Liver-specific gene editing nano-drug as well as preparation method and application thereof
A gene editing and nanomedicine technology, applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve the problems of increasing the difficulty of treatment of chronic HBV infection, unable to completely remove HBV, unable to cure chronic hepatitis B, etc., to improve the accuracy of gene editing, reduce off-target effects, The effect of increasing flexibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
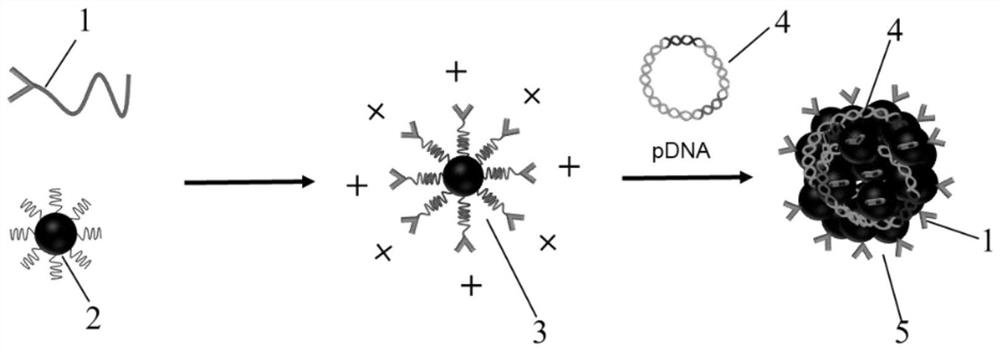
[0062] The examples of this application provide the preparation of oleic acid-modified magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs for short), and the specific methods include:
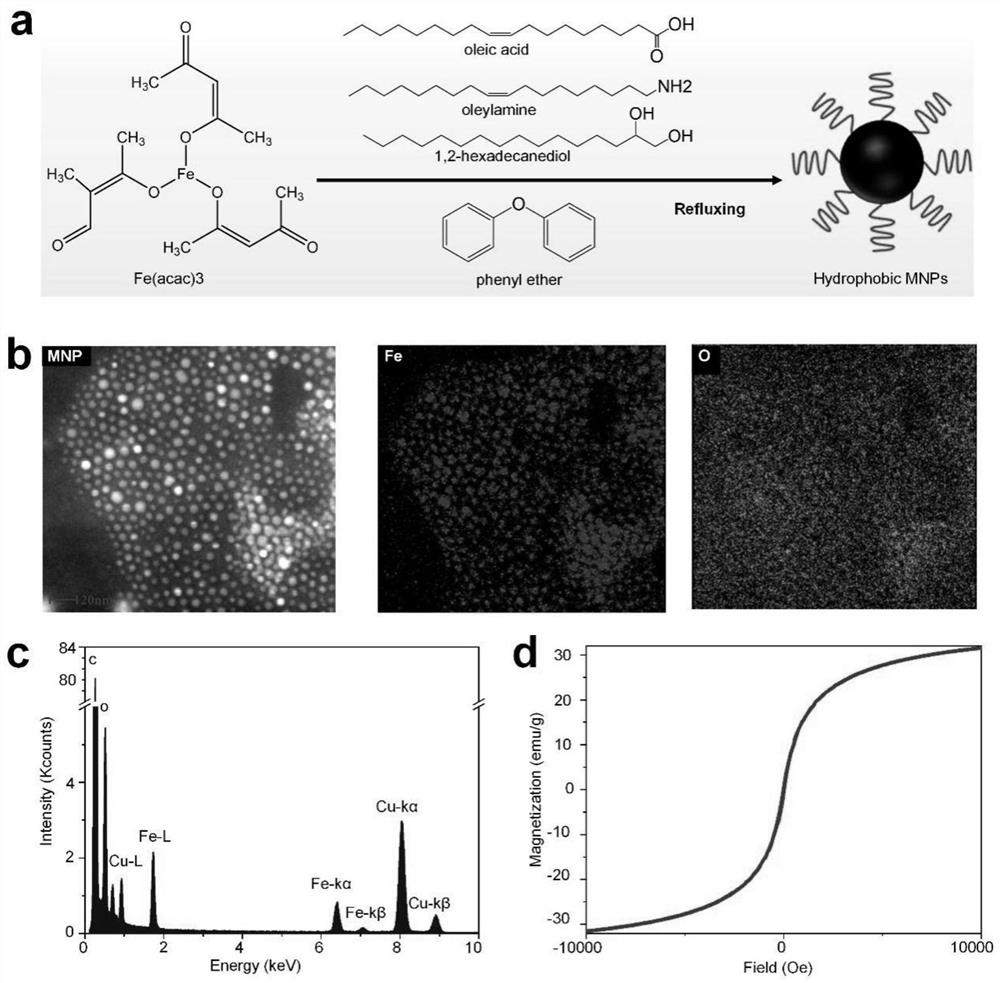
[0063] Iron acetylacetonate (2 mmol), 1,2-hexadecanediol (10 mmol), oleic acid (6 mmol), oleylamine (6 mmol), dibenzyl ether (20 mL) were combined in a three neck round bottom flask. Heated to 200°C with vigorous stirring under deoxygenation and maintained for 2h (using N 2 Bubble deoxygenation), and then continue to heat to 300 ° C, reflux for 1 h. After the reaction was completed, the temperature was sufficiently lowered to room temperature. The product was precipitated with 40 mL of ethanol, centrifuged (6000 rpm, 10 min), and finally dispersed in n-hexane for use to obtain oleic acid-modified magnetic nanoparticles (MNP for short). The morphology and elements of the synthesized nanoparticles were characterized by transmission electron microscopy, and the magnetic properties of the synthesized nanoparticles wer...
