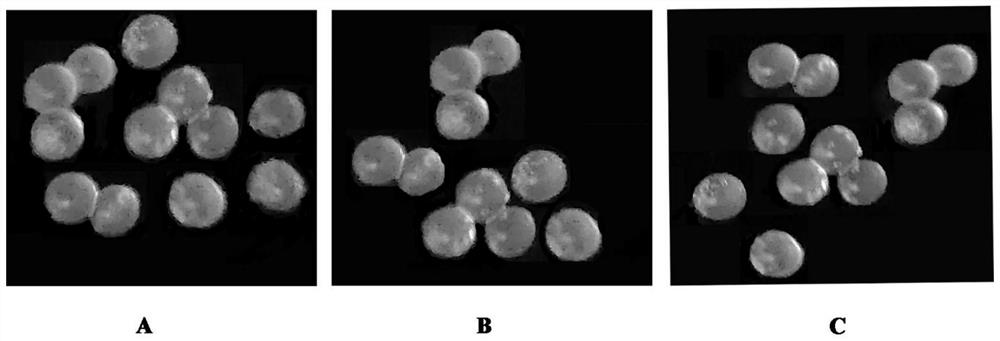
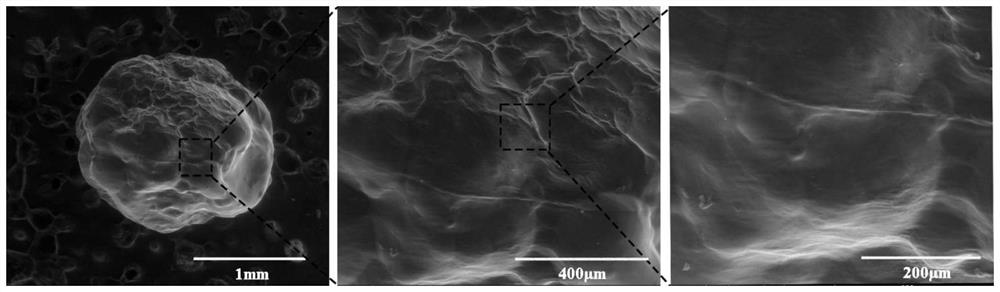
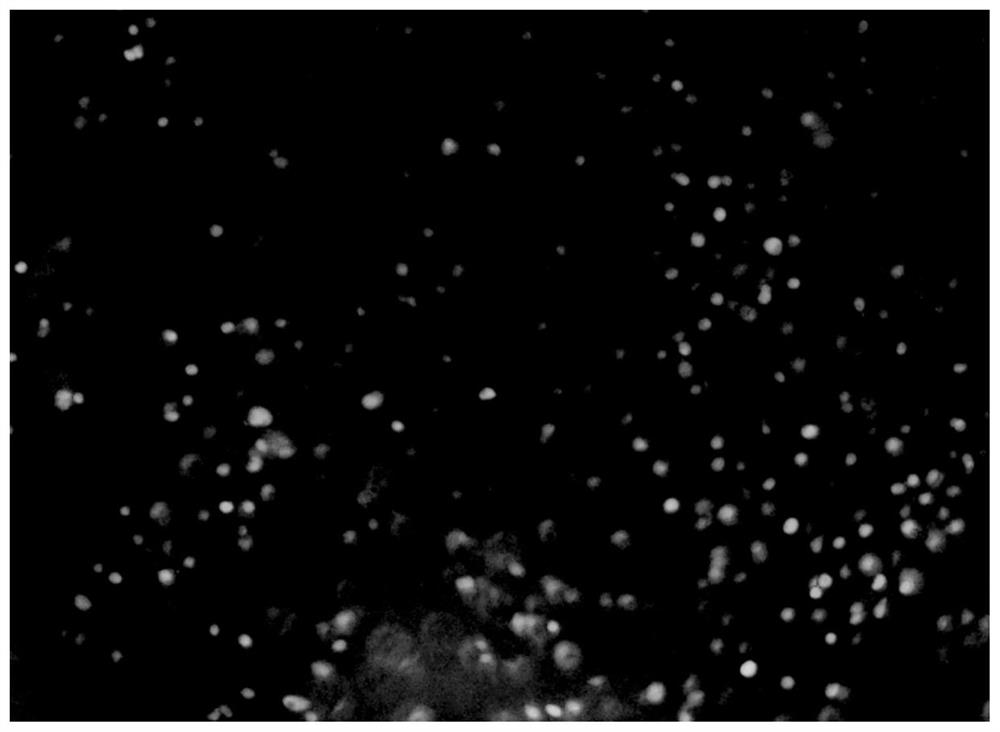
Controllable degradation embryo microsphere and preparation method thereof
A technology of microspheres and embryos, applied in embryonic cells, lysing enzymes, immobilized on/in organic carriers, etc., can solve the problems of low embryo survival rate, difficult to hatch, easy to be affected by the environment in the uterus, etc. Survival rate, promoting embryonic development, slowing down the effects of adverse external stimuli
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] 1) Add 1 mL of 1.4 M sodium sulfate solution to 19 mL of chitosan solution (0.25% w / v), stir evenly, react at 25°C at a stirring speed of 500 rpm for 4 hours, and then centrifuge at 12000g at 4°C After 30 min, the supernatant was discarded to obtain nanoparticles, and then washed three times with 50 mL of Tris buffer.
[0032] 2) Add 2% glutaraldehyde solution (prepared in the same buffer) to the nanoparticles obtained in step 1), and then place at 30° C. and react at 50 rpm for 2 hours to obtain cross-linked chitosan nanoparticles.
[0033] 3) The cross-linked chitosan nanoparticles obtained in step 2) and 1 mL of free alginate lyase solution were gently stirred at 4 °C for 36 h, and then centrifuged at 12,000 g for 30 min at 4 °C. Tris buffer was washed several times until no alginate lyase could be detected, then it was dissolved in physiological saline to make the alginate lyase activity 5U / g, and the immobilized alginate lyase solution was obtained after freeze-dry...
Embodiment 2
[0036] 1) Add 1 mL of 1.4 M sodium sulfate solution to 19 mL of chitosan solution (0.25% w / v), stir evenly, react at 25°C at a stirring speed of 500 rpm for 4 hours, and then centrifuge at 12000g at 4°C After 30 min, the supernatant was discarded to obtain nanoparticles, and then washed three times with 50 mL of Tris buffer.
