A kind of comprehensive treatment method of waste water produced by iron phosphate production
A comprehensive treatment, iron phosphate technology, applied in the direction of natural water treatment, water/sewage treatment, water/sewage multi-stage treatment, etc., can solve the problems of insufficient recycling of active ingredients, high operating costs, etc., and achieve good market promotion value, realize full utilization, and reduce the effect of fluoride ion content
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example 1
[0044] Take activated alumina, wash it with deionized water for 5 times to remove surface impurities, immerse it in 0.02mol / L ferric sulfate solution under ultrasonic conditions (100 Hz) at 30°C for 5 hours, and wash it with deionized water after taking it out. 5 times, placed in a muffle furnace, heated to 450°C at a heating rate of 5-10°C / min, and kept for 6 hours to obtain modified activated alumina.
Embodiment 1
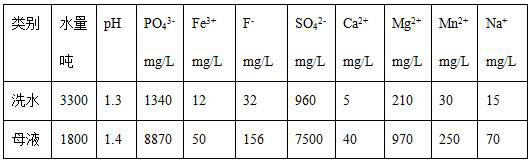
[0046] A certain annual output of 50,000 tons of iron phosphate production enterprises, the amount of wastewater and water quality are shown in Table 1 below:
[0047] Table 1 Composition of iron phosphate wastewater
[0048]
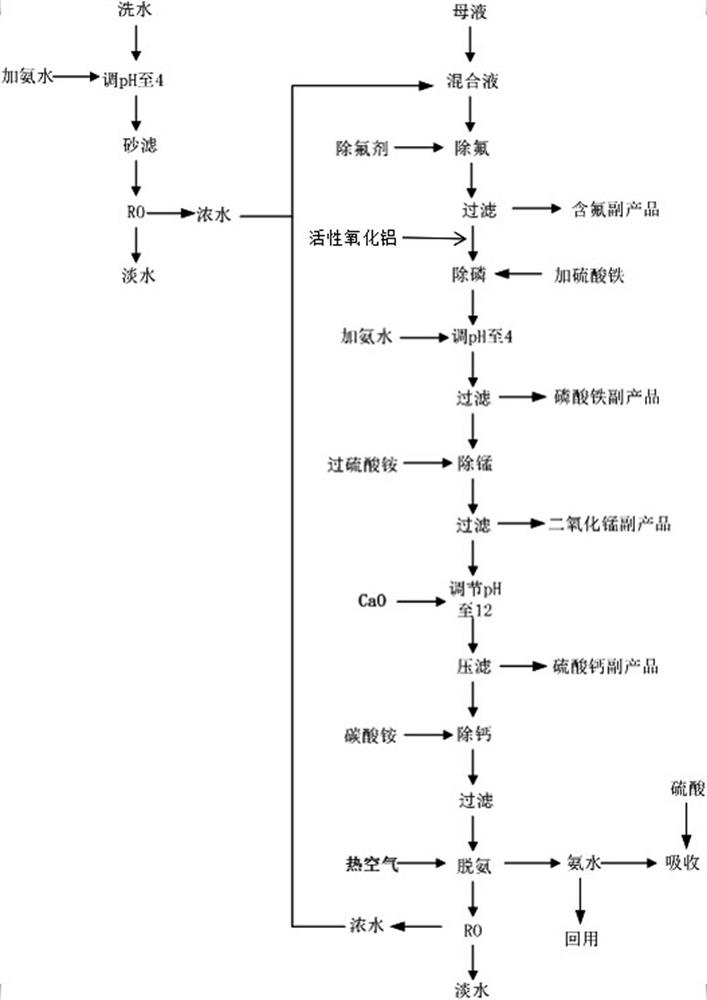
[0049] The following process scheme is used for processing:
[0050] (S1), the processing technique of washing water is: the washing water of ferric phosphate production waste water adds ammoniacal liquor, initially is outsourcing ammoniacal liquor, and after the technique goes through, use reclaimed ammoniacal liquor, adjust pH value to 3, filter, enter reverse osmosis membrane and concentrate, During concentration, the ratio of concentrated water and fresh water is 3:7, the gained concentrated water I is mixed with the mother liquor of ferric phosphate production wastewater, and the fresh water is directly reused or reused after advanced treatment according to the purpose.
[0051] (S2), the processing technique of mother liquor is:
[0052] (A) ...
Embodiment 2
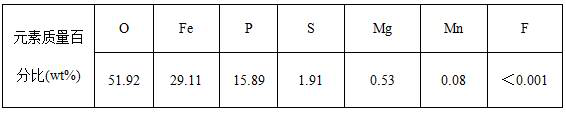
[0070] Other conditions and operations are the same as in Example 1, except that in step (A), the fluorine-removing agent is aluminum sulfate, that is, no ferric sulfate is added, and the F ion concentration in the combined liquid phase is 8.3 mg / L. It is necessary to use more modified activated alumina to reduce the F ion concentration in the liquid phase to less than 1 mg / L. In order to achieve high-quality fluorine-free iron phosphate by-products, the cost increases. Explain that the present invention only uses a small amount of ferric sulfate and aluminum sulfate as a fluoride removal agent. The possible reason is that on the one hand, ferric sulfate and aluminum sulfate can cooperate to produce a synergistic effect to reduce the F ion content in the waste water; on the other hand, the added sulfuric acid Iron may have a modified effect on the activated alumina added later, further reducing the concentration of F ions. In addition, adding iron sulfate will not introduce ne...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com