group at one end
[0060] The synthetic reaction formula is as follows:
[0061]
[0062] The specific preparation method is as follows:
[0063] Add BMS-OH (1g, 3mmol), DDMAT (2.2g, 6mmol), 4-dimethylaminopyridine (DMAP) (0.076g, 0.6mmol) and anhydrous dichloromethane (CH 2 CI 2 ) (60mL), stirred and dissolved in an ice-water bath, and when the temperature dropped to about 0°C, anhydrous dichloromethane solution containing dicyclohexylcarbodiimide (DCC) (1.3g, 6mmol) was added dropwise ( 10 mL) for more than 15 min, and continued to react for 1 h in an ice-water bath. Then transfer to room temperature and react for 48h. After the reaction, remove the insoluble matter DCU generated in the reaction solution by filtration in a suction filter bottle, then add 100mL of 5% sodium hydroxide aqueous solution to dissolve the rem...
Embodiment 2
[0064] Embodiment 2 prepares the macromolecular RAFT agent (BMS-PAA) that one end contains benzophenone derivative photoinitiator, one end contains RAFT active group 267 -DDMAT)
[0065] The synthetic reaction formula is as follows:
[0066]
[0067] In the formula, the value of n depends on the amount of acrylic acid (AA), and n=267 in this embodiment.
[0068] BMS-PAA 267 The specific preparation method of -DDMAT is as follows:
[0069] In a 100 mL one-necked flask, BMS-DDMAT (0.25 g, 0.375 mmol), acrylic acid (AA) (7.2 g, 100 mmol), AIBN (azobisisobutyronitrile, 0.0062 g, 0.00375 mmol) and anhydrous 1,4 - Dioxane (30 mL), blowing nitrogen gas for 30 min, and then putting the flask into a preheated oil bath at 70° C. for 4 hours to react. After the reaction, the product was precipitated with ether. In order to purify the product, it was necessary to repeat the operation many times, that is, first dissolve it with anhydrous 1,4-dioxane, then precipitate it with ether, ...
Embodiment 3
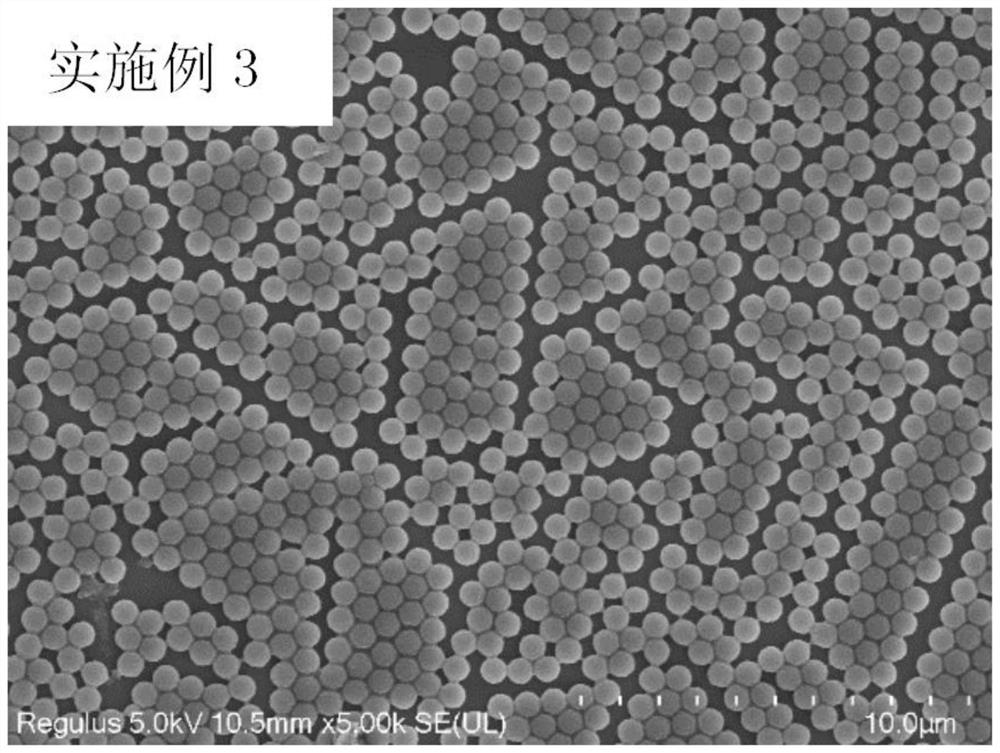
[0070] Embodiment 3 prepares photoactive polymer microsphere
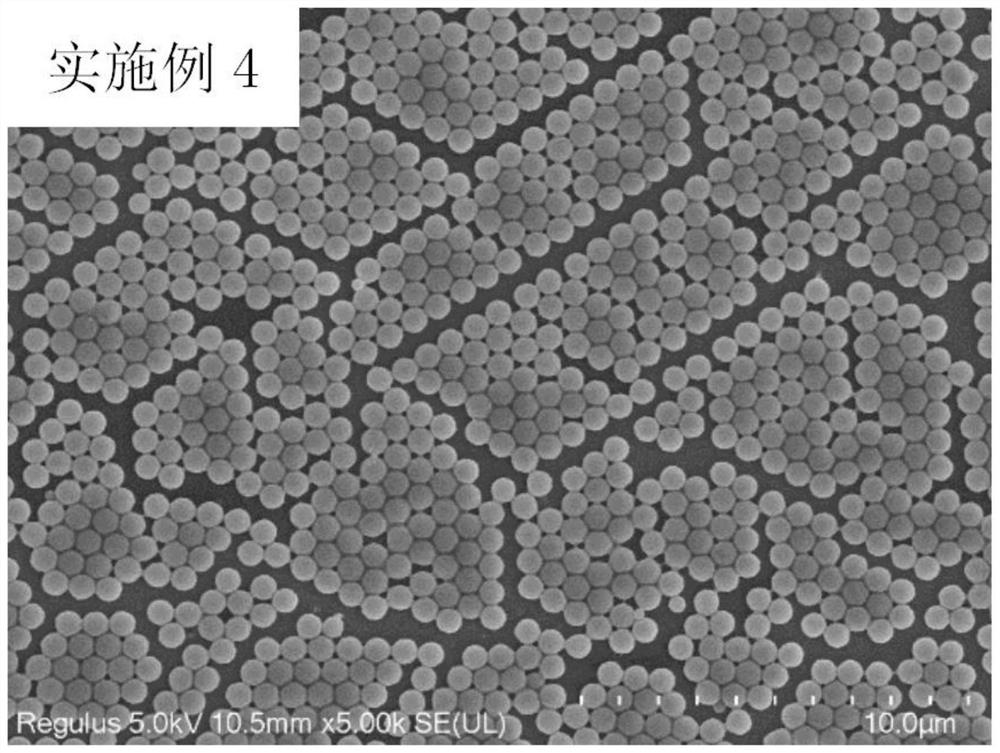
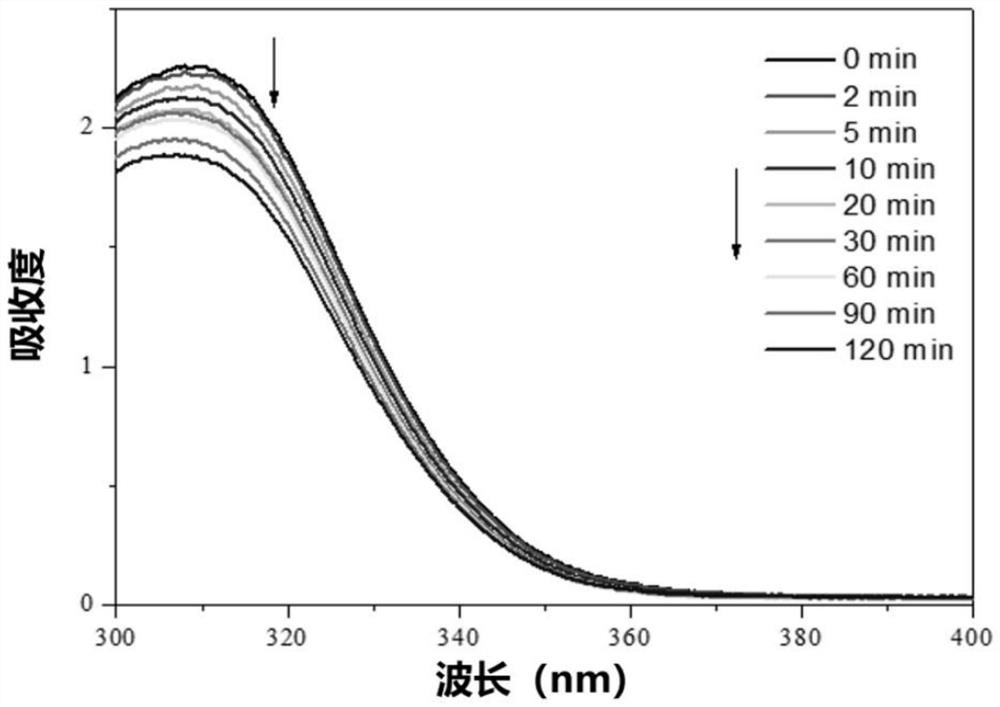
[0071] In a 25mL round bottom flask, add 18g of absolute ethanol and water mixed solvent (w / w=40 / 60), 2g of monomer MMA (10% relative to the system), 0.2g of stable dispersant BMS-PAA n -DDMAT (10% with respect to MMA monomer), the chain transfer agent DDMAT of 0.005g (0.5% with respect to MMA monomer), feed nitrogen 30min after stirring and dissolving, then add 0.08g hydrogen peroxide and ascorbic acid mixture (4wt% With respect to the MMA monomer, wherein the molar ratio of hydrogen peroxide and ascorbic acid is 1:1), a stable emulsion product, namely monodisperse photoactive polymer microspheres, is obtained after reaction at room temperature for 1 hour. Scanning electron micrographs of the product as figure 1 shown. From figure 1 It can be seen that the photoactive polymer microspheres prepared by this method exhibit a monodisperse distribution.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com