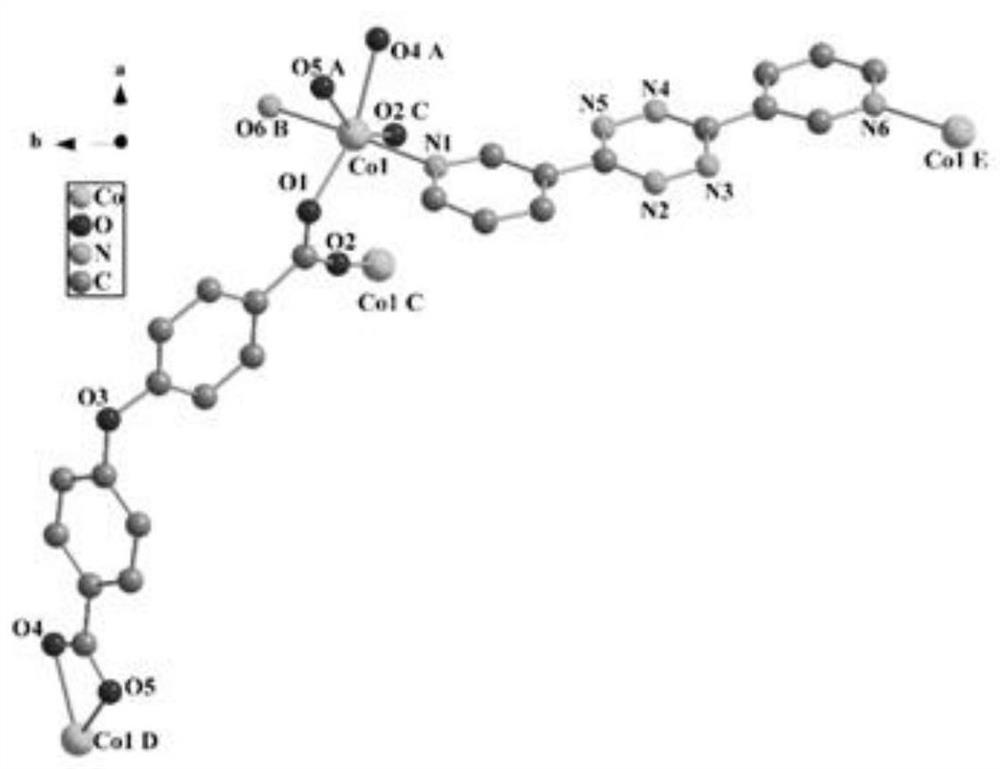
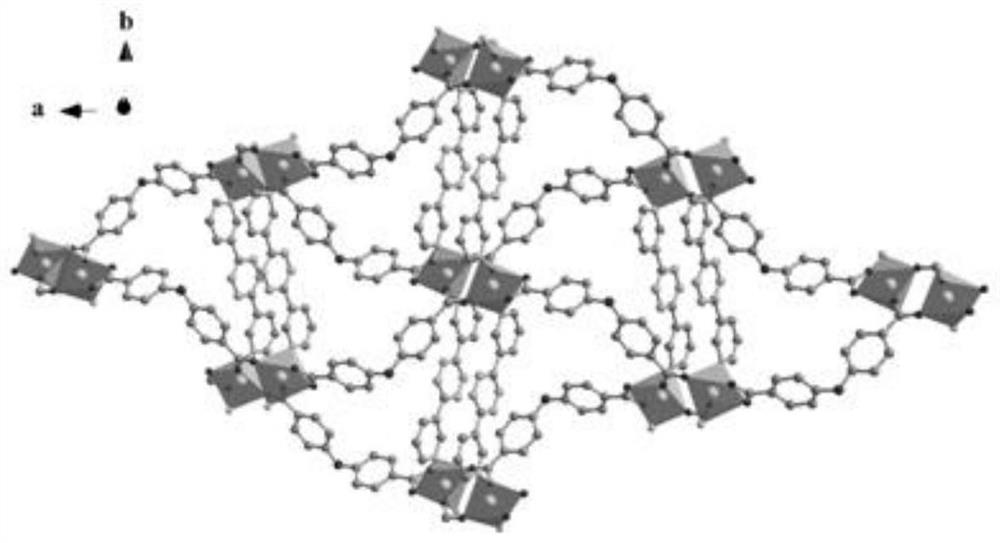
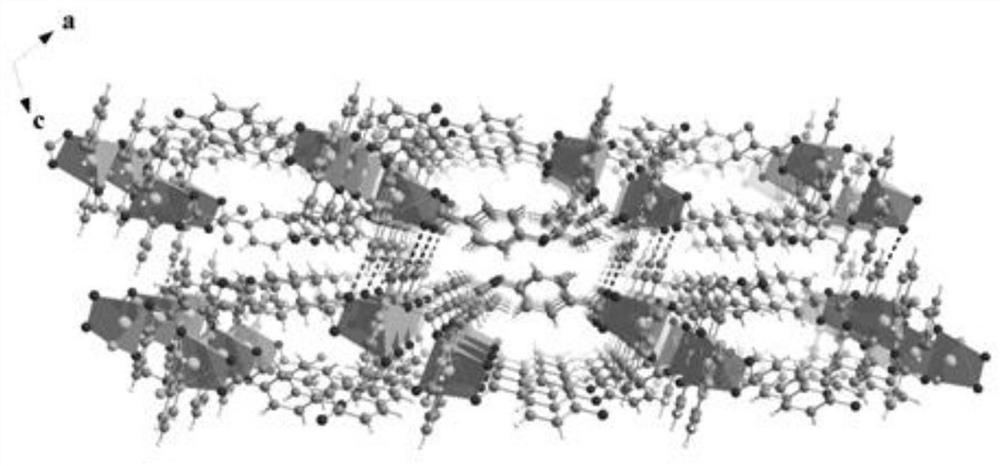
Fe-doped novel two-dimensional Co-MOFs composite material as well as preparation method and application thereof
A composite material and a new technology, applied in the field of electrochemical materials, can solve problems such as affecting the catalytic effect of catalysts, achieve excellent OER electrocatalytic activity and stability, enhance electrocatalytic performance, and improve OER performance.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] (1) 3,6-bis(pyridin-3-yl)-1,2,4,5-tetrazine (bptz) (0.0118g, 0.05mmol) was added to 2mL of DMF solution, stirred well, and then in a stirring state 4,4'-dicarboxydiphenyl ether (H 2 oba) (0.0129g, 0.05mmol) solution to obtain a mixed solution;
[0039] (2) After step (1), cobalt acetate (Co(OAc) dissolved in 2 mL of DMF was added to the mixed solution 2 ·6H 2 O) (0.0125g, 0.05mmol), stirred for 30 minutes to obtain a reaction solution;
[0040] (3) transferring the reaction solution obtained after step (2) into a polytetrafluoroethylene hydrothermal reaction kettle, and reacting at a constant temperature of 85 °C for 72 hours; programmatically lowered to room temperature at a speed of 5 °C / h to obtain a mixed solution a;
[0041] (4) filtering the mixed solution a obtained after the step (3), washing the obtained solid matter with deionized water and DMF in turn, and finally putting it into an oven for drying to obtain a novel Co-based two-dimensional metal-organic f...
Embodiment 2
