Genetically engineered antigen presenting extracellular vesicle as well as preparation method and application thereof
A genetic engineering and antigen technology, applied in the field of genetically engineered antigen-presenting extracellular vesicles and their preparation, to achieve the effect of inhibiting tumor metastasis, facilitating clinical transformation, and enhancing tumor immunotherapy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0069] Example 1 Construction of a dendritic cell tumor vaccine (Engineered DCs, eDCs) that highly expresses anti-CD19 scFv and PD-1 and knocks down PD-L1
[0070] (1) Isolation and culture of mouse bone marrow dendritic cells (BMDCs): Isolate mouse bone marrow cells from tibia and femur, add 20ng / mL GM-CSF and 10ng / mL to RPMI 1640 medium containing 10% fetal bovine serum IL-4 is cultured for 6-7 days, which is dendritic cells.
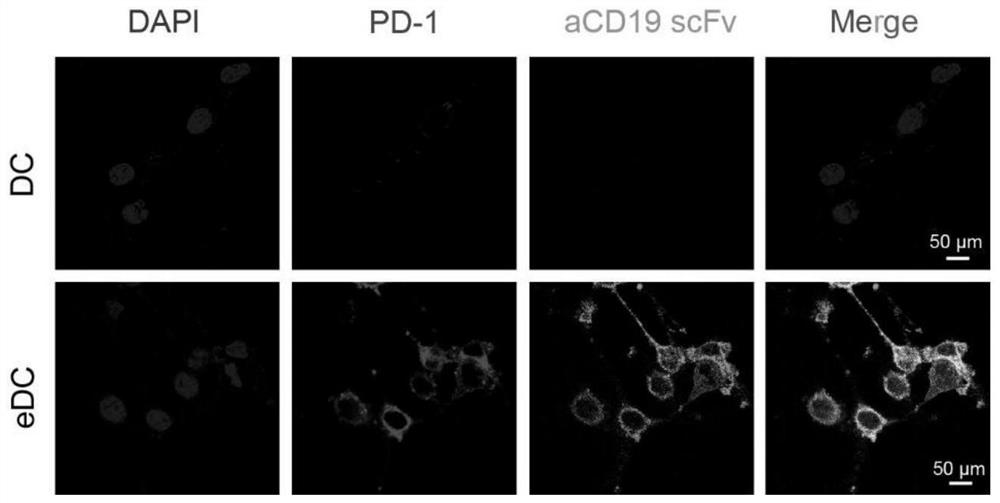
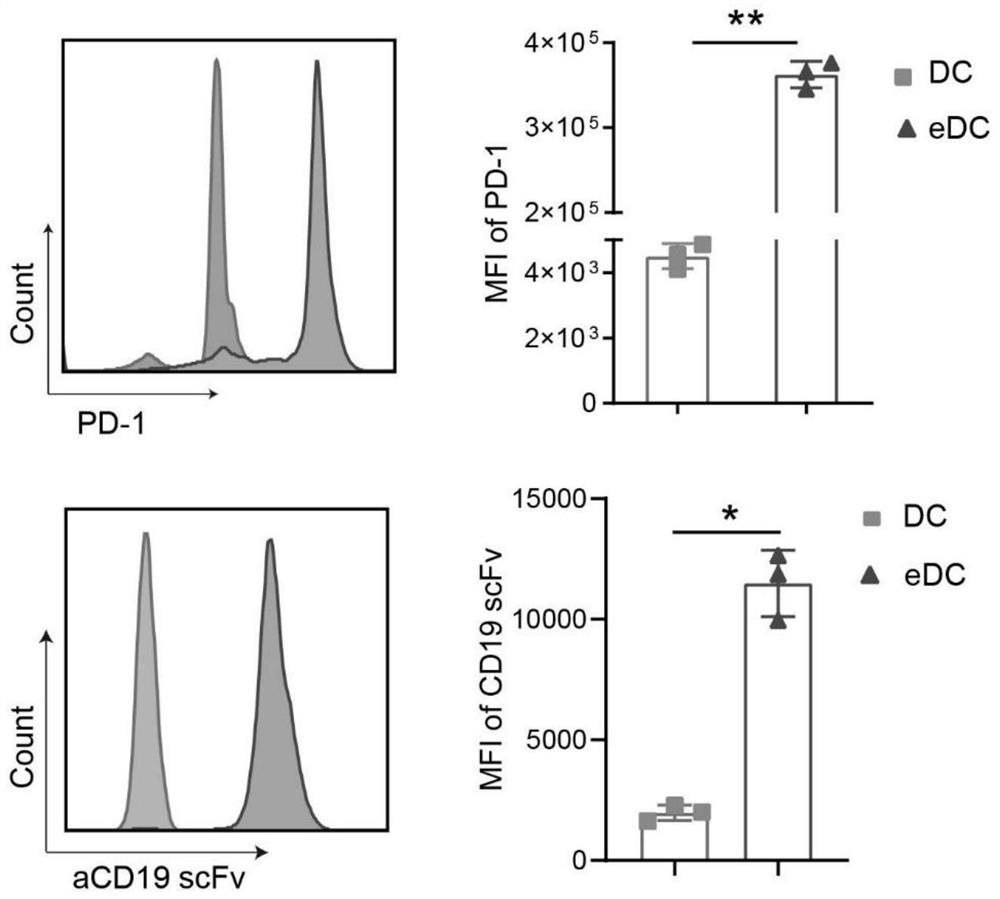
[0071] (2) Construction of dendritic cells highly expressing anti-CD19 scFv (HM852952) and PD-1 (NM_008798.3): After the formation of mouse bone marrow-derived dendritic cells (BMDCs), lentivirus-mediated gene transfer The staining method made BMDCs highly express anti-CD19 scFv and PD-1, and immunofluorescence ( figure 1 ) and flow cytometry ( figure 2 ) results showed that anti-CD19 scFv and PD-1 were highly expressed on BMDCs, indicating that BMDCs with high expression of anti-CD19 scFv and PD-1 were successfully established.