Embodiment 2
[0066] The examples of this application provide the preparation of oleic acid-modified magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs for short), and the specific methods include:
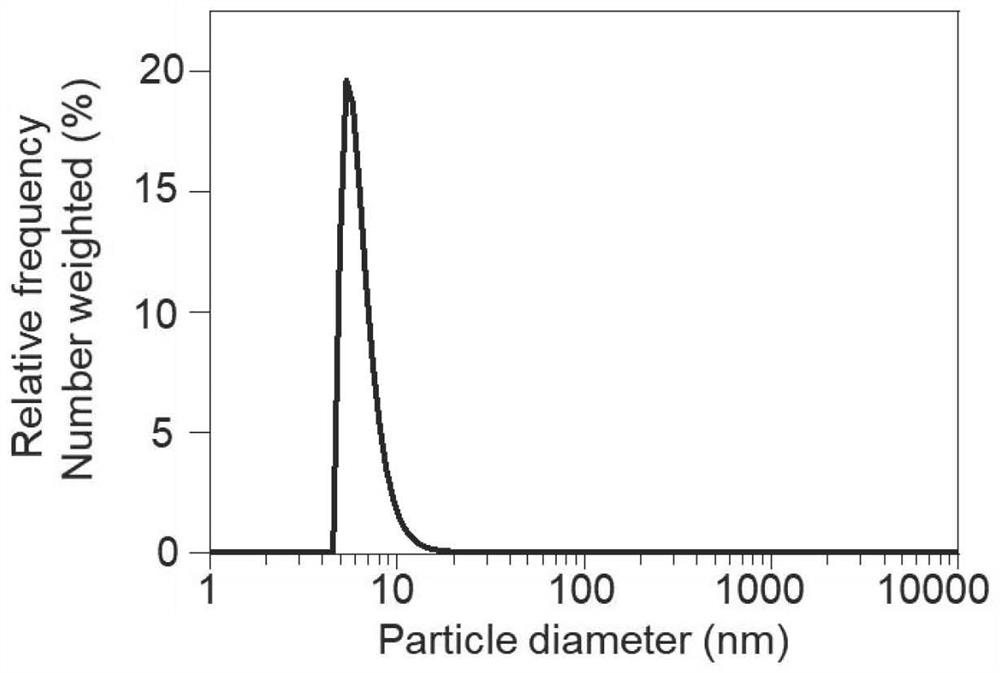
[0067] see figure 2 , figure 2 a The synthetic route of the oleic acid-modified superparamagnetic iron oxide particles provided in the examples of this application. Iron acetylacetonate (2 mmol), 1,2-hexadecanediol (10 mmol), oleic acid (6 mmol), oleylamine (6 mmol), diphenyl ether (20 mL) were combined in a three neck round bottom flask. Heat to 200°C with vigorous stirring in a deoxygenated environment and hold for 30 min (using N 2 Bubble deoxygenation), and then continue to heat to 265°C and reflux for 30min. After the reaction was completed, the temperature was sufficiently lowered to room temperature. The product was precipitated with 40 mL of ethanol, centrifuged (6000 rpm, 10 min), and finally dispersed in n-hexane for use to obtain oleic acid-modified magnetic nanoparticles (MNP for short). Particle ...
Embodiment 3
[0070] The examples of this application provide the preparation of oleic acid-modified magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs for short), and the specific methods include:
[0071] Mix the 6nm magnetic nanoparticles synthesized in Example 2, iron acetylacetonate (2mmol), 1,2-hexadecanediol (10mmol), oleic acid (2mmol), oleylamine (2mmol), and dibenzyl ether (20mL). in a three neck round bottom flask. Heat to 100°C with vigorous stirring in a deoxygenated environment and hold for 30 min (using N 2Bubble deoxygenation), then continue to heat to 200°C, reflux for 1 h, heat to 300°C and maintain for 30min. After the reaction was completed, the temperature was sufficiently lowered to room temperature. The product was precipitated with 40 mL of ethanol, centrifuged (6000 rpm, 10 min), and finally dispersed in n-hexane for use to obtain oleic acid-modified magnetic nanoparticles (MNP for short). The morphology and elements of the synthesized nanoparticles were characterized by transmission ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap