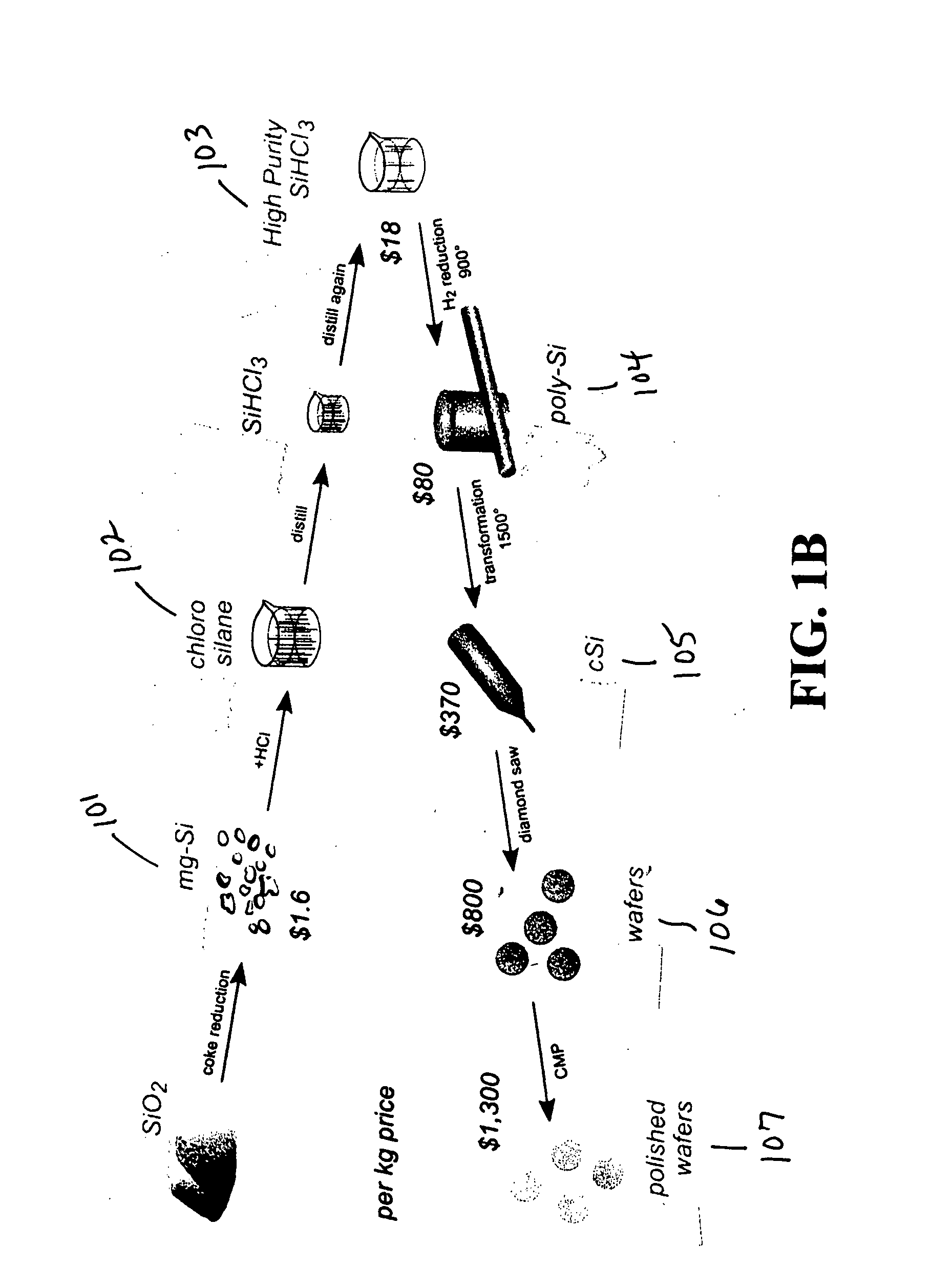
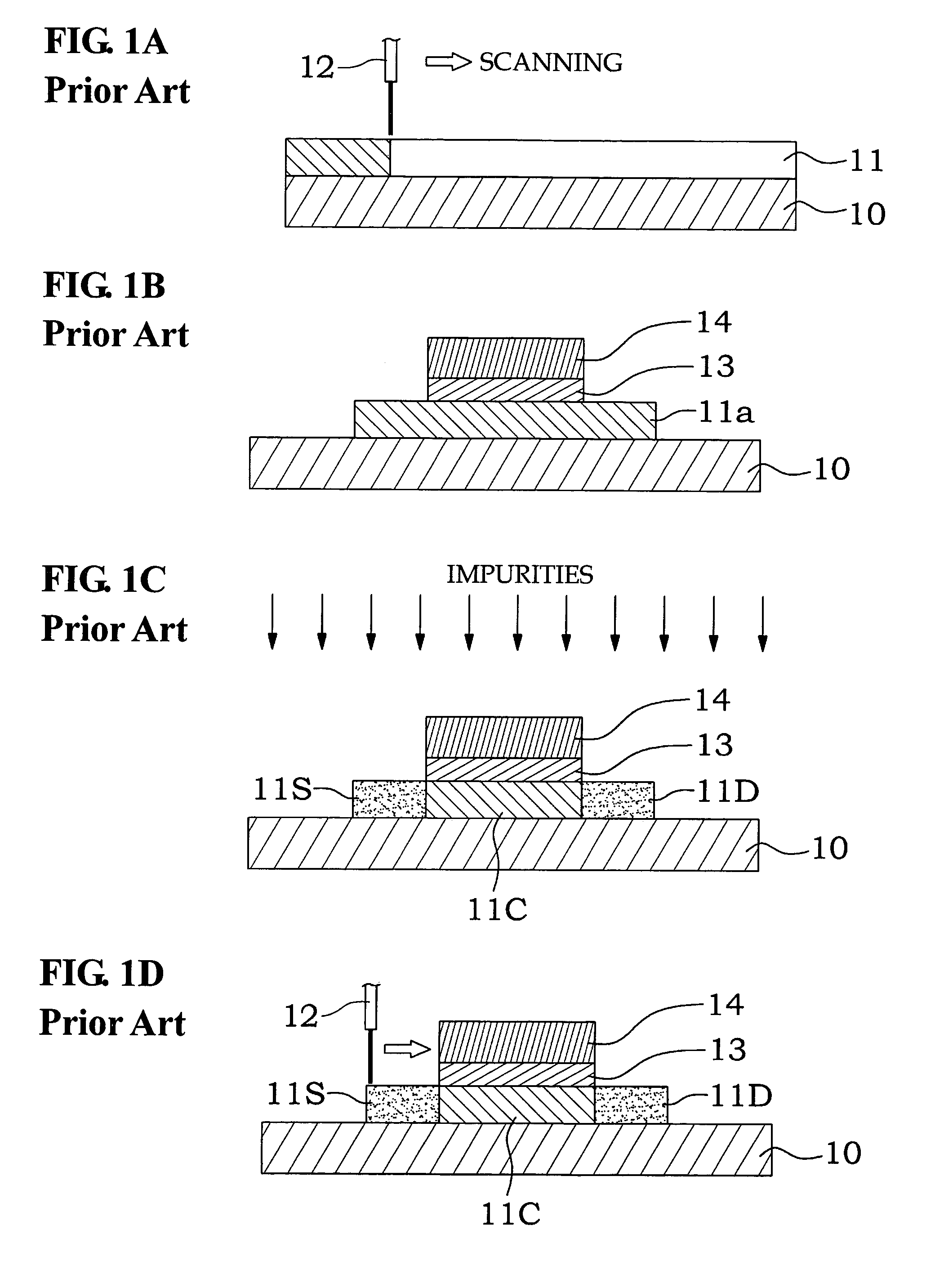
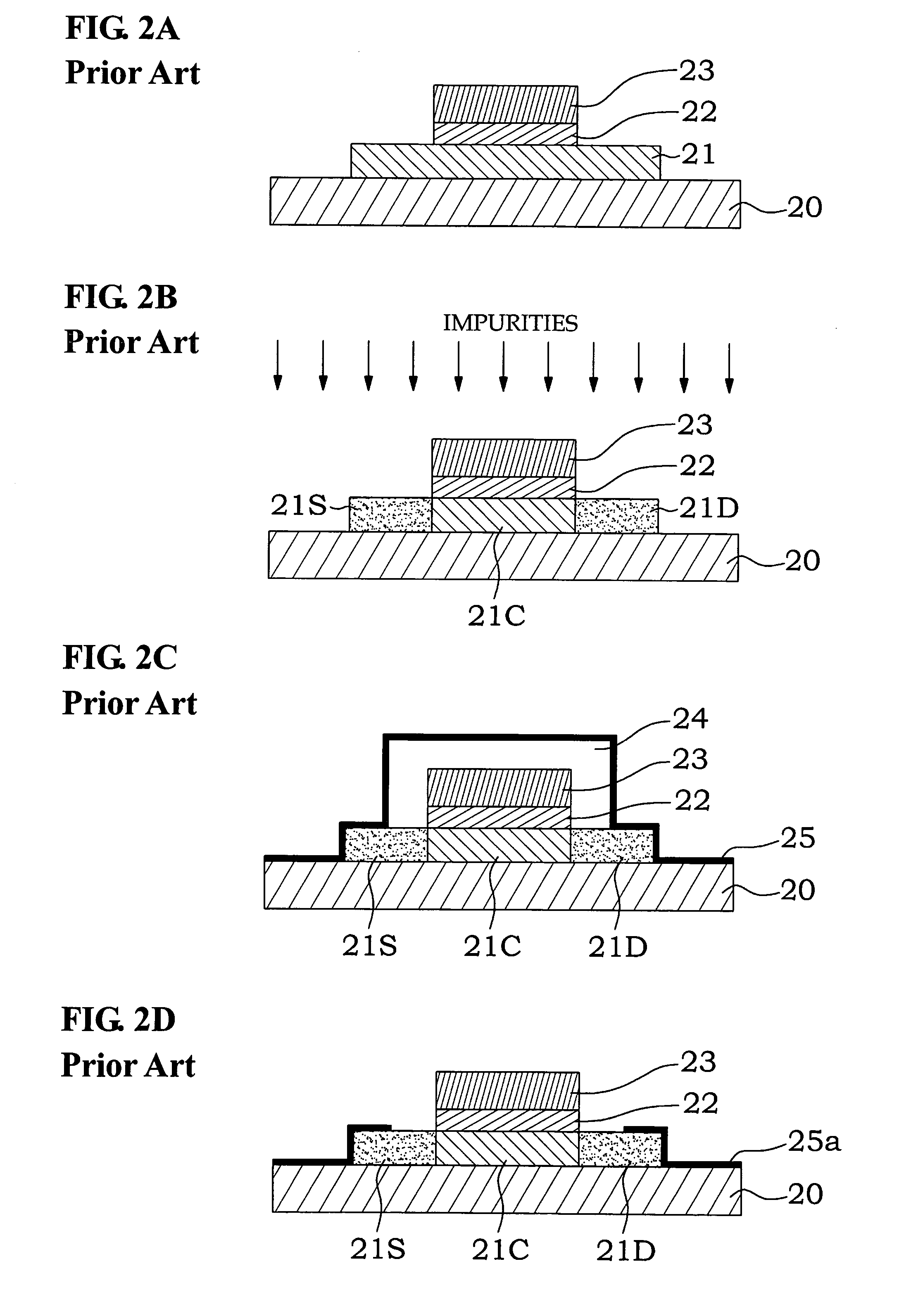
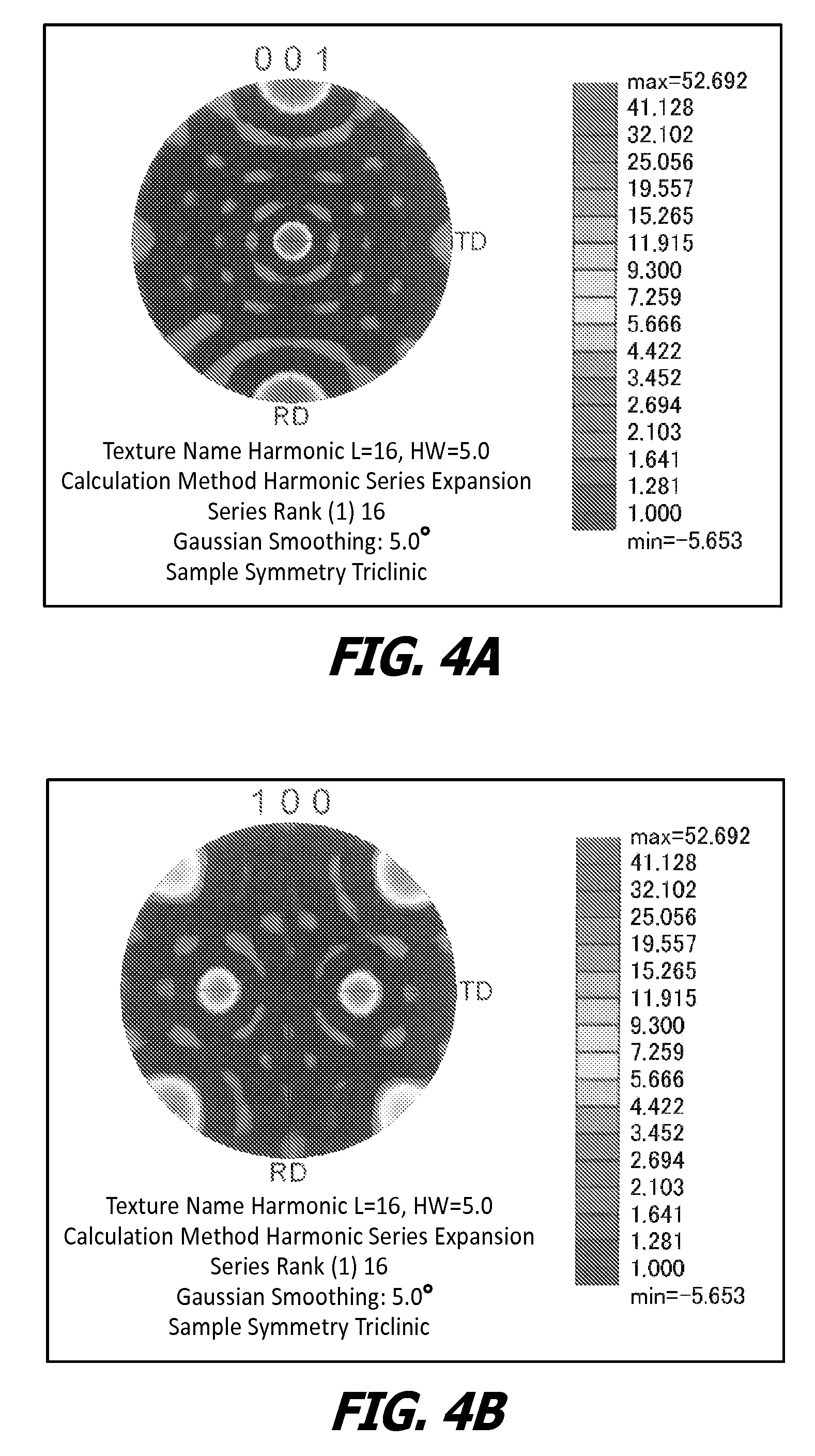
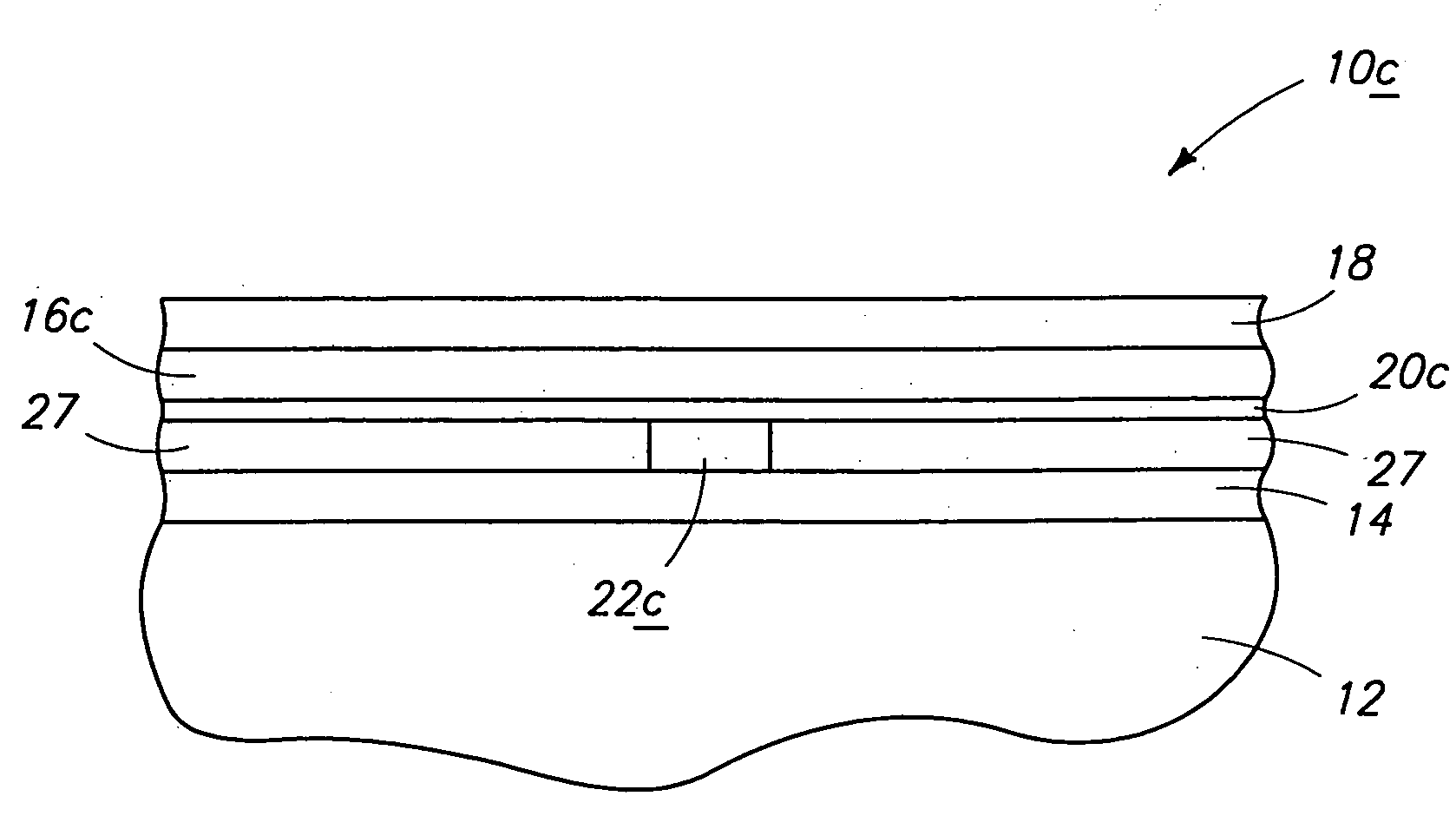
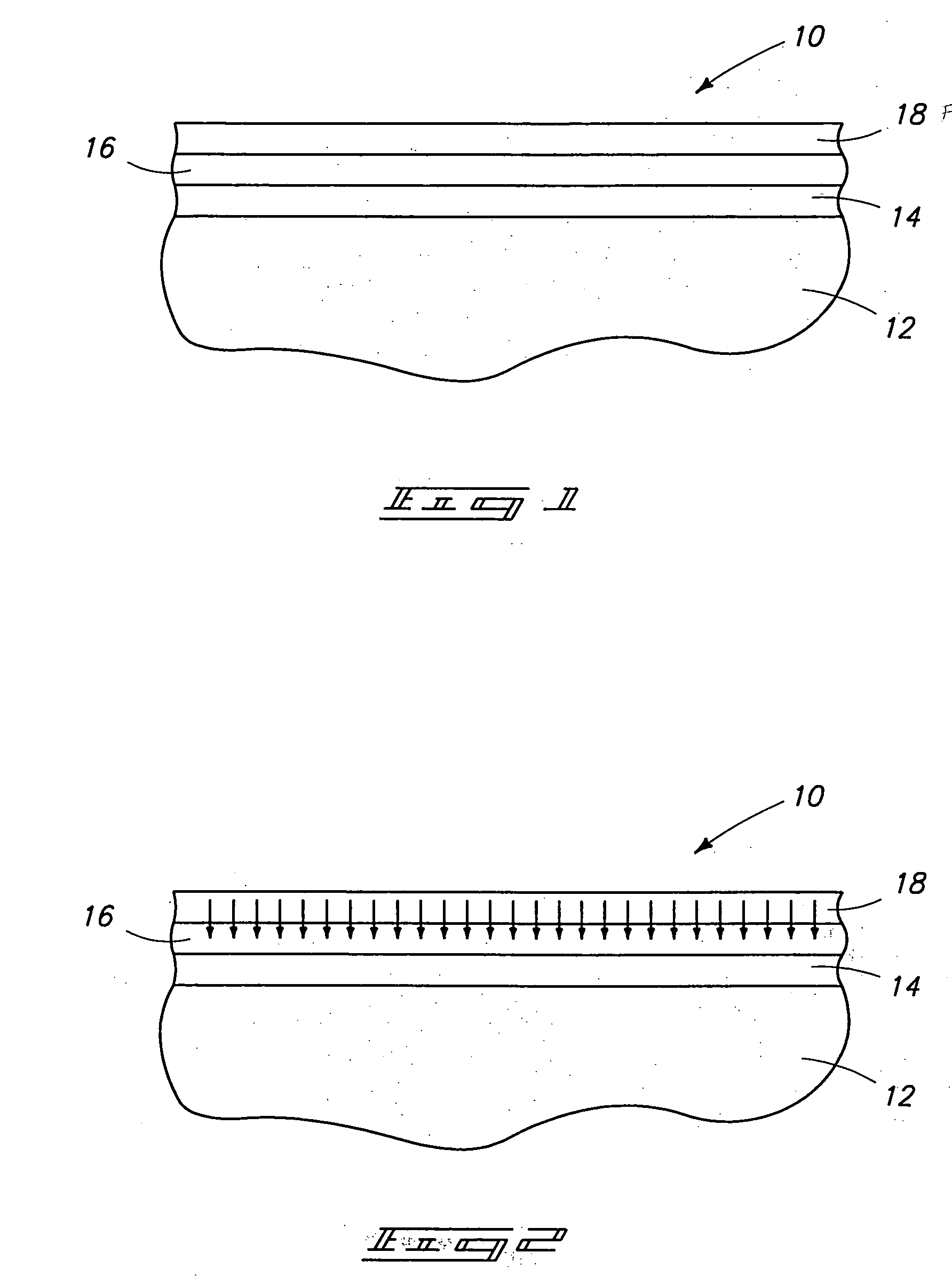
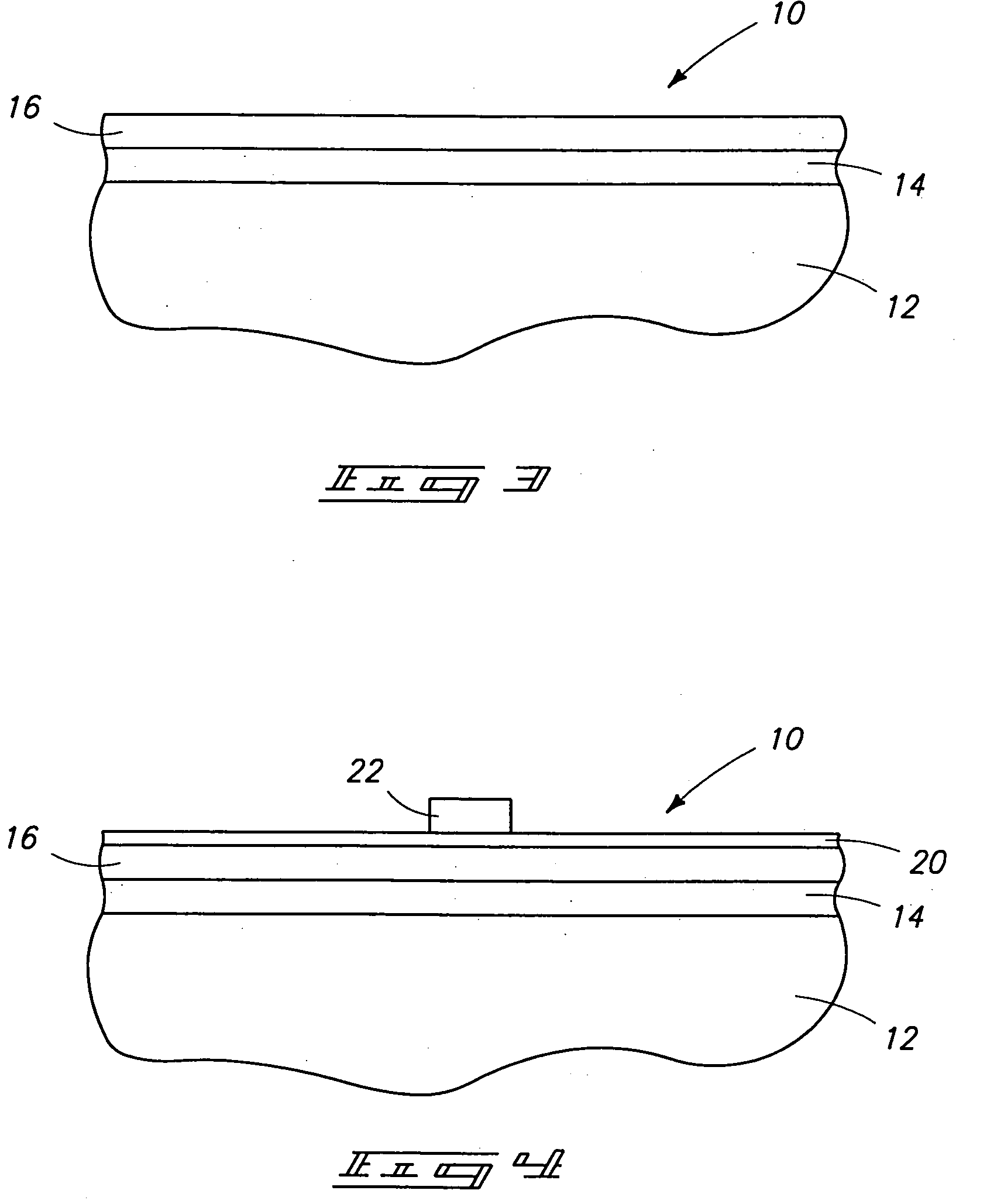
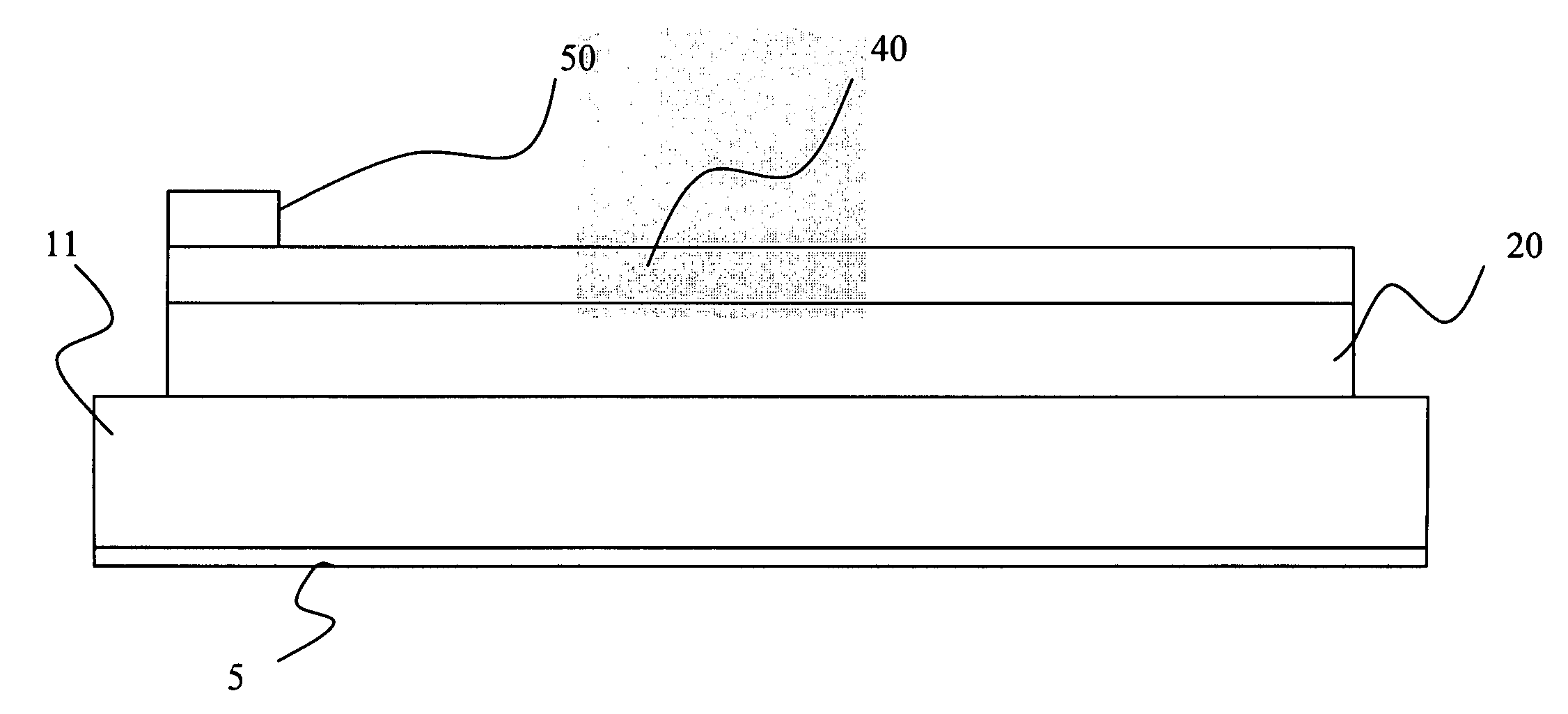
Patents
Literature
151 results about "Polycrystalline thin films" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
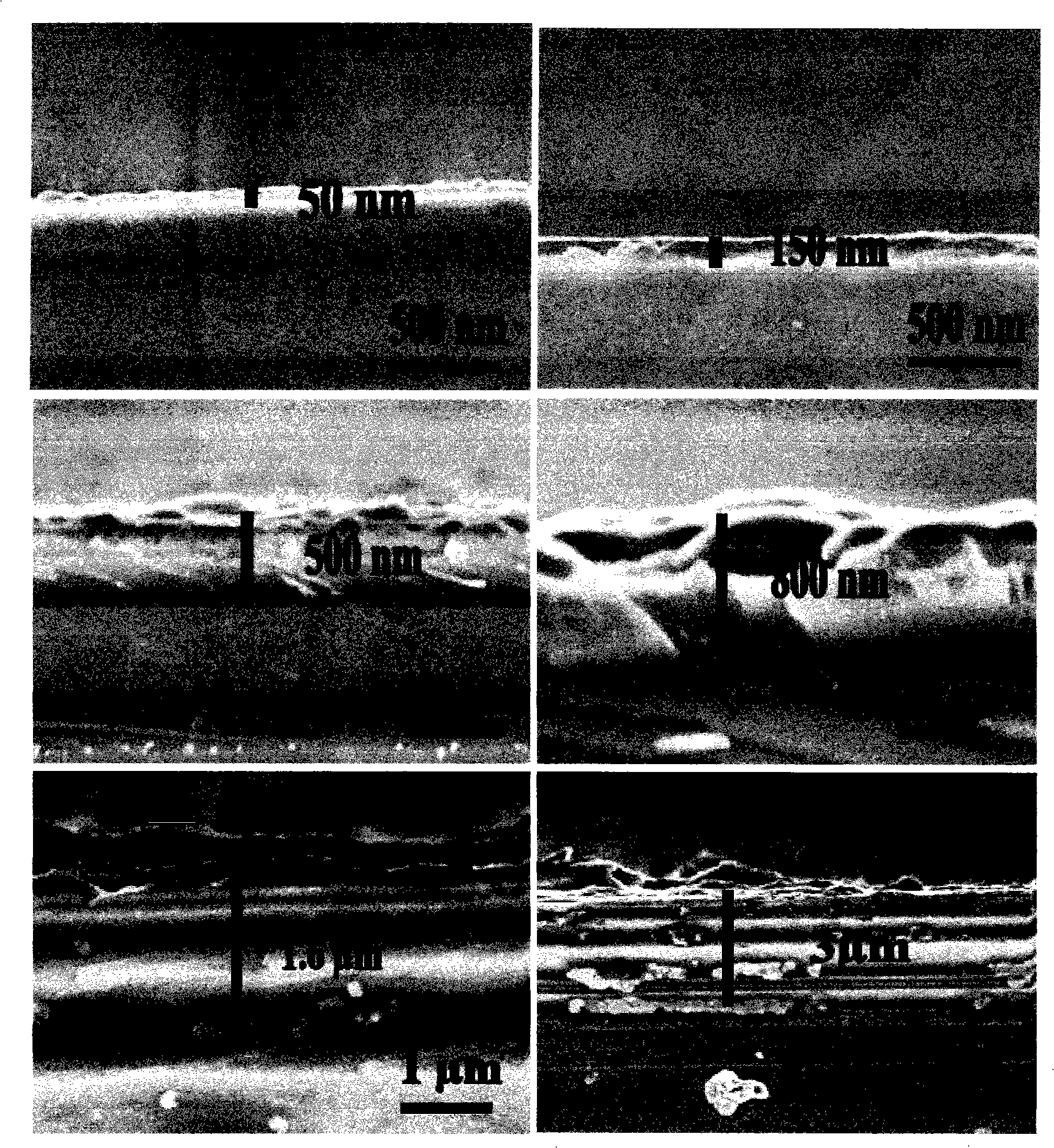
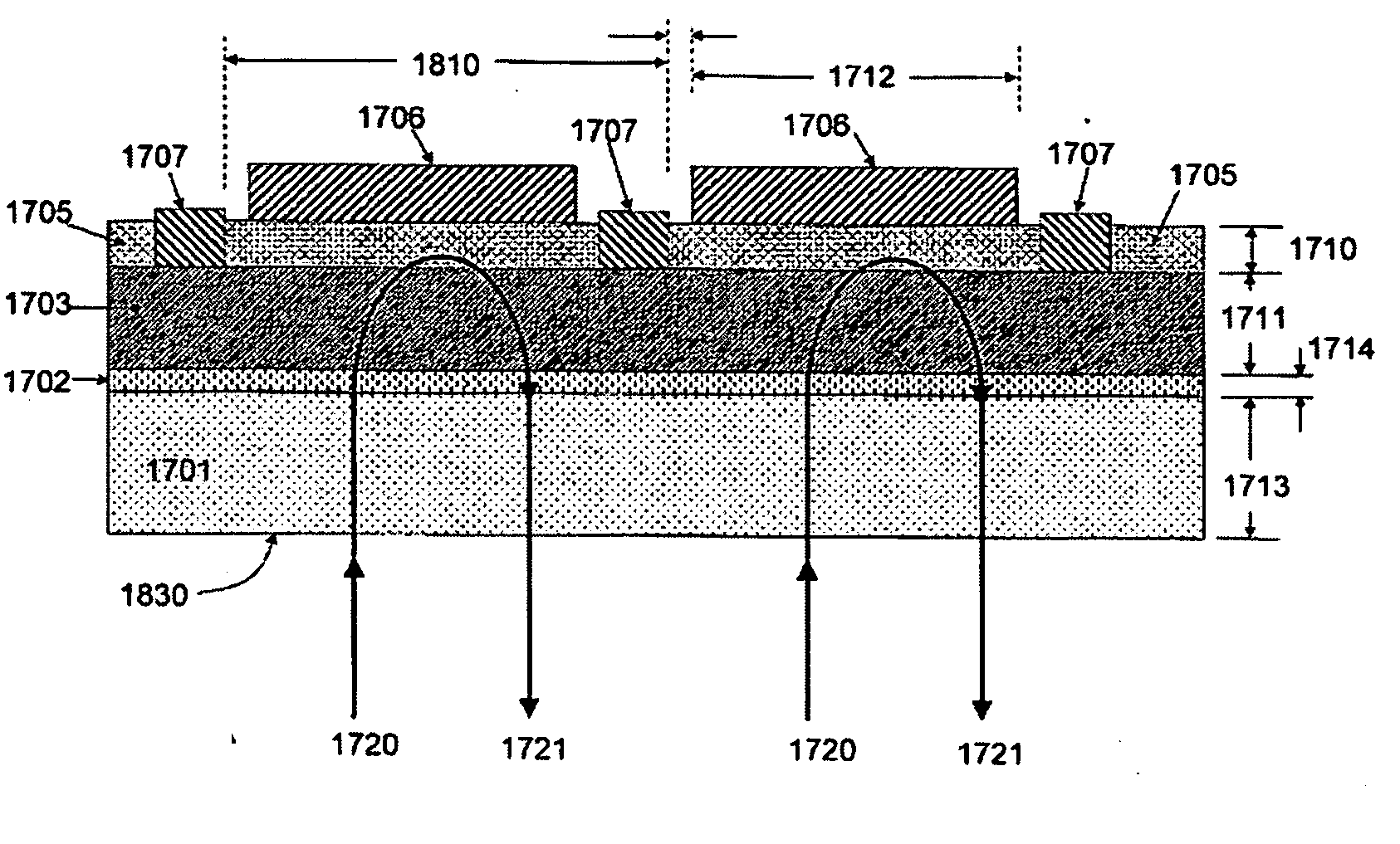
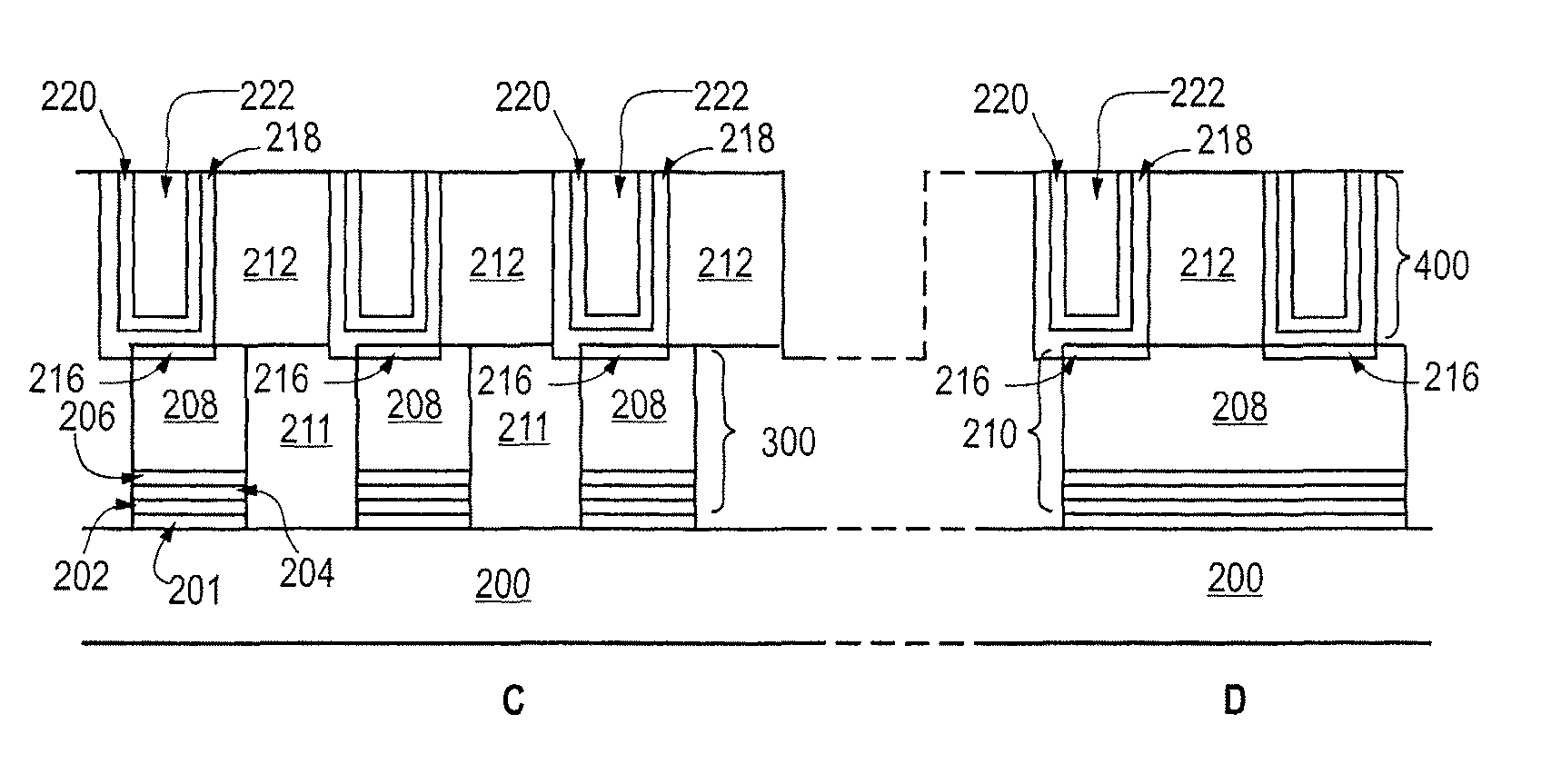
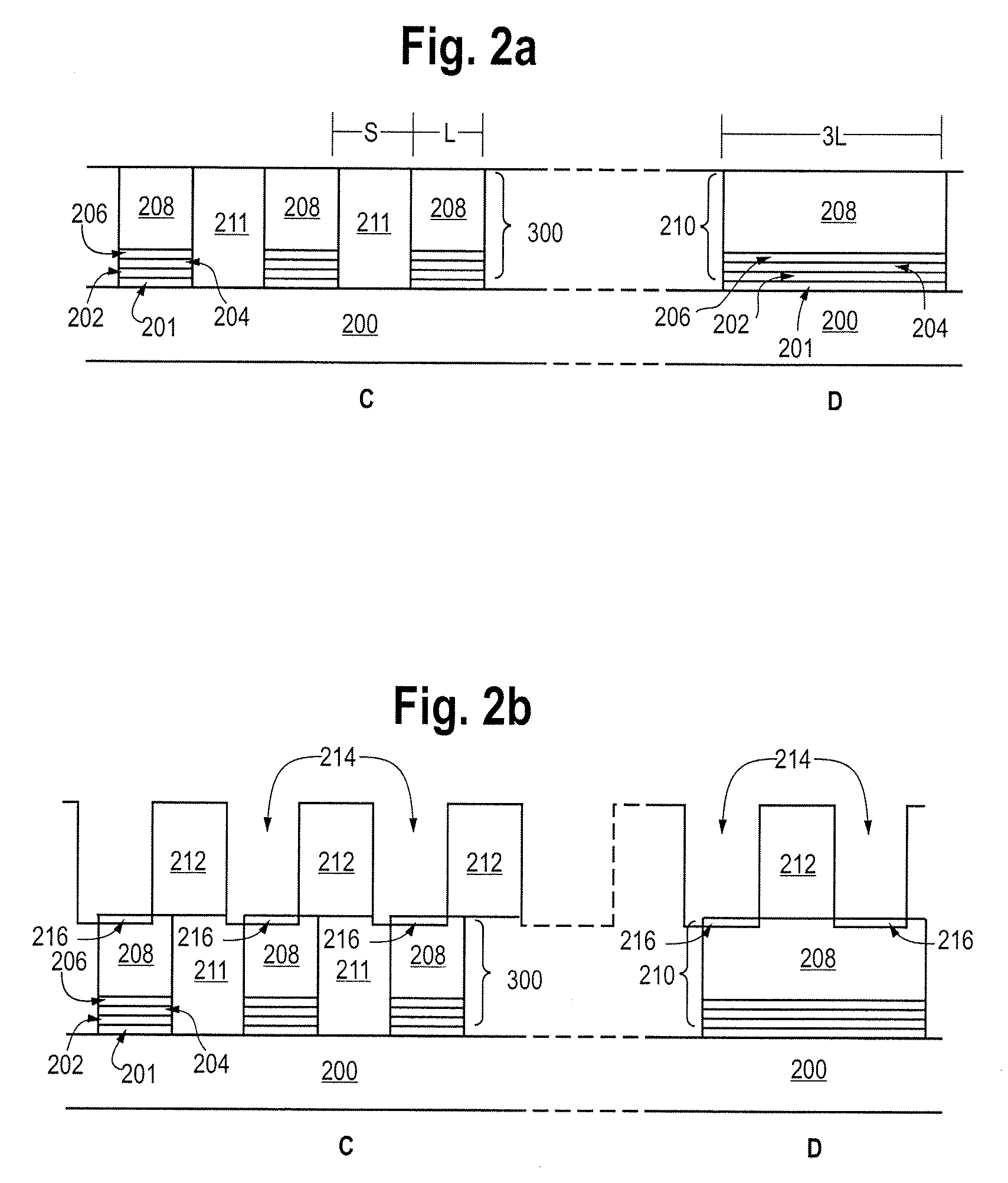
Methods for producing uniform large-grained and grain boundary location manipulated polycrystalline thin film semiconductors using sequential lateral solidification
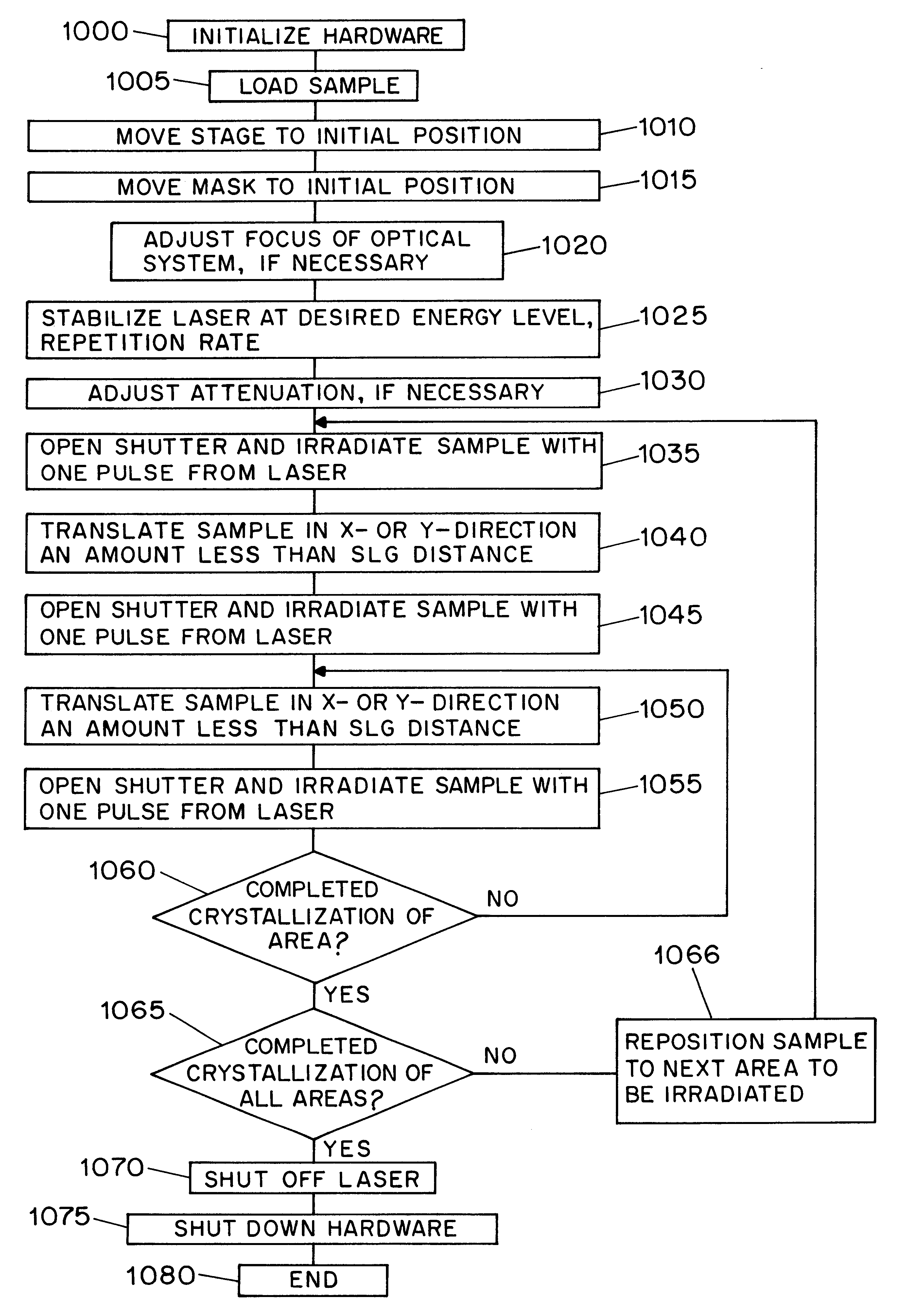
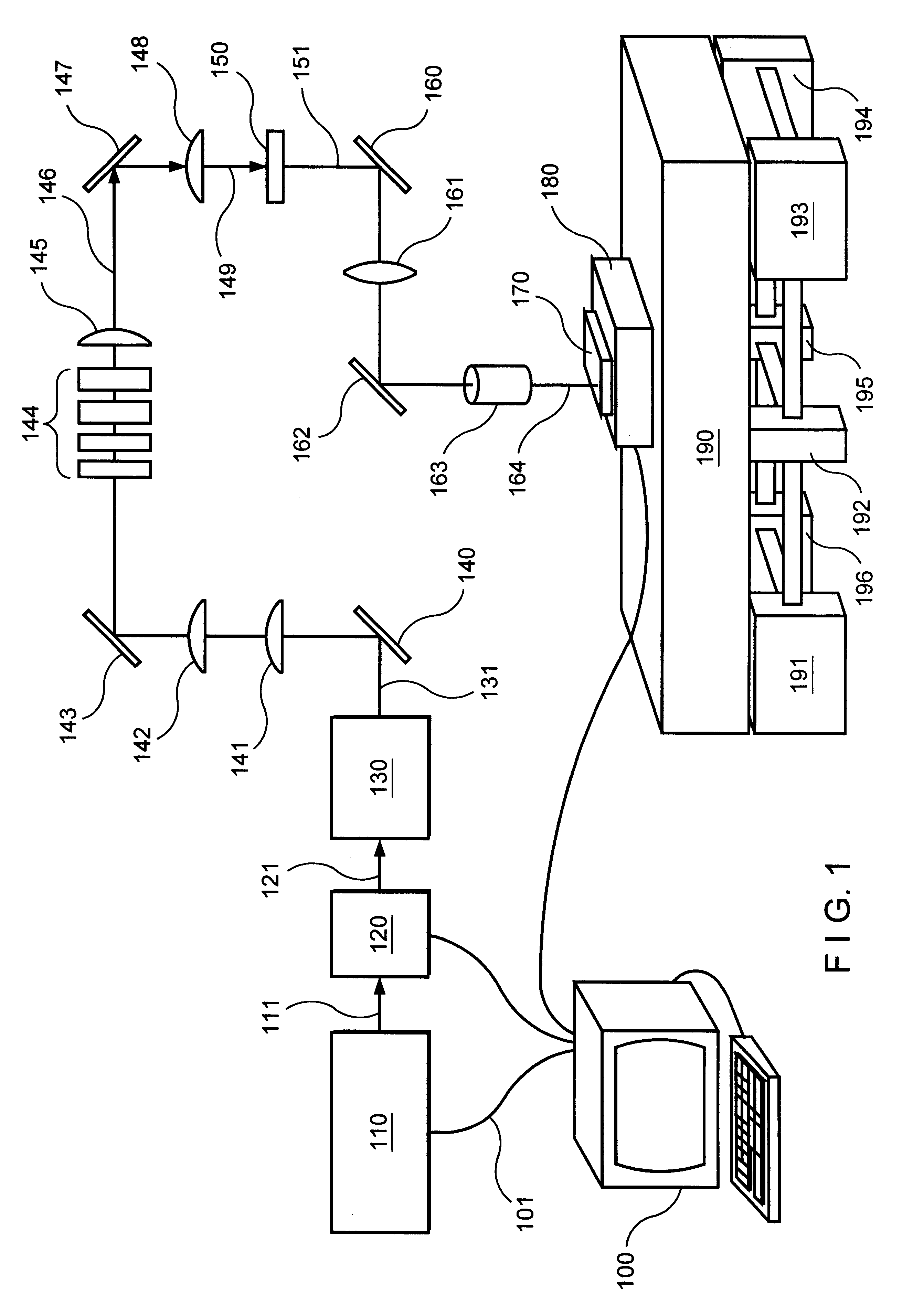
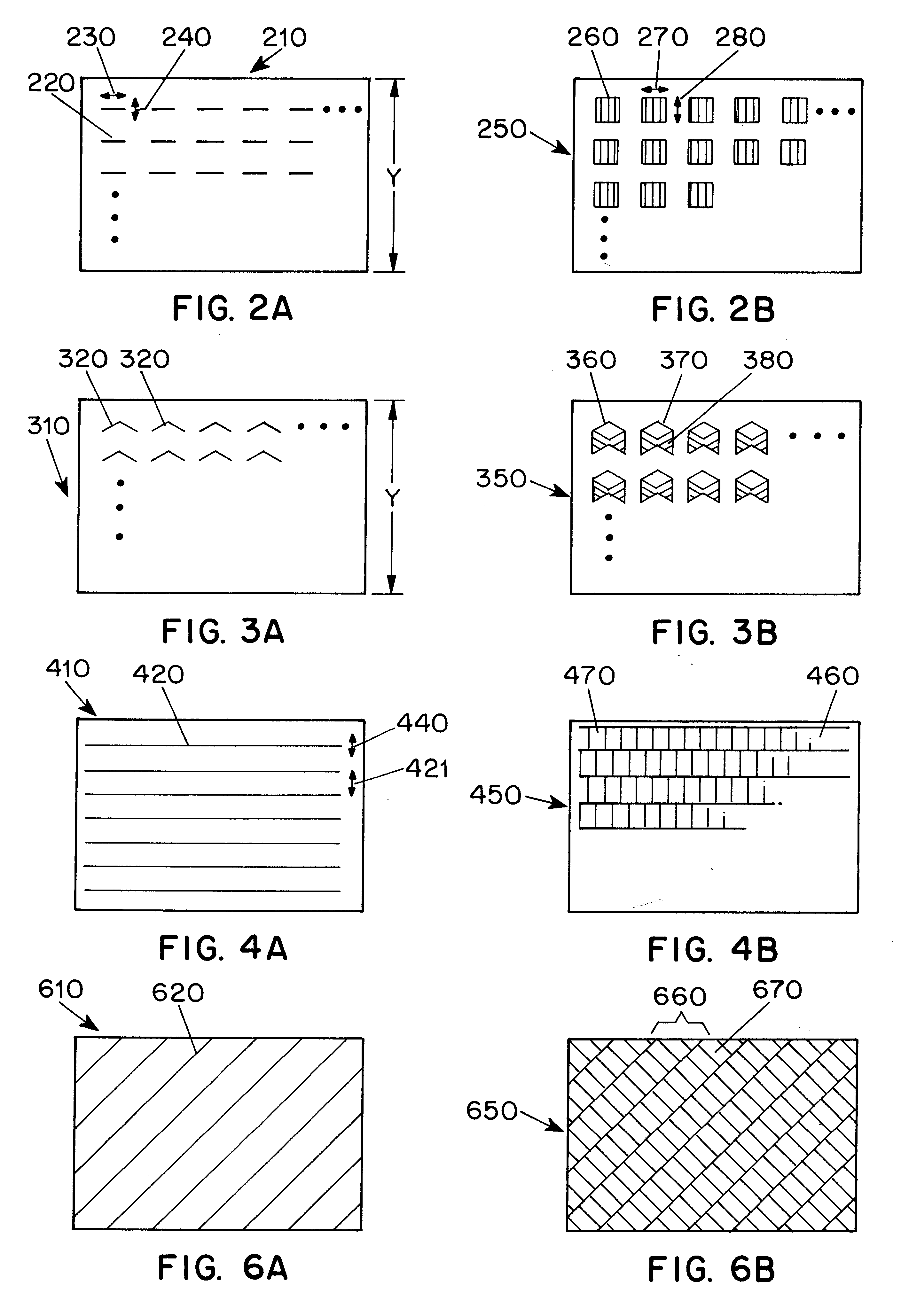
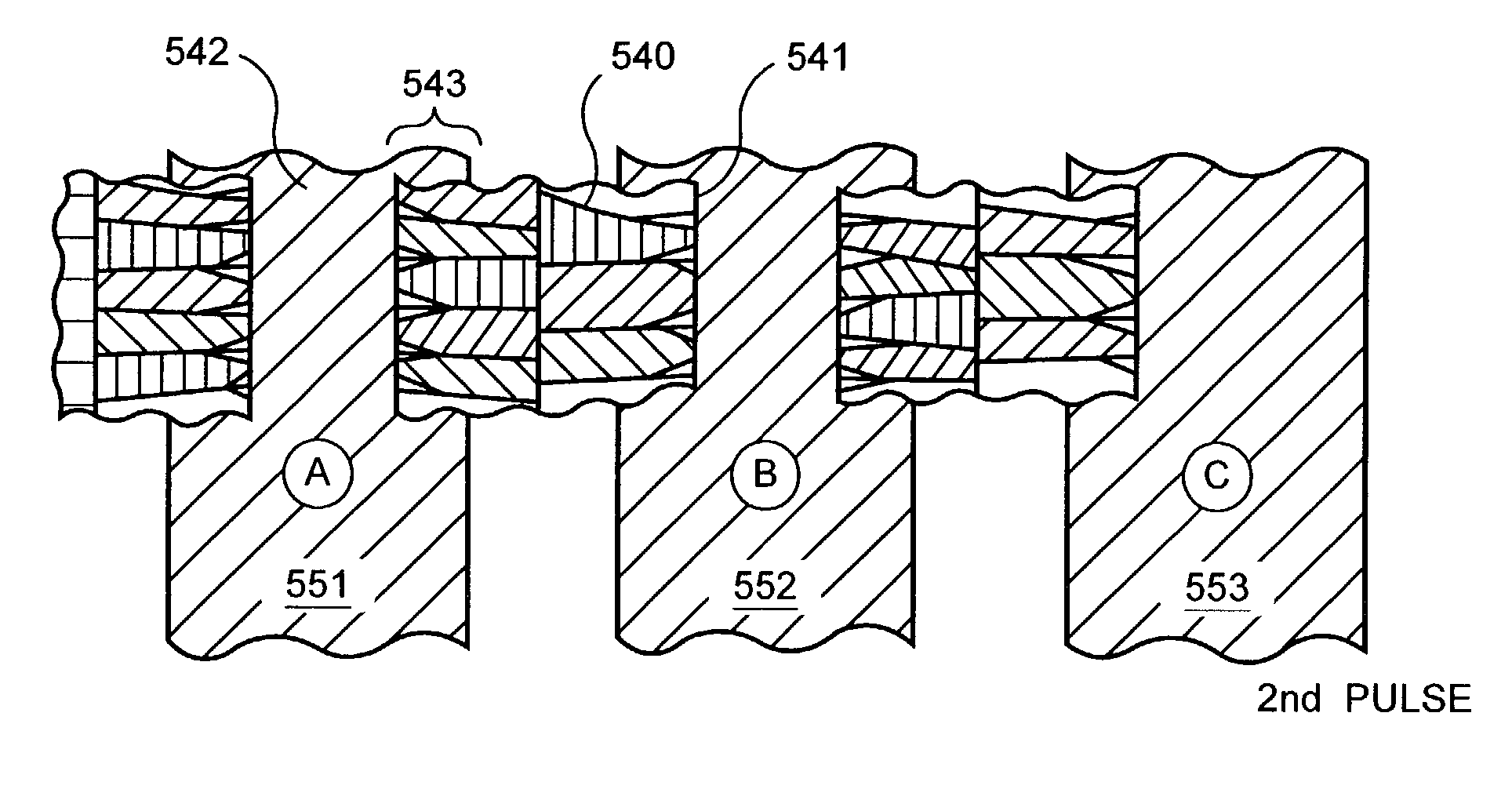
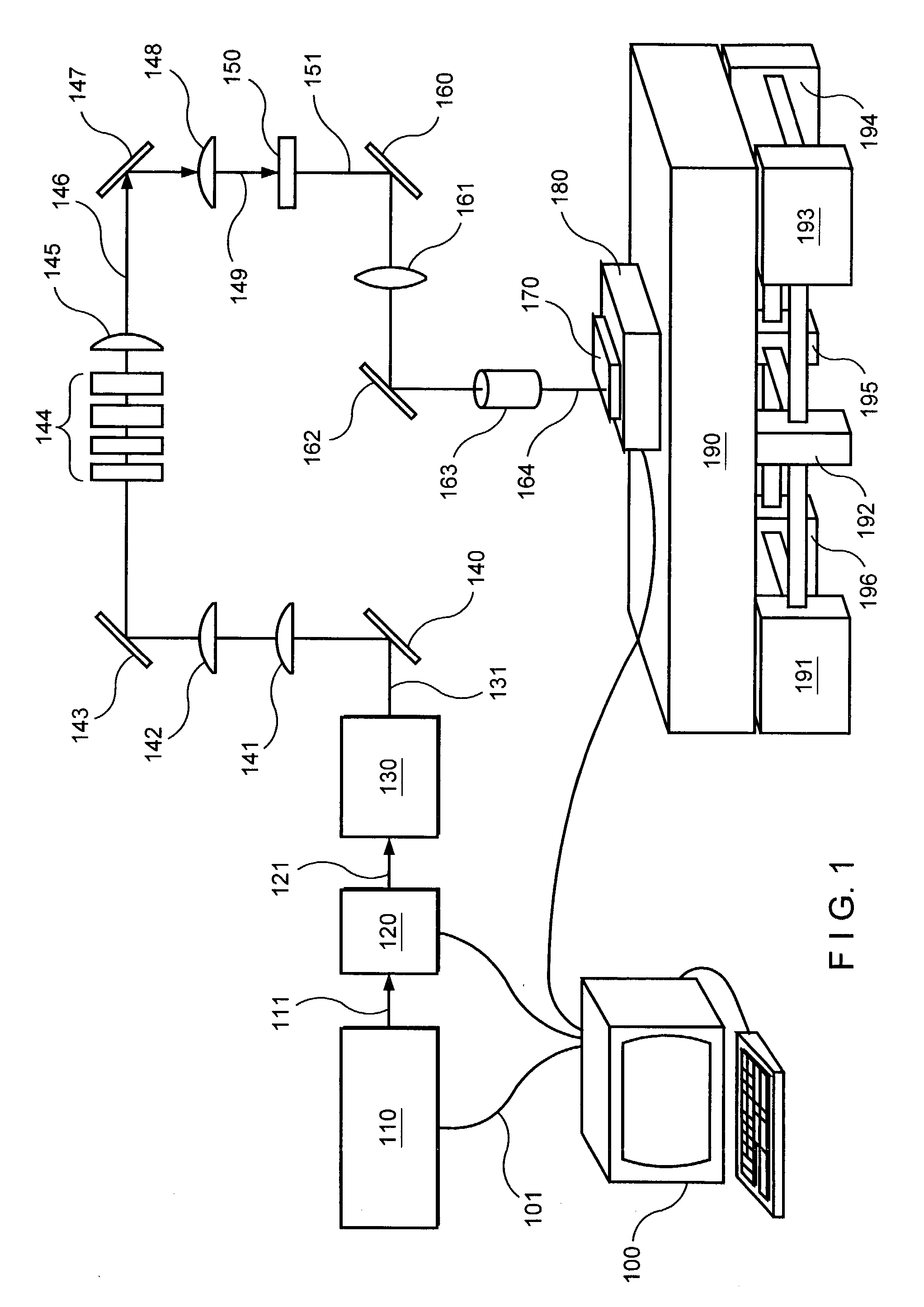
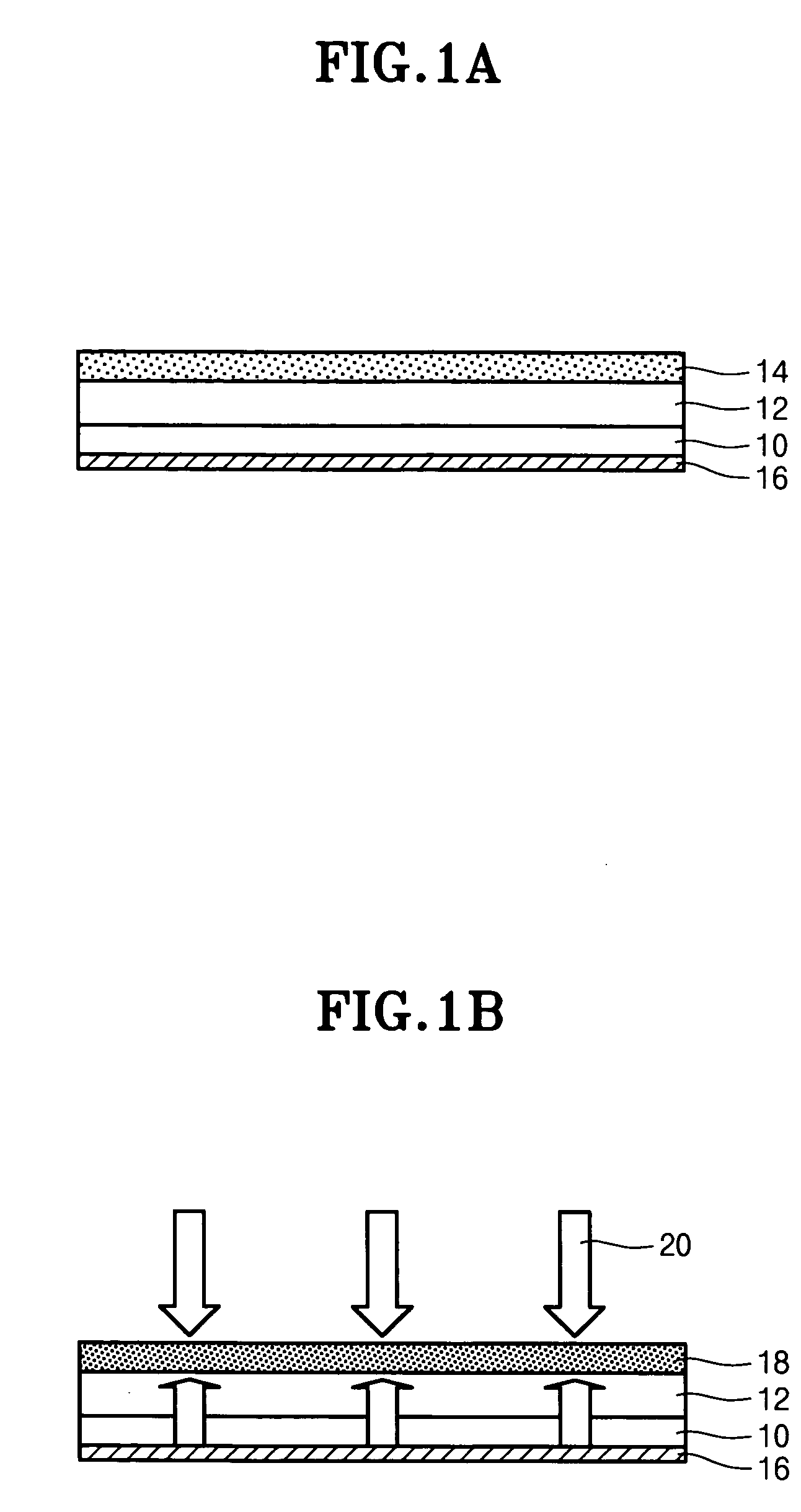
Methods for processing an amorphous silicon thin film sample into a polycrystalline silicon thin film are disclosed. In one preferred arrangement, a method includes the steps of generating a sequence of excimer laser pulses, controllably modulating each excimer laser pulse in the sequence to a predetermined fluence, homoginizing each modulated laser pulse in the sequence in a predetermined plane, masking portions of each homogenized fluence controlled laser pulse in the sequence with a two dimensional pattern of slits to generate a sequence of fluence controlled pulses of line patterned