[0037] 2) Add 2% glutaraldehyde solution (prepared in the same buffer) to the nanoparticles obtained in step 1), then place at 30° C. and react at 50 rpm for 2 hours to obtain cross-linked chitosan nanoparticles.
[0038] 3) The cross-linked chitosan nanoparticles obtained in step 2) and 2 mL of free alginate lyase solution were gently stirred at 4 °C for 36 h, and then centrifuged at 12000 g for 30 min at 4 °C, the supernatant was discarded, and then 50 mM Tris buffer was washed several times until no alginate lyase could be detected, then it was dissolved in physiological saline to make the alginate lyase activity 10 U / g, and the immobilized alginate l...
Embodiment 3
[0041] 1) Add 1 mL of 1.4 M sodium sulfate solution to 19 mL of chitosan solution (0.25% w / v), stir evenly, react at 25°C at a stirring speed of 500 rpm for 4 hours, and then centrifuge at 12000g at 4°C After 30 min, the supernatant was discarded to obtain nanoparticles, and then washed three times with 50 mL of Tris buffer.
[0042] 2) Add 2% glutaraldehyde solution (prepared in the same buffer) to the nanoparticles obtained in step 1), then place at 30° C. and react at 50 rpm for 2 hours to obtain cross-linked chitosan nanoparticles.
[0043] 3) The cross-linked chitosan nanoparticles obtained in step 2) and 3 mL of free alginate lyase solution were gently stirred at 4 °C for 36 h, and then centrifuged at 12,000 g for 30 min at 4 °C. Tris buffer was washed for several times until no alginate lyase could be detected, then it was dissolved in physiological saline to make the alginate lyase activity 15U / g, and the immobilized alginate lyase solution was obtained after freeze-dr...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com