Engineering strain with high yield of FK228 as well as construction and application of engineering strain
An engineering strain, high-yield technology, applied in the direction of bacteria, virus/bacteriophage, microorganism-based methods, etc., can solve the problem of insufficient industrial production
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] Example 1: Construction of knockout plasmids and helper plasmids for constructing Chassis bacteria E264Δtdp
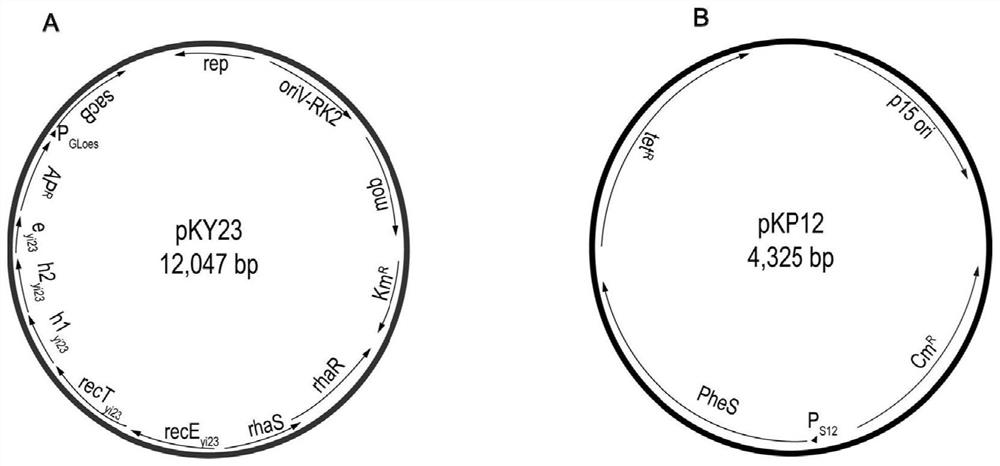
[0039] For the construction process of plasmid pKY23 and pKP12, see figure 1 .
[0040] The specific steps are as follows: use pBBR1-Rha-ETh1h2e_yi23-kan as the initial plasmid, perform single enzyme digestion on it with Hind III, and perform gel recovery on the plasmid cut into linear fragments; obtain the apramycin resistance gene and the reaction gene by PCR. The sacB gene was screened, and then the two genes were connected in series by tandem PCR; the obtained linear vector fragment and the tandem PCR product were co-transformed into E.coli GB05-dir for line-line recombination, and the obtained recombinant was verified by enzyme digestion. Sequencing, thereby obtaining the Burkholderiathailandensis E264 homologous recombination knockout plasmid, the series of expression plasmids named pKY23, its nucleotide sequence is shown in SEQ ID No.1.
[0041] The p15...
Embodiment 2
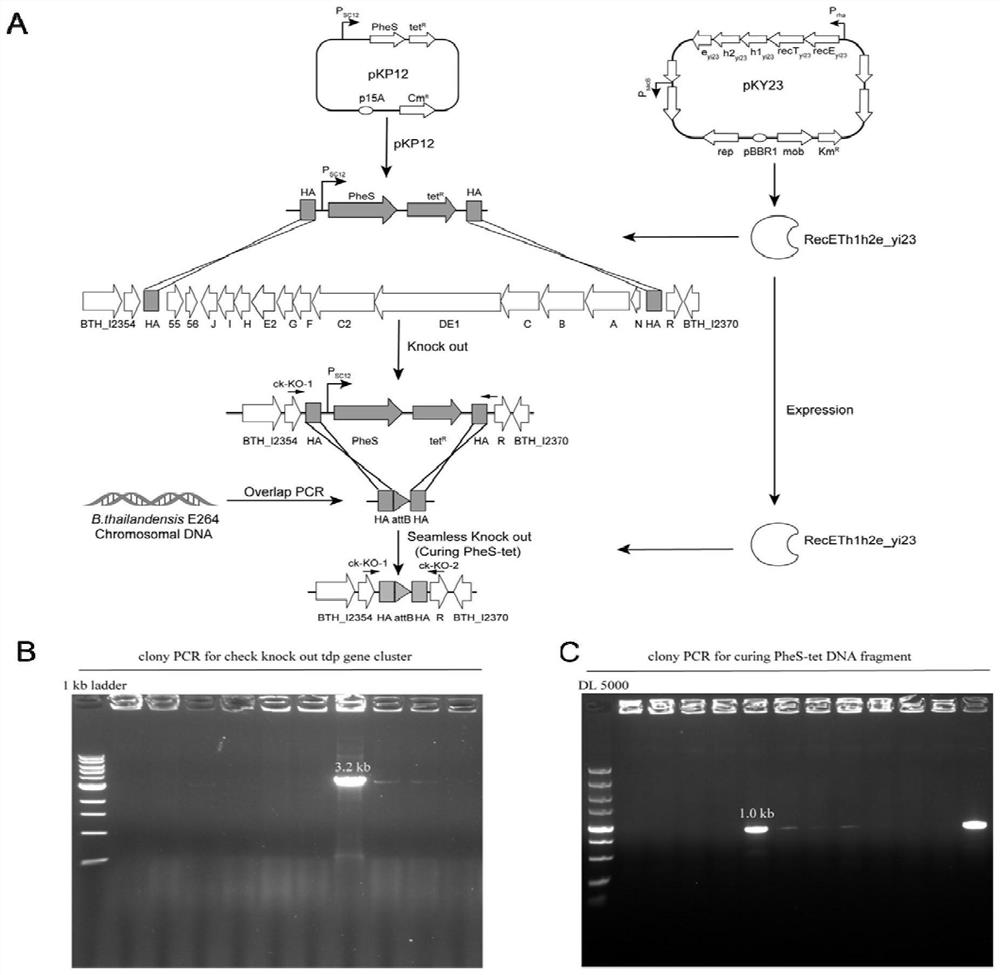
[0042] Example 2: Knockout of the tdp gene cluster in thailandepsin biosynthesis in Burkholderiathailandensis E264 For the scheme of knocking out the tdp gene cluster, see figure 2 a.