beamlets, each slit in the pattern of slits being sufficiently narrow to prevent inducement of significant nucleation in region of a silicon thin film sample irradiated by a beam let corresponding to the slit, irradiating an amorphous silicon thin film sample with the sequence of fluence controlled slit patterned beamlets to effect melting of portions thereof corresponding to each fluence controlled patterned beamlet pulse in the sequence of pulses of patterned beamlets, and controllably sequentially translating a relative position of the sample with respect to each of the fluence controlled pulse of slit patterned beamlets to thereby process the amorphous silicon thin film sample into a single or polycrystalline silicon thin film.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Methods for producing uniform large-grained and grain boundary location manipulated polycrystalline thin film semiconductors using sequential lateral solidification
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Highly scalable thin film transistor
ActiveUS7888205B2Minimizing dopant diffusionSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDopantOptoelectronics
Shrinking the dimensions of PMOS or NMOS thin film transistors is limited by dopant diffusion. In these devices an undoped or lightly doped channel region is interposed between heavily doped source and drain regions. When the device is built with very short gate length, source and drain dopants will diffuse into the channel, potentially shorting it and ruining the device. A suite of innovations is described which may be used in various combinations to minimize dopant diffusion during fabrication of a PMOS or NMOS polycrystalline thin film transistor, resulting in a highly scalable thin film transistor. This transistor is particularly suitable for use in a monolithic three dimensional array of stacked device levels.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
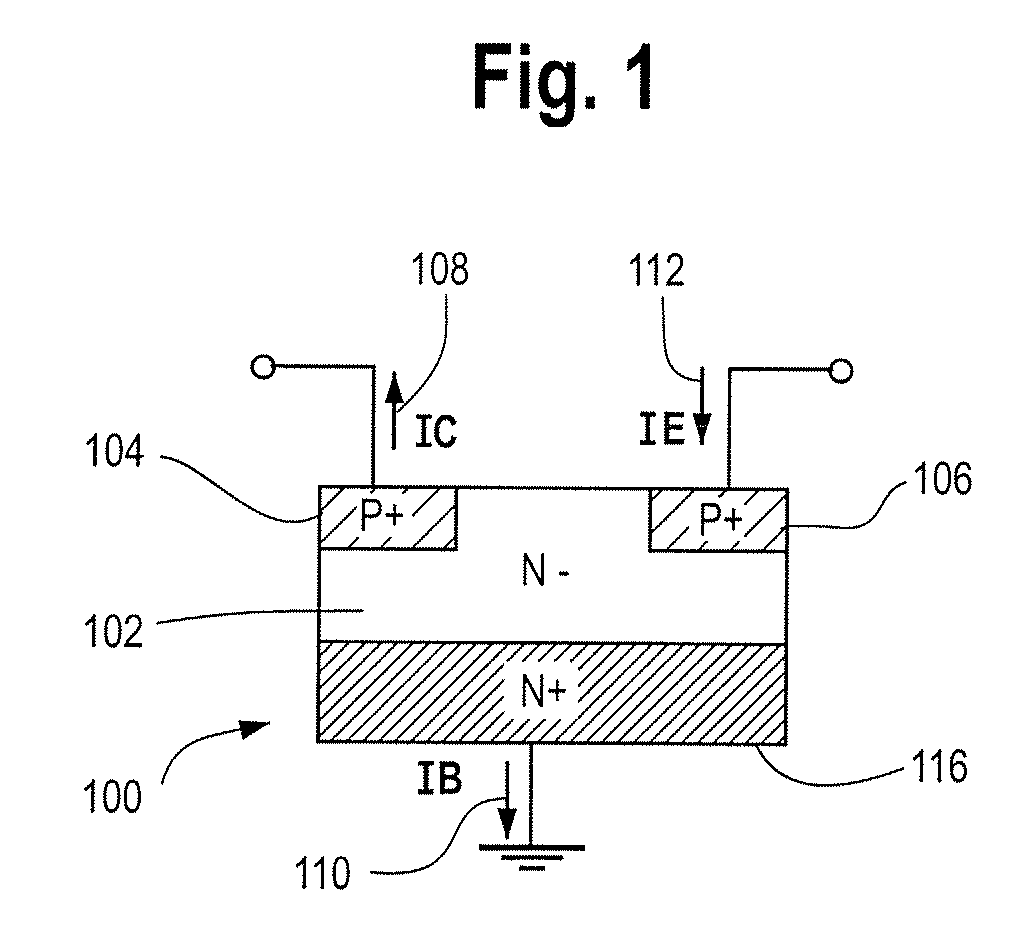
Method for forming polycrystalline thin film bipolar transistors
ActiveUS20080311722A1Read-only memoriesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGermanideMaterials science
A method is described for forming a semiconductor device comprising a bipolar transistor having a base region, an emitter region and a collector region, wherein the base region comprises polycrystalline semiconductor material formed by crystallizing silicon, germanium or silicon germanium in contact with a silicide, germanide or silicide germanide. The emitter region and collector region also may be formed from polycrystalline semiconductor material formed by crystallizing silicon, germanium or silicon germanium in contact with a silicide, germanide or silicide germanide forming metal. The polycrystalline semiconductor material is preferably silicided polysilicon, which is formed in contact with C49 phase titanium silicide.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Thin Film Semi-Conductor-on-Glass Solar Cell Devices
InactiveUS20080308143A1Inhibit transport and deleterious actionLower performance requirementsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotovoltaic energy generationAlkali ionsRare earth
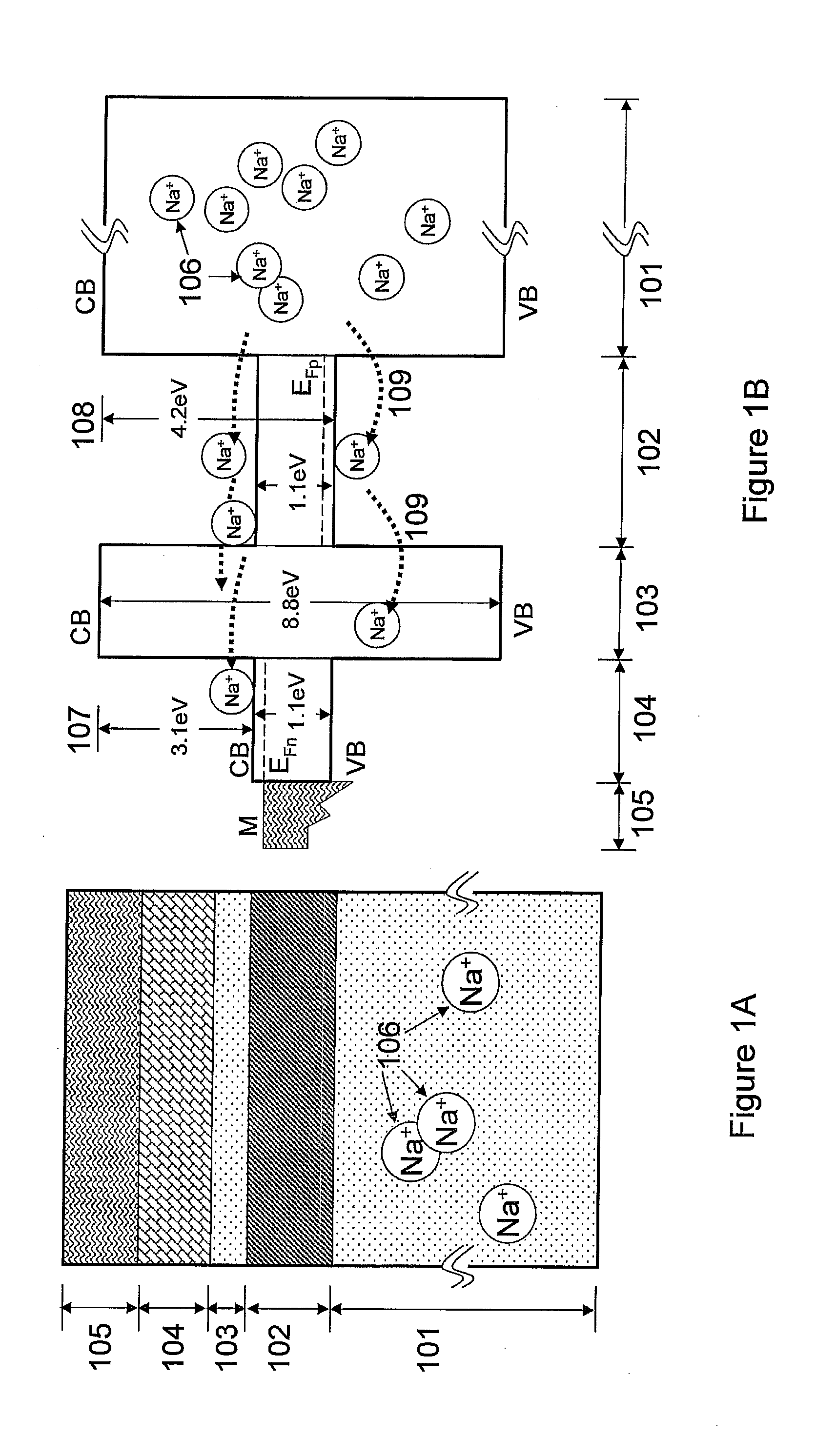