[0072](3) Constr...
Embodiment 2
[0075] Example 2Extraction and characterization of Engineered DC-derived extracellular vesicles (eDC-EVs)
[0076] (1) The BMDCs loaded with tumor-associated antigens and highly expressed anti-CD19 scFv and PD-1 and knocked down PD-L1 were replaced with RPMI 1640 medium without exosome serum for 48 hours, and the medium supernatant was collected;
[0077] (2) The supernatant of the medium was centrifuged at 300g for 10min at 4°C to remove the precipitation, 1000g for 10min to remove the precipitation, 2000g for 20min to remove the precipitation, 10000g for 30min to remove the precipitation, 100000g for 70min, and the supernatant was discarded. Add PBS to suspend and precipitate, namely the obtained genetically engineered DC-derived extracellular vesicles (eDC-EVs);
[0078] (3) Using transmission electron microscopy and DLS to analyze the morphology and particle size of the extracellular vesicles obtained in step (2) ( Image 6 , Figure 7 ), Zeta potential -20mV or so ( F...
Embodiment 3e
[0080] Example 3 The ability of eDC-EVs to interact with CD19 on PD-L1 and CT26 cells in vitro and the effect on the anti-tumor efficiency of T cells
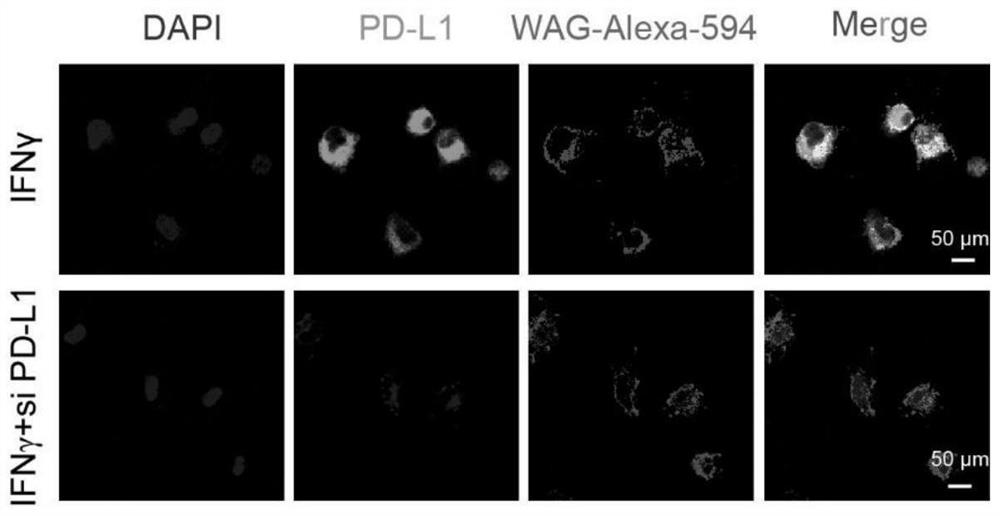
[0081] (1) eDC-EVs and PD-L1 + Cellular interactions: CT26 colon cancer cells, bone marrow-derived dendritic cells (BMDCs) and macrophages (BMDMs) express PD-L1 under the induction of 20 ng / mL IFN-γ, and Cy5. The cells expressing PD-L1 were co-incubated for 24h, and the co-localization of Cy5.5 and PD-L1 was observed by Confocal Microscopy. The results showed ( Figure 11 ), PD-1 on extracellular vesicles has a strong interaction with PD-L1.
[0082] (2) Interaction between eDC-EVs and human-CD19 expressed on CT26 colon cancer cells: CT26 colon cancer cells highly expressed human-CD19 under the mediation of lentivirus encoding human-CD19 gene, and then interacted with Cy5.5-labeled The eDC-EVs were co-incubated for 24 hours, and the co-localization of Cy5.5 and CD19 was observed by Confocal Microscopy. The results showed ( ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com