[0051] In this example, the preparation method of the novel two-dimensional Co-based metal-organic frameworks (Co-MOFs) is exactly the same as that in Example 1, the difference is that the reaction solution is in a polytetrafluoroethylene hydrothermal reactor at a constant temperature of 85°C. The reaction time is 48h, and the doping method is also the same as the preparation method in Example 1, the difference is the doped ferrous sulfate FeSO 4 ·7H 2 The amount of O was 0.0184 g (0.067 mmol).
[0052] The XRD patterns of the Fe-doped new two-dimensional Co-MOFs composites (Fe@Co-MOFs-2) composites prepared above are as follows: Figure 4 shown.
[0053] The composite Fe@Co-MOFs-2 prepared above was tested for OER performance. The test method was the same as the test method in Example 1. The test results showed that the Fe@Co-MOFs-2 composite material of this example was tested at 50 mA cm. -2 Under the current density of , the overpotential is between 270 and 290 mV, such...
Embodiment 3
[0055] In this example, the preparation method of the novel two-dimensional Co-based metal organic frameworks (Co-MOFs) is exactly the same as that in Example 1, and the doping method is also the same as the preparation method in Example 1, the difference is the doping method. Ferrous sulfate FeSO 4 ·7H 2 The amount of O was 0.0278 g (0.1 mmol).
[0056] The XRD patterns of the Fe-doped new 2D Co-MOFs composites (Fe@Co-MOFs-3) prepared above are as follows: Figure 4 shown. With the increase of Fe doping amount, the crystallinity of the as-prepared composite material gradually decreased until it became an amorphous material Fe@Co-MOFs-3.
[0057] The dark-field high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM) images (200 nm and 2 nm) of the composite Fe@Co-MOsFs-3 prepared above are as follows Figure 5 As shown, the 2 nm map clearly reflects the amorphous structure of Fe@Co-MOFs-3.
[0058] The mapping image of the dark-field high-resolution transmission electron...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com