Manufacture of film semiconductor device
A thin-film semiconductor and manufacturing method technology, used in semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, semiconductor devices, transistors, etc., can solve problems such as damage, difficulty in enlarging polycrystalline film grains, and decline in semiconductor characteristics and product yield.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
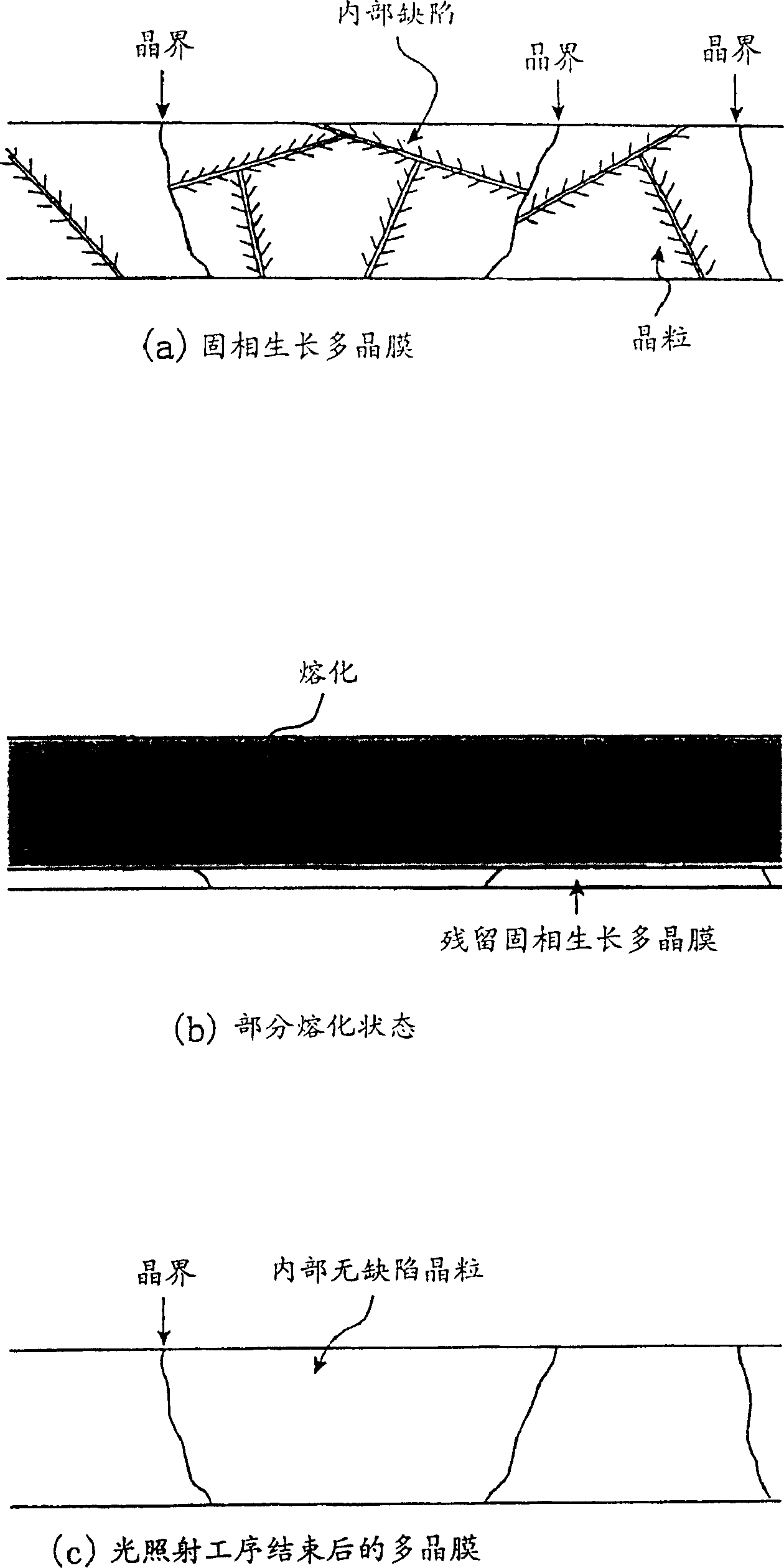
[0116] Figure 11 a to d are cross-sectional views showing the manufacturing process of a thin film semiconductor device forming a MOS-type electric field effect transistor. In the first embodiment, crystallized glass having a glass deformation point temperature of 750 degrees Celsius was used as the substrate 101 . However, even other substrates are not limited in their kind and size if they can withstand the highest temperature during the fabrication of thin film semiconductor devices. First, a silicon oxide film to be the base protective film 102 is deposited on the substrate 101 . When unnecessary impurities are included on the semiconductor film such as a ceramic substrate for the substrate, it is only necessary to deposit a first base protection film such as a tantalum oxide film and a silicon nitride film before depositing the silicon oxide film. In the first embodiment, a silicon oxide film of about 200 nm is deposited as the base protection film 102 on the substrate...
Embodiment 2
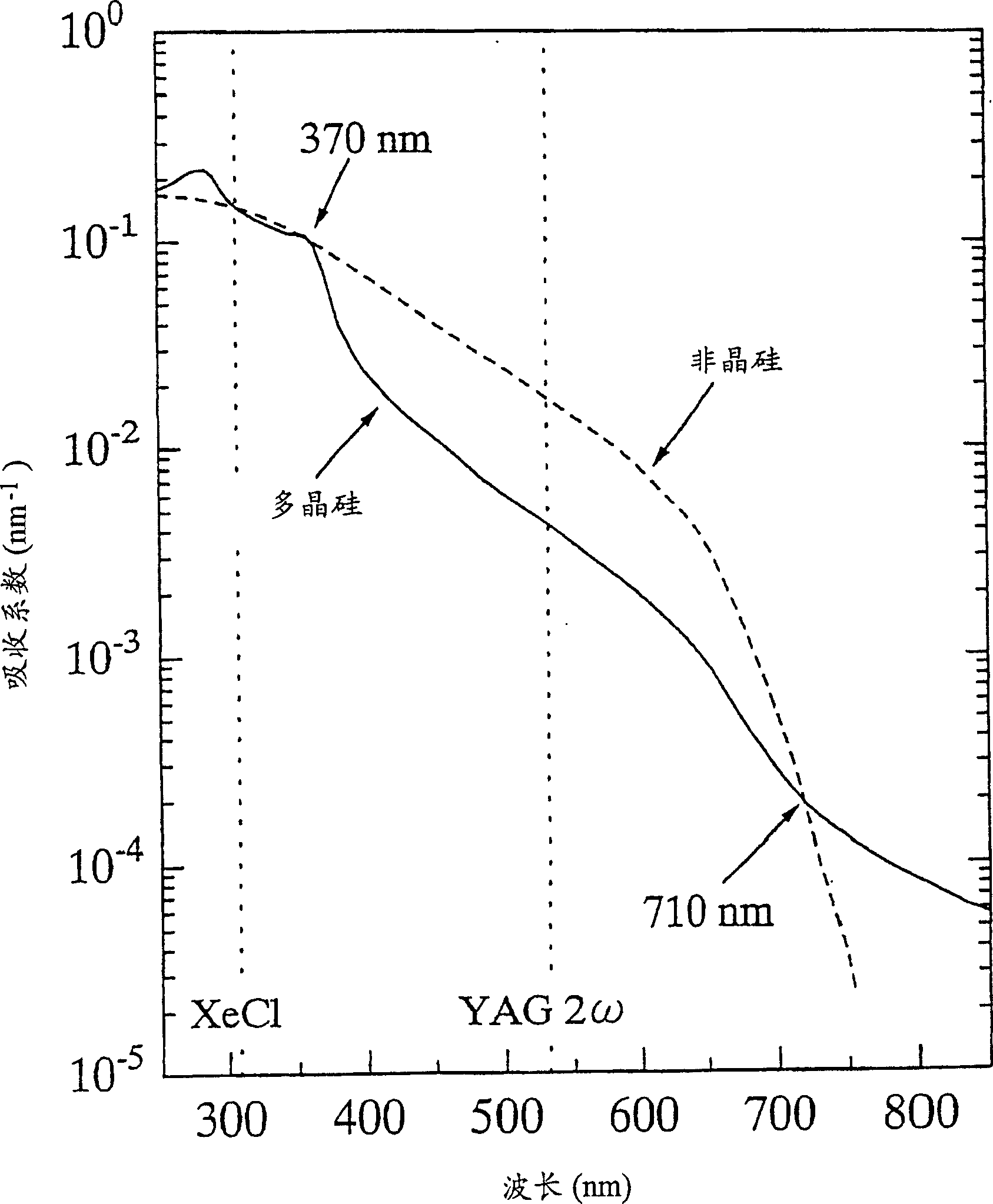
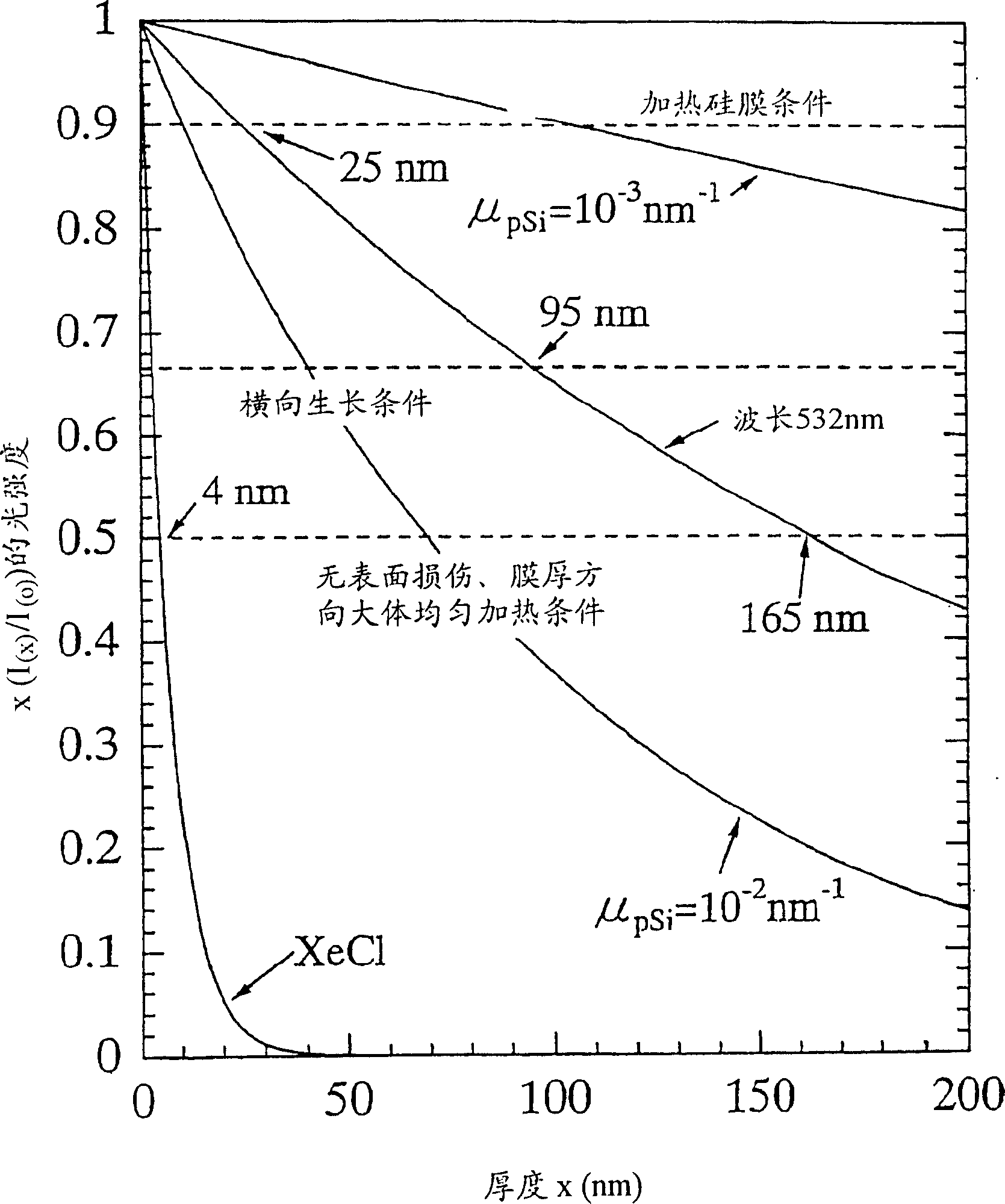
[0141] Except for irradiating the semiconductor film with the second harmonic wave of the pulsed Nd:YAG laser in the light irradiation process, the other manufacturing steps are exactly the same as in Example 1, so that a thin film semiconductor device can be produced. In Example 2, only the line-focused YAG2ω pulse laser with a width of 270 μm and a length of 10 mm is staggered in the width direction of each irradiation, and the laser irradiation energy density on the semiconductor film is different from that of Example 1. Four levels of 10%, 5%, 2.5%, and 1.67% are selected for the stagger ratio of the linear laser in the width direction of each irradiation. Accordingly, arbitrary points on the semiconductor film were irradiated with laser light about 10 times, 20 times, 40 times, and 60 times, respectively. The change in energy density of laser irradiation on the semiconductor film is 400mJ·cm -2 ~800mJ·cm -2 . The maximum change of the laser energy density gradient prop...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com