[0043] The specific steps are: analyze the position of the tdp gene cluster on the chromosome by antiSMASH, and determine that it is located in chromosome I of Burkholderiathailandensis E264 (Accession Number: CP000086.1), and the knockout region is from BTH_I2355 to BTH_I2368, totaling 38.58 kb.
[0044] In order to facilitate the expression of exogenous target biosynthetic gene clusters at the original position of the tdp gene cluster in the later stage, the attB site of the phCi31 site-specific integrase was designed and added.
[0045] The knockout fragment HAUP-tet-PheS-HAUD( ~2.8kb), the knockout fragment contains 160bp homology arms upstream and downstream of the tdp gene cluster, a tetracycline resistance fragment and a PheS reverse selection tag. Wherein, the nucleotide sequence of ...
Embodiment 3
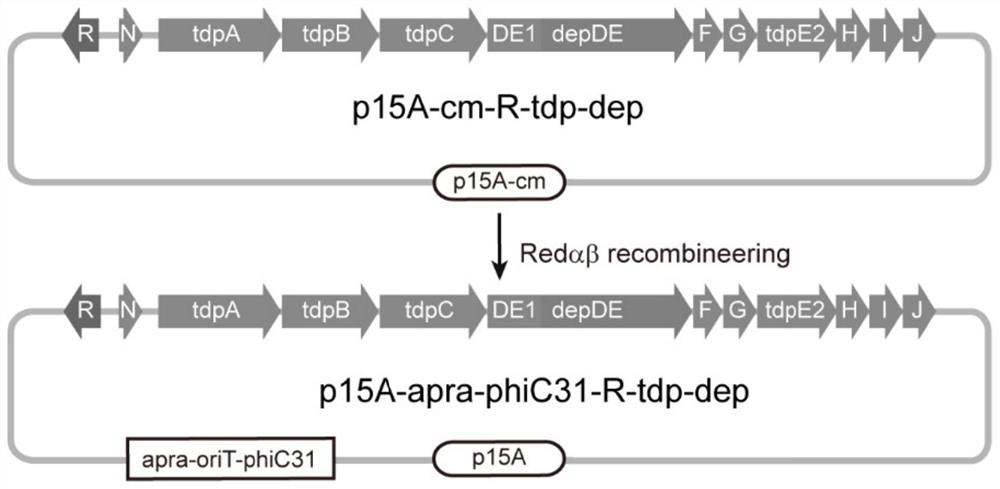
[0075] Example 3: Construction of expression plasmid p15A-oriT-phiC31-kan-R-tdp-dep
[0076] For the construction process of the expression plasmid p15A-oriT-phiC31-kan-R-tdp-dep, see image 3 .
[0077] First, pR6K-oriT-phiC31-kan was used as a template, and oriT-phiC31-kan-1 and oriT-phiC31-kan-2 were used as primers to amplify the fragment oriT-phiC31-kan with p15A-cm-R-tdp on it The homology arms at both ends of the chloramphenicol gene sequence on the -dep plasmid, and the amplified fragments are recovered and purified by gel.
[0078] Electrotransform the purified fragment oriT-phiC31-apra into E.coli GB08-red containing plasmid p15A-cm-R-tdp-dep and induced by 10% L-arabinose. 20 μg / ml apramycin LB plates were placed in a constant temperature incubator at 37°C and cultured overnight. Pick a single colony and digest it with restriction endonuclease PstI (see Figure 4 ), to screen the correct recombinant plasmid p15A-apra-phiC31-R-tdp-dep. The recombinant plasmids w...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com