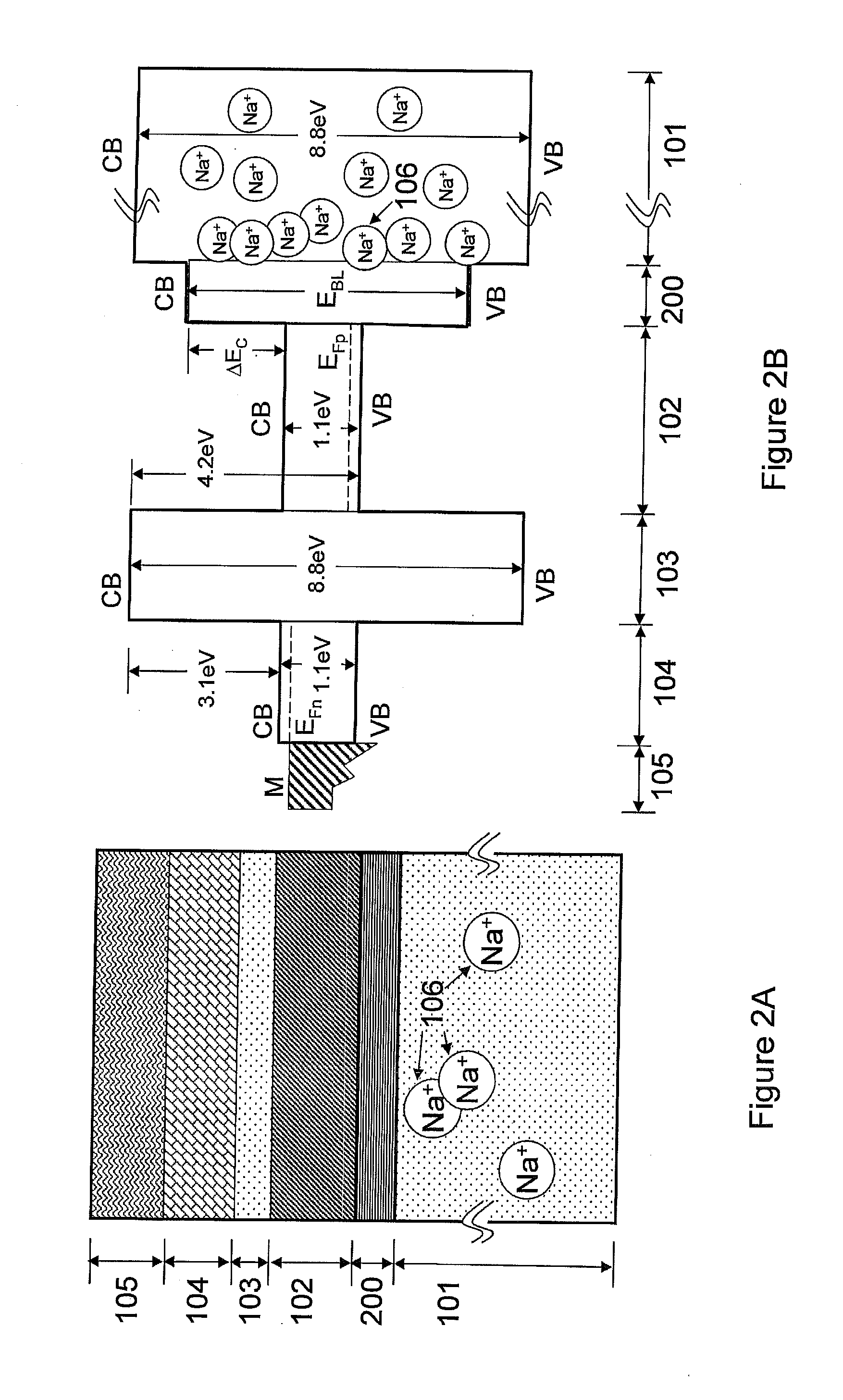
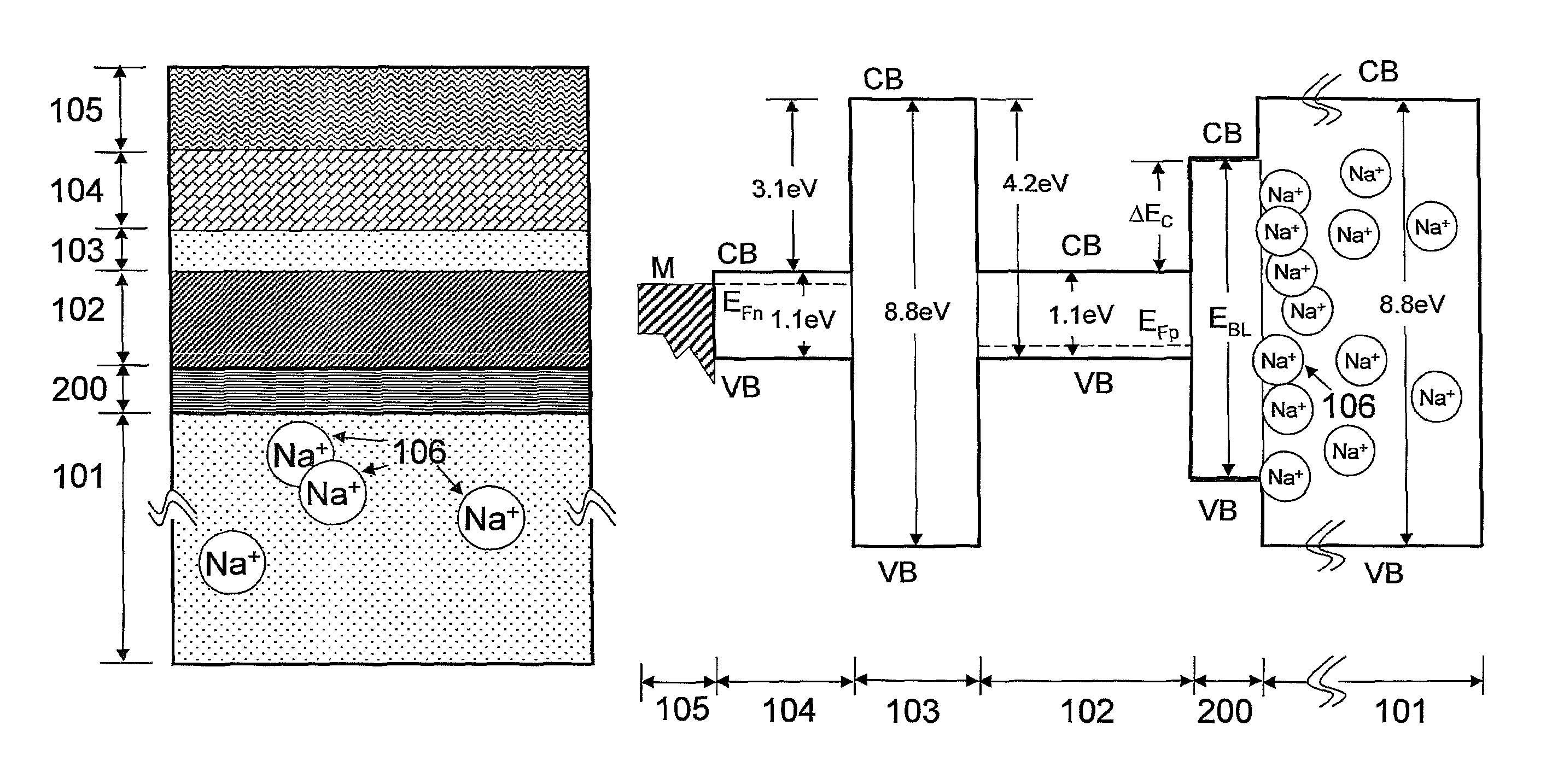
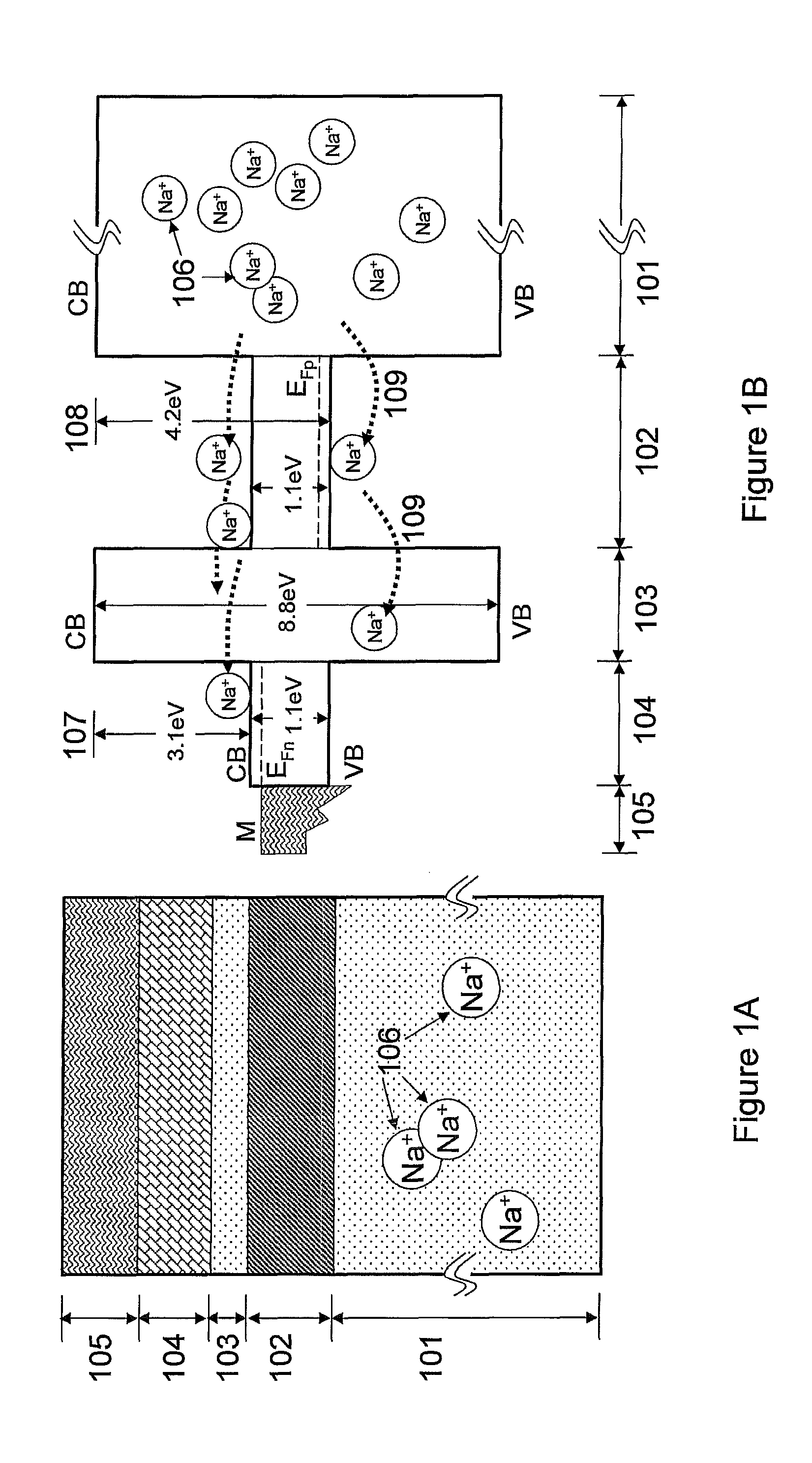
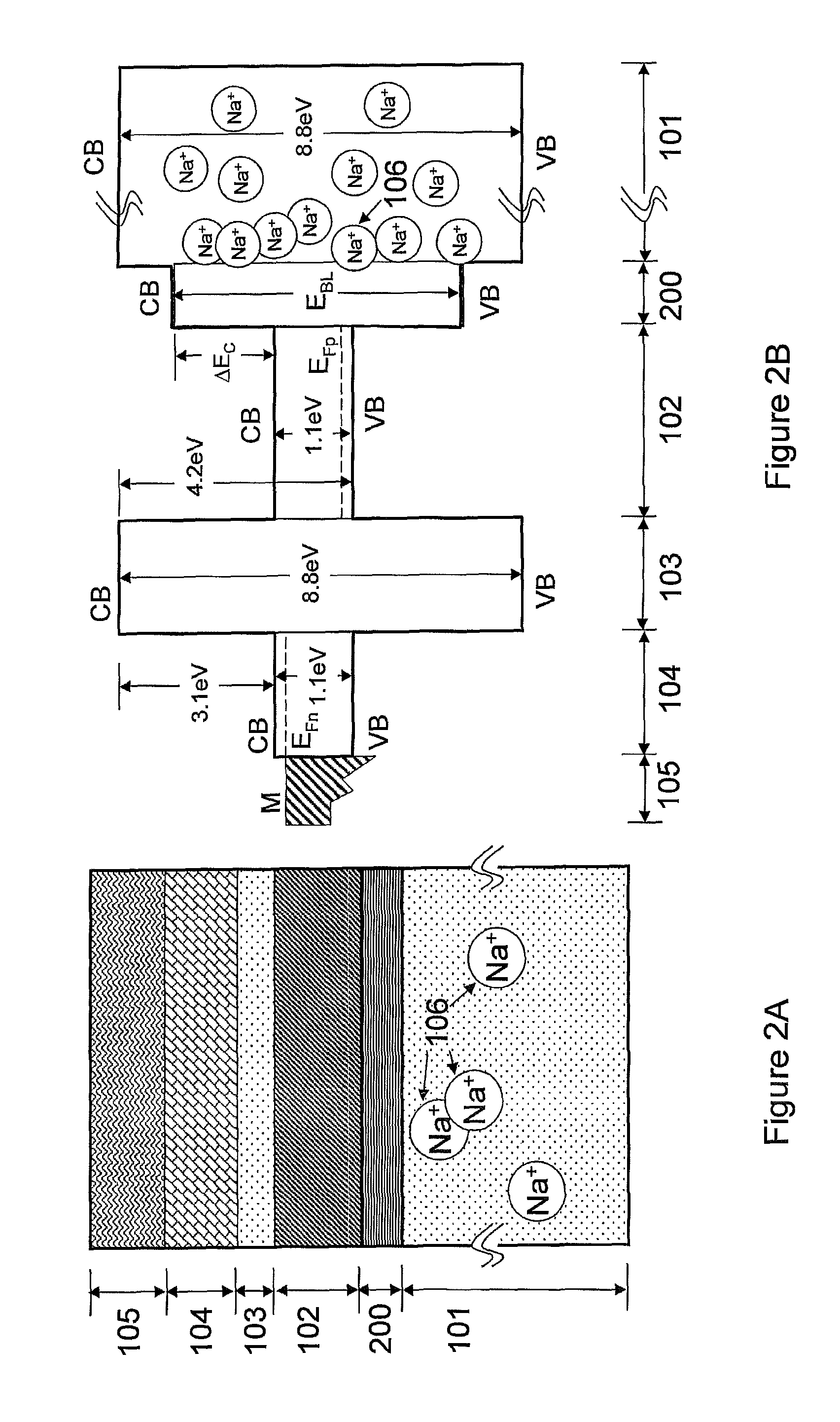
The present invention relates to semiconductor devices suitable for electronic, optoelectronic and energy conversion applications. In a particular form, the present invention relates to the fabrication of a thin film solar cells and thin film transistors through the advantageous combination of semiconductors, insulators, rare-earth based compounds and amorphous and / or ceramic and / or glass substrates. Crystalline or polycrystalline thin film semiconductor-on-glass formation using alkali ion impurity barrier layer(s) are disclosed. Example embodiment of crystalline or polycrystalline thin film semiconductor-on-glass formation using rare-earth based material as impurity barrier layer(s) is disclosed. In particular, thin film silicon-on-glass substrate is disclosed as the alternate embodiment, with impurity barrier designed to inhibit transport of deleterious alkali species from the glass into the semiconductor thin film.
Owner:IQE
Method for fabricating single crystal silicon film
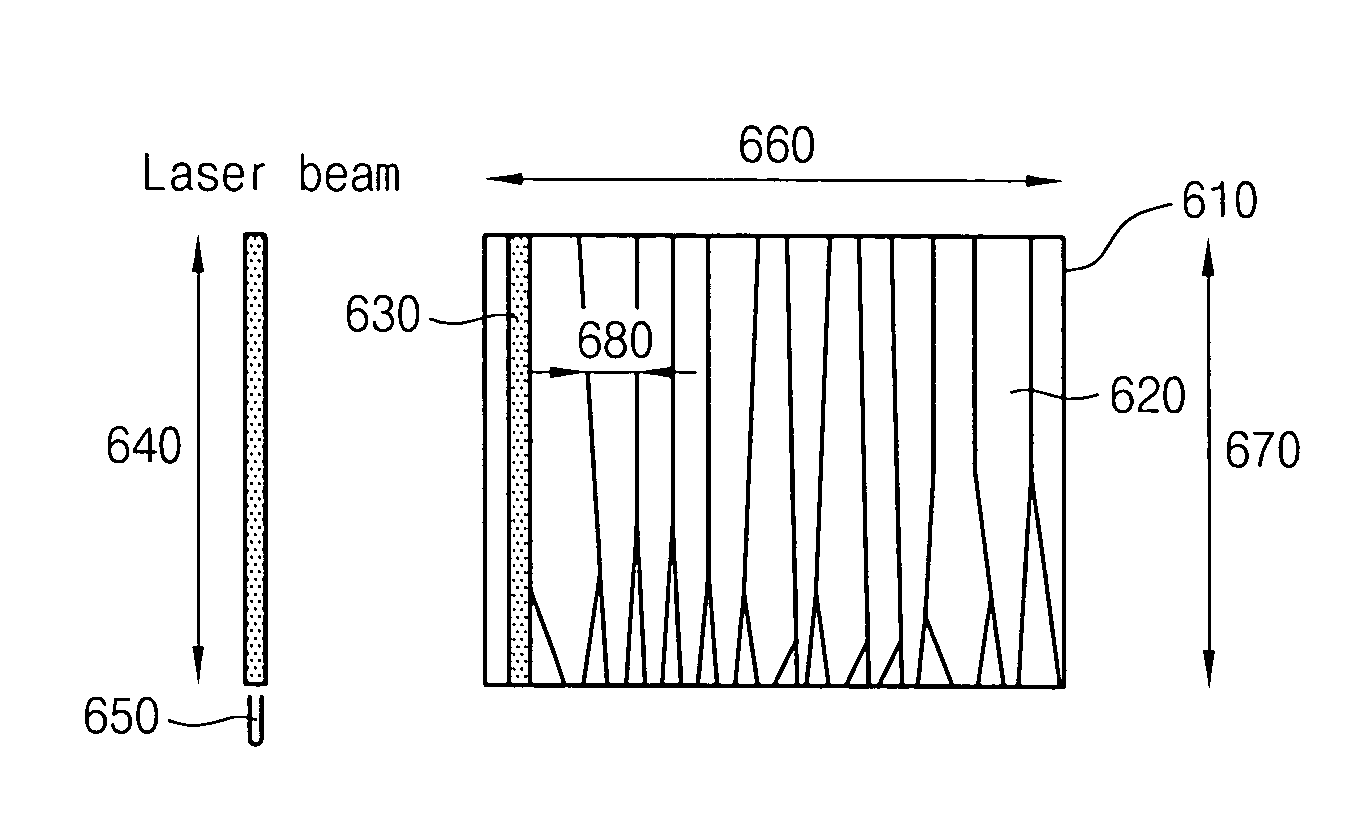
The present invention relates to a method for fabricating a single crystal silicon thin film at the desired location to the desired size from an amorphous or polycrystalline thin film on a substrate using laser irradiation and laser beam movement along the substrate having the semiconductor thin films being irradiated. This method comprises the steps of: forming a semiconductor layer or a metal thin film on a transparent or semi-transparent substrate; forming a single crystal seed region on the substrate of the desired size by a crystallization method using laser irradiation; and converting the desired region of the semiconductor layer or metal thin film into a single crystal region, using the single crystal seed region.
Owner:BOE HYDIS TECH
Rapid energy transfer annealing device and process
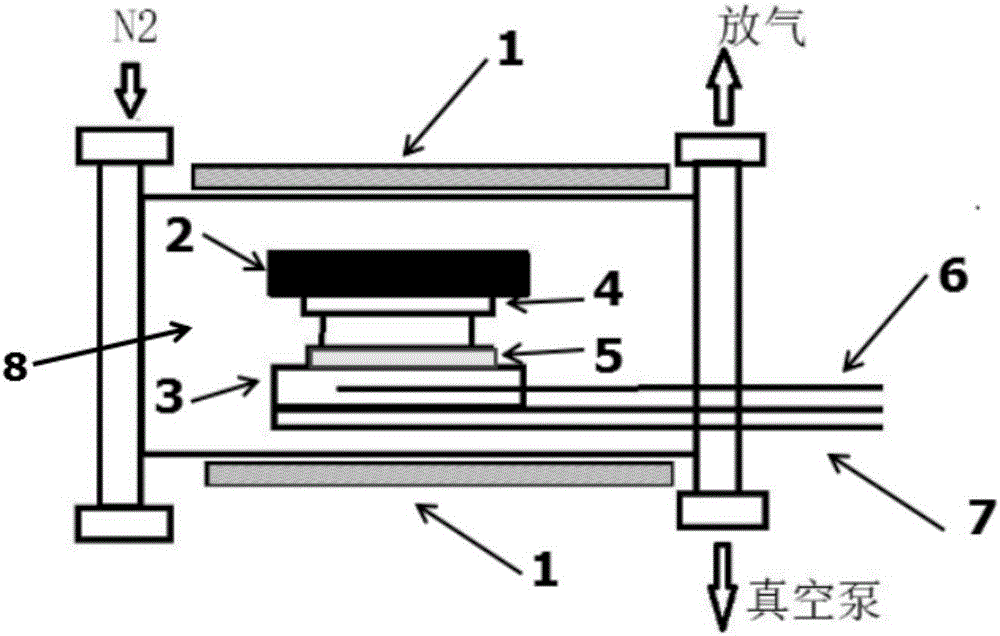
InactiveUS20040147139A1Easy to prepare in large areaQuick layeringFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHeat sinkLight source
Disclosed is a rapid energy transfer annealing (RETA) device and process, where an energy plate is used to rapidly absorb the primary photonic energy of the light source, such as a tungsten halogen lamp (or an xenon Arc lamp), to allow temperature elevation. The energy plate faces an amorphous thin film deposited above a glass or plastic substrate and releases the heat energy transferred by a gas or solid medium to the amorphous thin film,, so as to heat the amorphous thin film for transforming the amorphous thin film into a polycrystalline film. On another side of the glass or plastic substrate may be further provided with a heat sink plate and a supporting plate. The heat sink plate absorbs energy of the glass substrate, protects glass substrate from damages due to overheating. The heat sink plate or the supporting plate may be moved to freely adjust distance between the amorphous thin film and the energy plate and that between the glass substrate and the heat sink plate, so as to control energy transferred to the amorphous thin film and energy released by the glass substrate transfer. The adjustment of distance may be fixed or varied as a function of time so as to randomly adjust the energy transfer. Further, between the glass substrate and the amorphous film may be provided with a heat conducting layer and a heat shielding layer. On another side of the glass substrate may be provided with a heat sink layer. On the amorphous thin film may be provided with a heat absorption layer to control and allow selective crystallization, or to control direction of heat transfer thereby guiding the crystallization to grow in a specific direction.
Owner:JIANG YEU LONG
Tandem solar cell structures and methods of manufacturing same
The present invention relates to thin film solar cell structures and methods of manufacturing them, particularly tandem cell structures and components thereof. In one aspect there is provided a polycrystalline thin film solar cell structure that is semi-transparent and allows a predetermined wavelength range of light to pass therethrough, in which a bottom semi-transparent conductive layer includes at least one of a ruthenium oxide, an osmium oxide and an iridium oxide. In another aspect there is provided a tandem cell structure in which a top cell bottom contact layer includes at least one of a ruthenium oxide, an osmium oxide and an iridium oxide. In a preferred aspect, the tandem cell structure contains a single contact layer between the absorber layer of the top cell and the absorber layer of the bottom cell. In a particular aspect, this single contact layer is a ruthenium oxide layer.
Owner:SOLOPOWER
Bulk-heterojunction perovskite thin film, production method thereof and solar cell
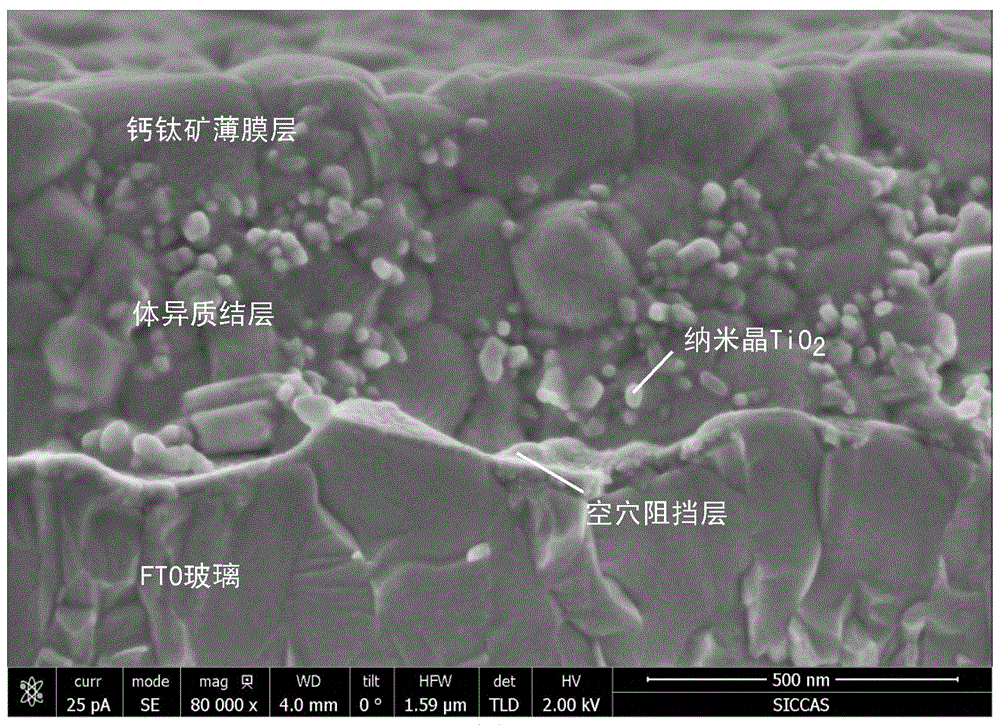
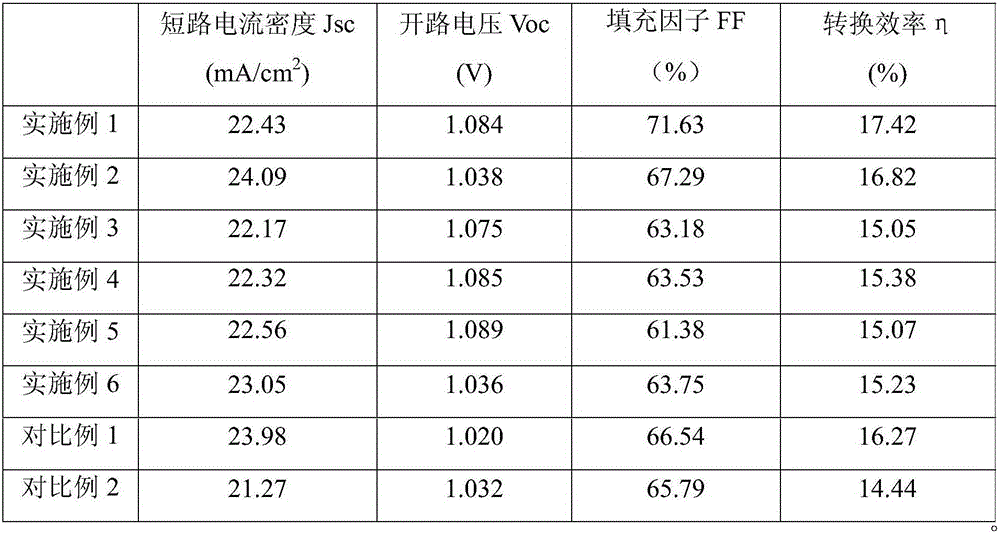
ActiveCN106654020AImprove extraction abilitySimple structureSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHeterojunctionPerovskite solar cell
The invention relates to a bulk-heterojunction perovskite thin film, a production method thereof and a solar cell. The bulk-heterojunction perovskite thin film comprises a bulk-heterojunction layer and a perovskite thin film layer located on the surface of the bulk-heterojunction layer, wherein the bulk-heterojunction layer comprises a perovskite polycrystalline thin film serving as an electron donor material and an electron acceptor material located at the crystal boundary position of the perovskite polycrystalline thin film. The bulk-heterojunction perovskite thin film has the advantages that when the bulk-heterojunction perovskite thin film is applied to the perovskite solar cell, the bulk-heterojunction perovskite thin film can replace an existing mesoporous electron transfer layer and an existing perovskite light absorption layer, and accordingly the structure of the cell can be simplified; the high-temperature sintering process needed by the production of the independent mesoporous layer can be omitted, and the bulk-heterojunction perovskite thin film is suitable for producing the efficient and flexible perovskite solar cell on a plastic substrate.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF CERAMIC CHEM & TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Methods and systems for manufacturing polycrystalline silicon and silicon-germanium solar cells
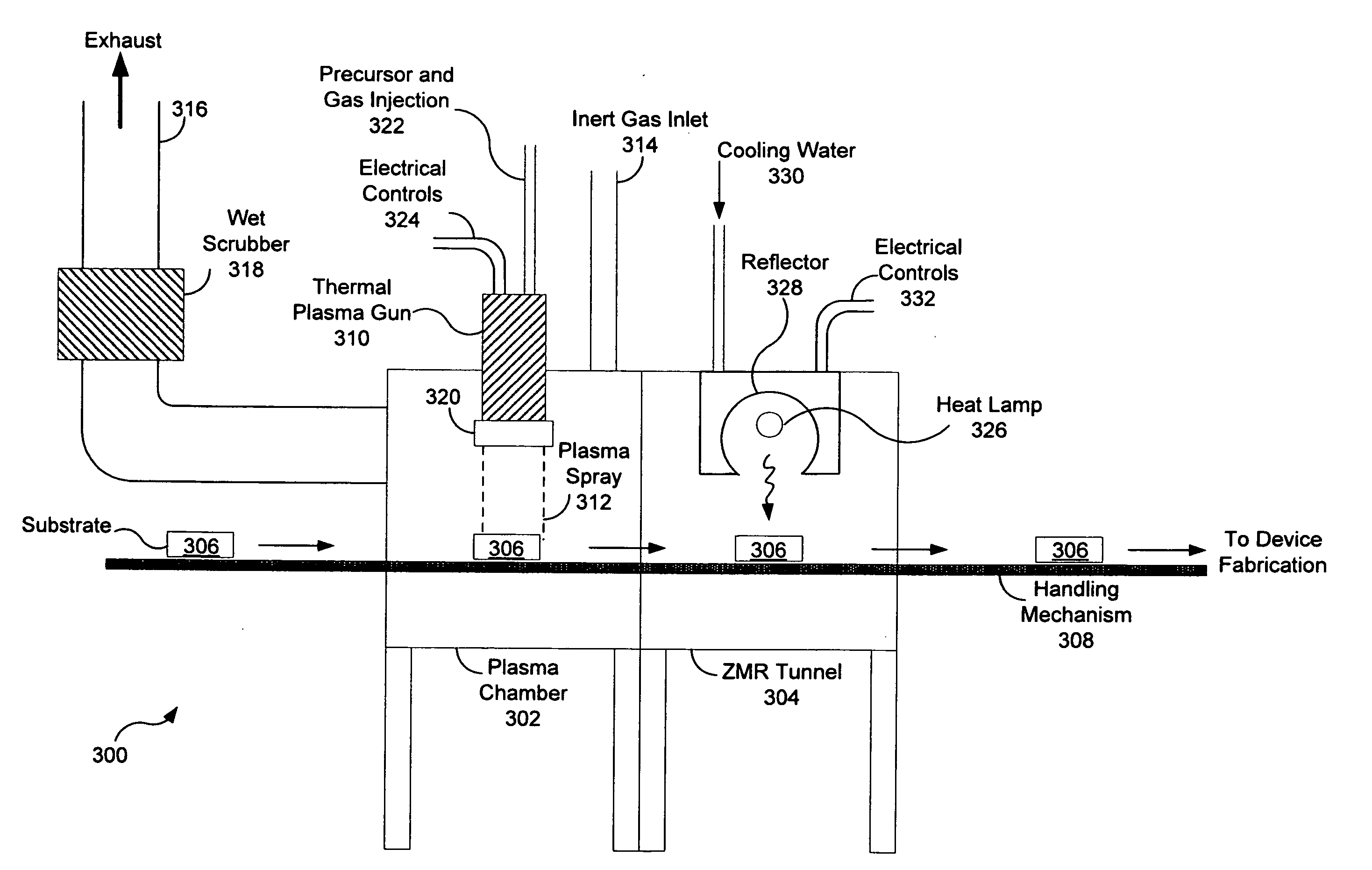
InactiveUS20080023070A1Low costPromoting acceptanceMolten spray coatingFinal product manufactureGas phaseSolar cell
The present invention relates to a novel, unconventional methods and systems for the fabrication of silicon or silicon-germanium photovoltaic cell applications. In some embodiments high purity gaseous and / or liquid intermediate compounds of silicon (or silicon germanium) are converted directly to polycrystalline films by a thermal plasma chemical vapor deposition process or by a thermal plasma spraying technique. The intermediate compounds of silicon (or silicon germanium) are injected into the thermal plasma source where temperatures range from 2000 K to about 20,000 K. The compounds dissociate and silicon (or silicon germanium) is deposited onto substrates. Polycrystalline films having densities approaching the bulk value are obtained on cooling. PN junction photovoltaic cells can be directly prepared by spraying, or doped films after heat treatment are subsequently transformed to viable photovoltaic cells having high efficiency, low cost at a high throughput. In some embodiments a roll-to-roll or a cluster-tool type automated, continuous system is provided.
Owner:SENERGEN DEVICES
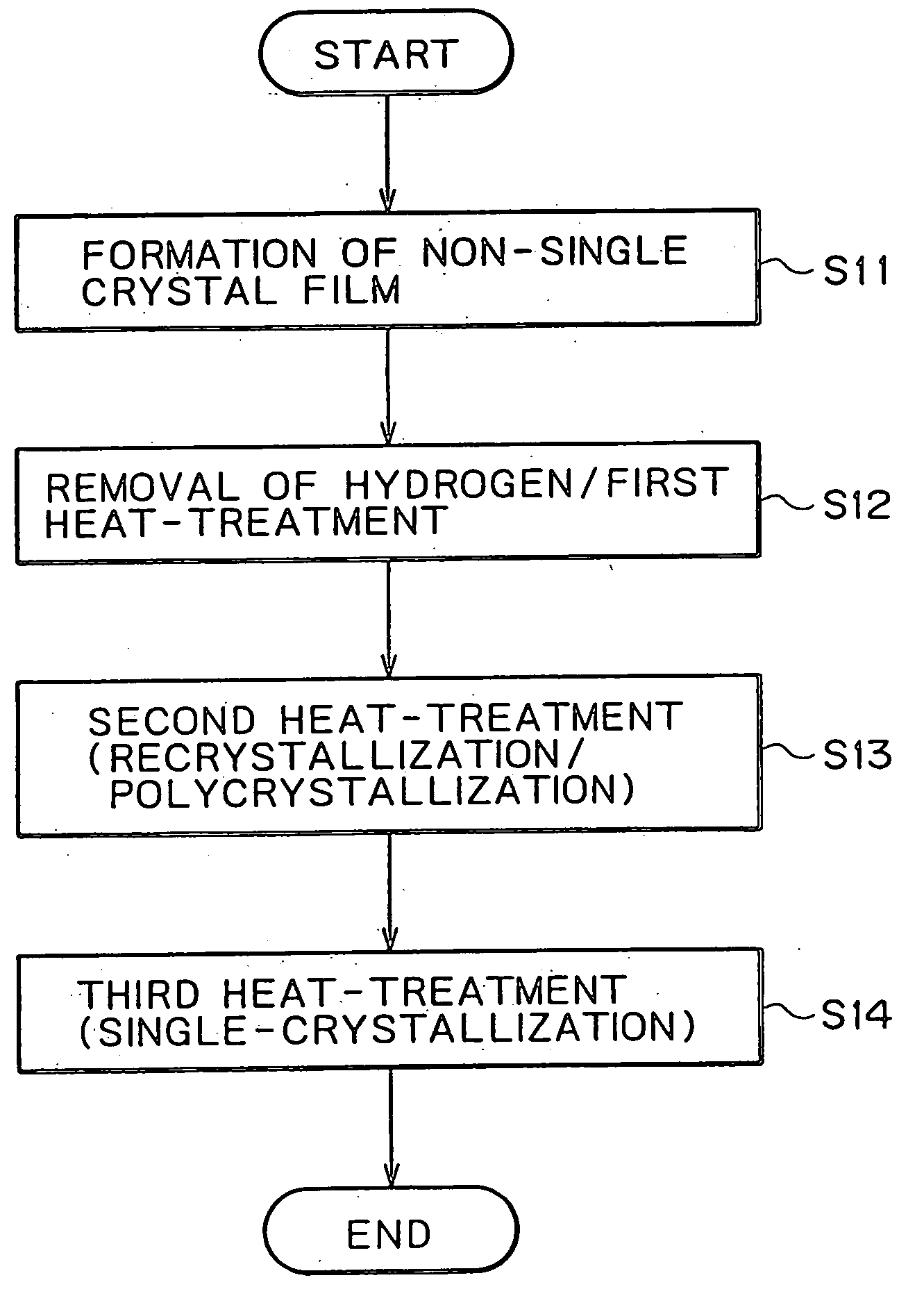
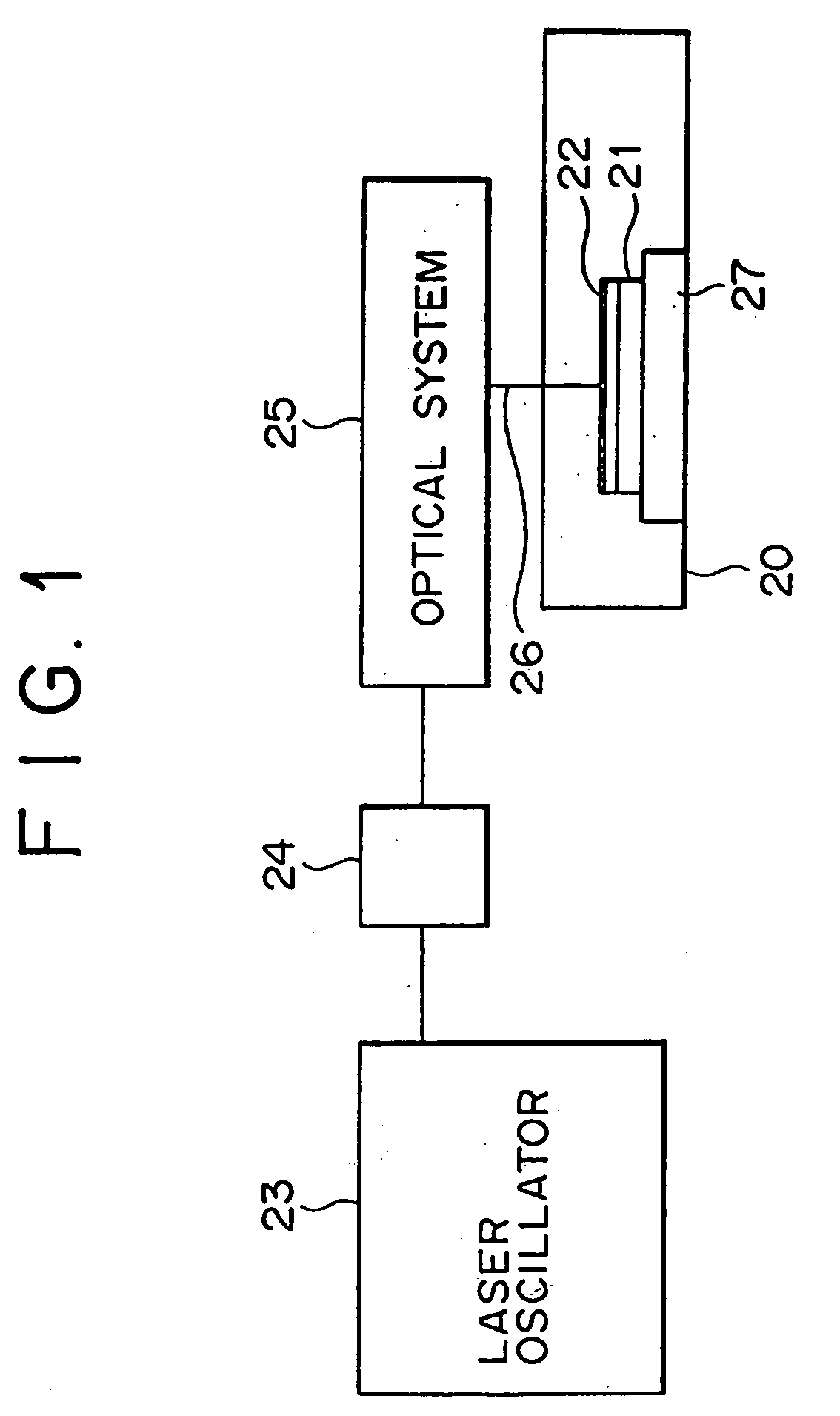
Semiconductor thin film and method of fabricating semiconductor thin film, apparatus for fabricating single crystal semiconductor thin film, and method of fabricating single crystal thin film, single crystal thin film substrate, and semiconductor device
InactiveUS20050104125A1Shorten the timeEliminate needPolycrystalline material growthRadiation pyrometryRegular patternDevice material
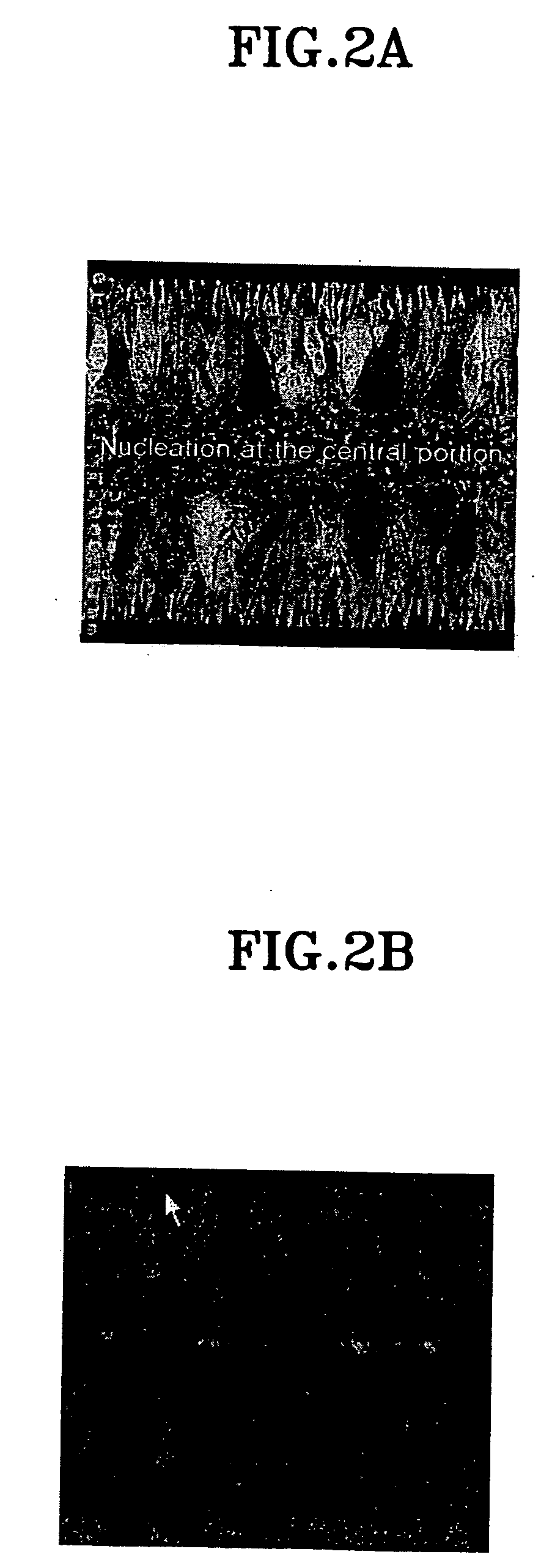
A method of fabricating a single crystal thin film includes forming a non-single crystal thin film on an insulating base; subjecting the non-single crystal thin film to a first heat-treatment, thereby forming a polycrystalline thin film in which polycrystalline grains are aligned in an approximately regular pattern; and subjecting the polycrystalline thin film to a second heat-treatment, thereby forming a single crystal thin film in which the polycrystalline grains are bonded to each other. In this method, either the first heat-treatment or the second heat-treatment may be performed by irradiation of laser beams, preferably, emitted from an excimer laser. A single crystal thin film formed by this fabrication method has a performance higher than a related art polycrystalline thin film and is suitable for fabricating a device having stable characteristics. The single crystal thin film can be fabricated for a short-time by using laser irradiation as the heat-treatments.
Owner:SONY CORP
Method for forming polycrystalline silicon film
InactiveUS20050142708A1Maximize grain sizeMaximize sizeTransistorSolid-state devicesAmorphous siliconOptoelectronics
Disclosed herein is a method for forming a polycrystalline (poly-Si) film by the crystallization of an amorphous silicon film using laser light irradiation. The disclosed method comprises the steps of: sequentially depositing a buffer film and an amorphous silicon film on a glass substrate; depositing a metal film having laser light reflection function on the back side of the glass substrate; and irradiating the front side of the amorphous silicon film with laser light to crystallize the amorphous silicon film. In the laser light irradiation step, the irradiated laser light is absorbed into the amorphous silicon film, and a portion of the absorbed laser light is transmitted through the amorphous silicon film. The transmitted light is reflected from the metal film and absorbed into the amorphous silicon film again, thus crystallizing the amorphous silicon film twice over. According to the present invention, the amorphous silicon film is crystallized twice over so that a polycrystalline film having very large grains can be formed.
Owner:BOE HYDIS TECH
Flexible CdTe thin-film solar cell and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102800719AHigh temperature resistantAcid resistantFinal product manufactureVacuum evaporation coatingPolycrystalline thin filmsThin film solar cell
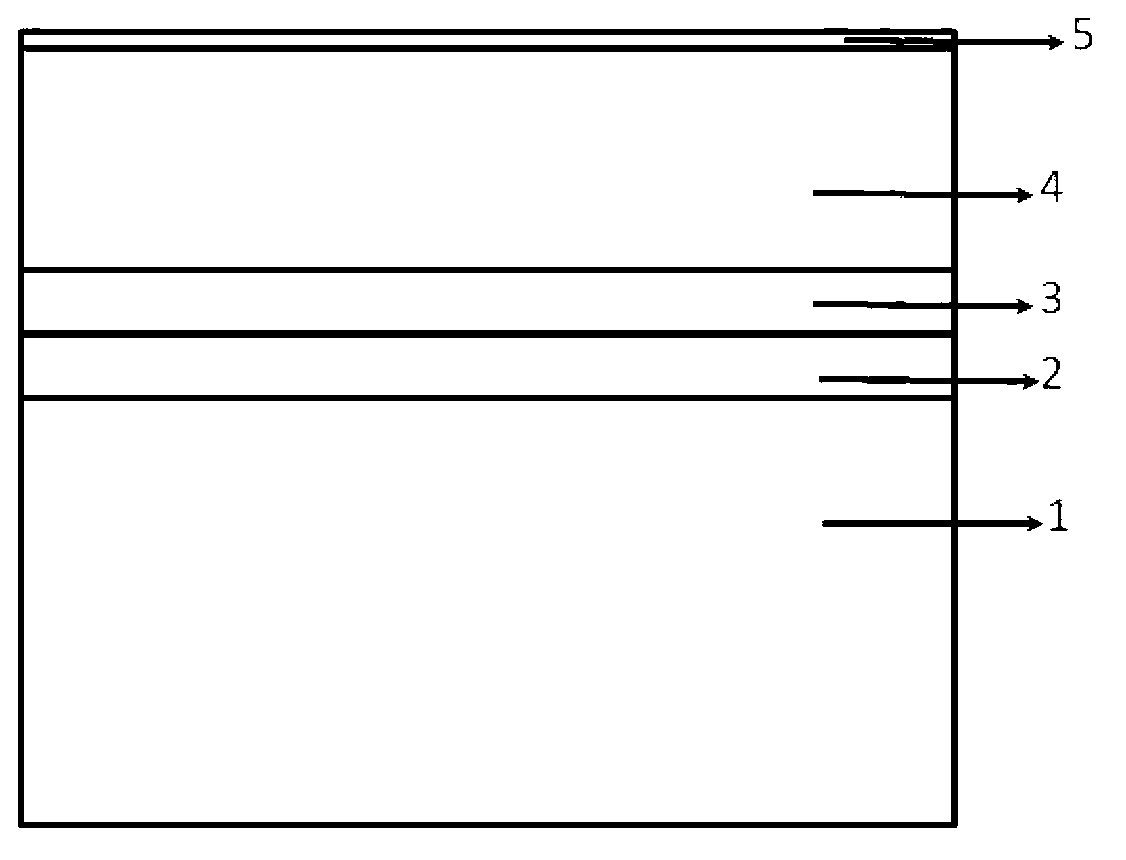
The invention discloses a preparation method of a flexible CdTe thin-film solar cell. The preparation method comprises the following processing steps: 1) cleaning a mica substrate (1); 2) growing a transparent conductive thin film (2) on the mica substrate (1); 3) growing CdS (3) on the transparent conductive thin film (2) of the substrate (1) and then growing a CdTe (4) thin film on the CdS (3); 4) carrying out annealing treatment for the CdS and CdTe thin films prepared in the step (3) in an atmosphere with CdCl2 steam; and 5) vapor depositing a conductive back electrode on the CdTe thin film after the annealing treatment to prepare the flexible CdTe polycrystalline thin-film solar cell.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Laser Device Using an Inorganic Electro-Luminescent Material Doped With a Rare-Earth Element
InactiveUS20090080486A1Excitation process/apparatusSemiconductor lasersRare-earth elementPolycrystalline material
A laser device using an inorganic electro-luminescent material doped with a rare-earth element is provided. A dielectric layer such as SiO2 is arranged on a silicon substrate. A polycrystalline thin film of Er-doped ZnS or ZnSe is arranged on the dielectric layer. An electrode is formed on the dielectric layer. After a waveguide structure is substantially formed, a reflector is formed at both ends of the waveguide structure to form a laser resonator. An active medium is a polycrystalline material of Er-doped ZnS or ZnSe. When an AC voltage is applied between an electrode attached to the substrate and an electrode attached to an uppermost part, the effect of emitting light at 1550 nm and generating population inversion is used.
Owner:KYUNGPOOK NAT UNIV IND ACADEMIC COOP FOUND
Piezoelectric substance and piezoelectric element
ActiveUS7701121B2Piezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesIn planeOptoelectronics
Owner:SUMITOMO CHEM CO LTD
System and method for manufacturing semiconductor thin film solar cell
ActiveCN102024870AExcellent workmanshipAvoid temperatureFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringSolar battery
The invention discloses a system and a method for manufacturing a semiconductor thin film solar cell, which can provide continuous and stable thermalchemical temperature-variable reaction conditions in the process of generating a compound thin film by a thermalchemical reaction. The system and the method are particularly suitable for continuously, stably and controllably manufacturing absorbing layers of copper-indium-gallium-selenium polycrystalline thin film solar cells with high yield.
Owner:FUJIAN OUDESHENG ELECTRO OPTICAL TECH +1
Method for crystallizing amorphous semiconductor thin film by epitaxial growth using non-metal seed and method for fabricating poly-crystalline thin film transistor using the same
InactiveUS7390705B2Function increaseReduce heat treatment requirementsPolycrystalline material growthSolid-state devicesOptoelectronicsSeed crystal
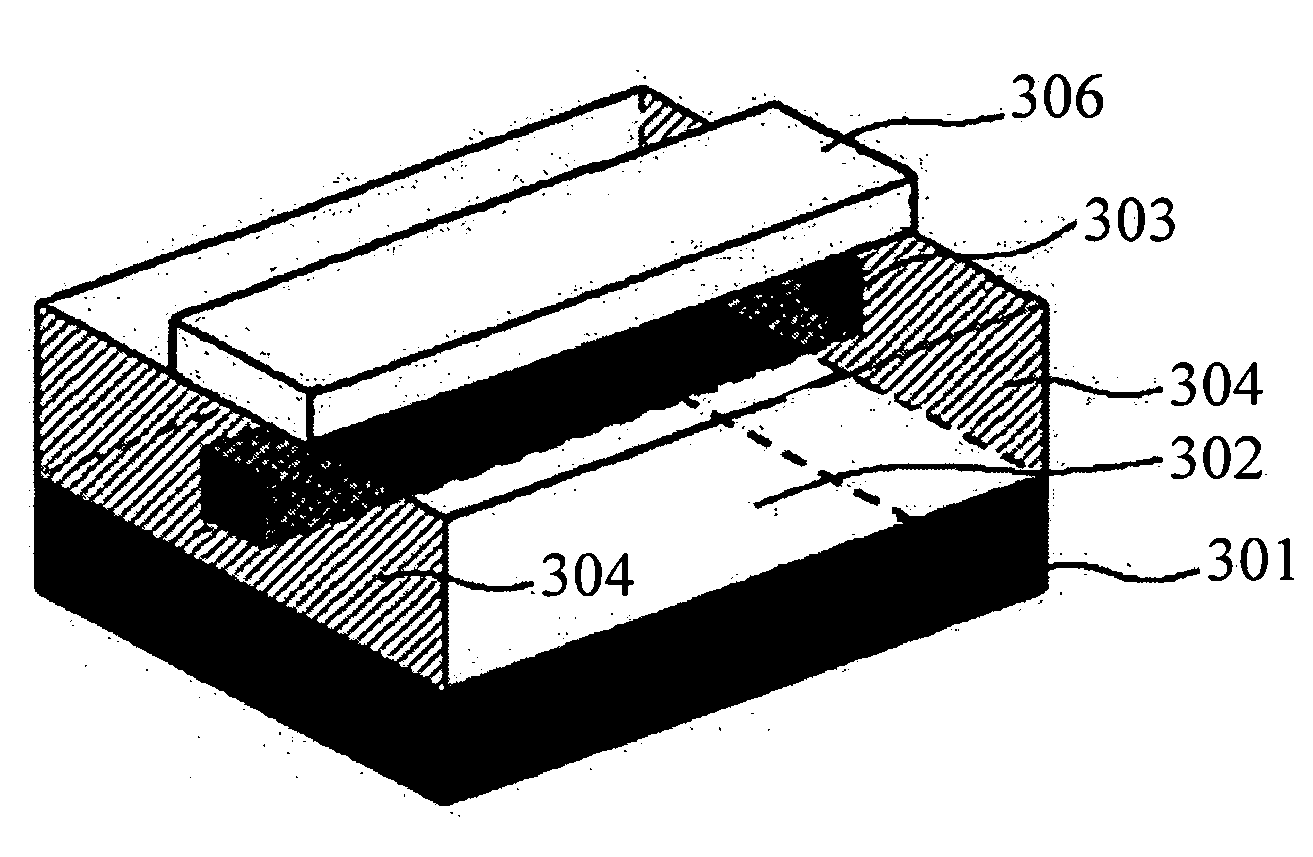
A method for crystallizing an amorphous semiconductor thin film using a non-metal seed epitaxial growth (NSEG) is provided. The method includes the steps of: forming a pair of non-metal seeds for inducing a crystallization of an amorphous semiconductor thin film at a predetermined distance on a transparent insulation substrate; depositing the amorphous semiconductor thin film on the insulation substrate; and heat-treating the insulation substrate to thereby epitaxially grow a poly-crystalline semiconductor thin film from the non-metal seeds, and to thus crystallize the amorphous semiconductor thin film. In the crystallization method, non-metal seeds are used instead of using crystallization induced metal to thereby epitaxially grow the poly-crystalline semiconductor thin film and to thus realize the amorphous semiconductor thin film without having metal pollution.
Owner:PAIK WOON SUH
Piezoelectric substance and piezoelectric element
ActiveUS20080303377A1Piezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesIn planeOptoelectronics
Owner:SUMITOMO CHEM CO LTD
Thin film semi-conductor-on-glass solar cell devices
InactiveUS8071872B2Inhibit transport and deleterious actionLower performance requirementsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotovoltaic energy generationAlkali ionsRare earth
Owner:IQE
Semiconductor film and producing method and equipment, and method for producing single crystal film
InactiveCN1354495AWork at high speedContains changes in critical voltageTransistorPolycrystalline material growthRegular patternSingle crystal
A method of fabricating a single crystal thin film includes forming a non-single crystal thin film on an insulating base; subjecting the non-single crystal thin film to a first heat-treatment, thereby forming a polycrystalline thin film in which polycrystalline grains are aligned in an approximately regular pattern; and subjecting the polycrystalline thin film to a second heat-treatment, thereby forming a single crystal thin film in which the polycrystalline grains are bonded to each other. In this method, either the first heat-treatment or the second heat-treatment may be performed by irradiation of laser beams, preferably, emitted from an excimer laser. A single crystal thin film formed by this fabrication method has a performance higher than a related art polycrystalline thin film and is suitable for fabricating a device having stable characteristics. The single crystal thin film can be fabricated for a short-time by using laser irradiation as the heat-treatments.
Owner:SONY CORP
Lanthanum molybdate based solid electrolyte film material and preparation thereof
InactiveCN101348279AHigh densityGood adhesionMolybdeum compoundsRare earth metal compoundsFilm materialPolymer
The invention discloses a lanthanum molybdate group solid electrolyte thin film material and a preparation method thereof. The material is a solid electrolyte polycrystalline thin film formed by covering a substrate with lanthanum molybdate group with the thickness between 50 nm and 10 mu m, and is formed by lanthanum molybdate group particles with the particle size between 10 and 90 nm. The method comprises the following steps: (a) according to the composition ratio of (La2-xAx)(Mo2-yBy)O9-delta, lanthanum oxide and lanthanum-site dopant oxide, nitrate or acetate, ammonium molybdate and molybdenum-site dopant oxide, nitrate or acetate are weighed and prepared into solution, and lanthanum nitrate solution, lanthanum-site dopant, molybdenum-site dopant solution and citric acid are orderly added to the ammonium molybdate solution under stirring, and then the ammonium molybdate solution is stirred for 2 to 10 hours at a temperature between 60 and 100 DEG C and then is filtered so as to obtain sol; (b) the sol is mixed with water-soluble high molecular polymer to obtain a coating colloid; and (c) the substrate coated with the coating colloid is heated to between 600 and 650 DEG C and has the heat insulated for 10 to 50 hours at a temperature between 550 and 660 DEG C, and then the material can be obtained. The material can be used as a solid electrolyte and an electrode material on a medium-temperature fuel battery or an oxygen sensor.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for forming polycrystalline thin film bipolar transistors
ActiveUS7855119B2Read-only memoriesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGermanideMaterials science
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
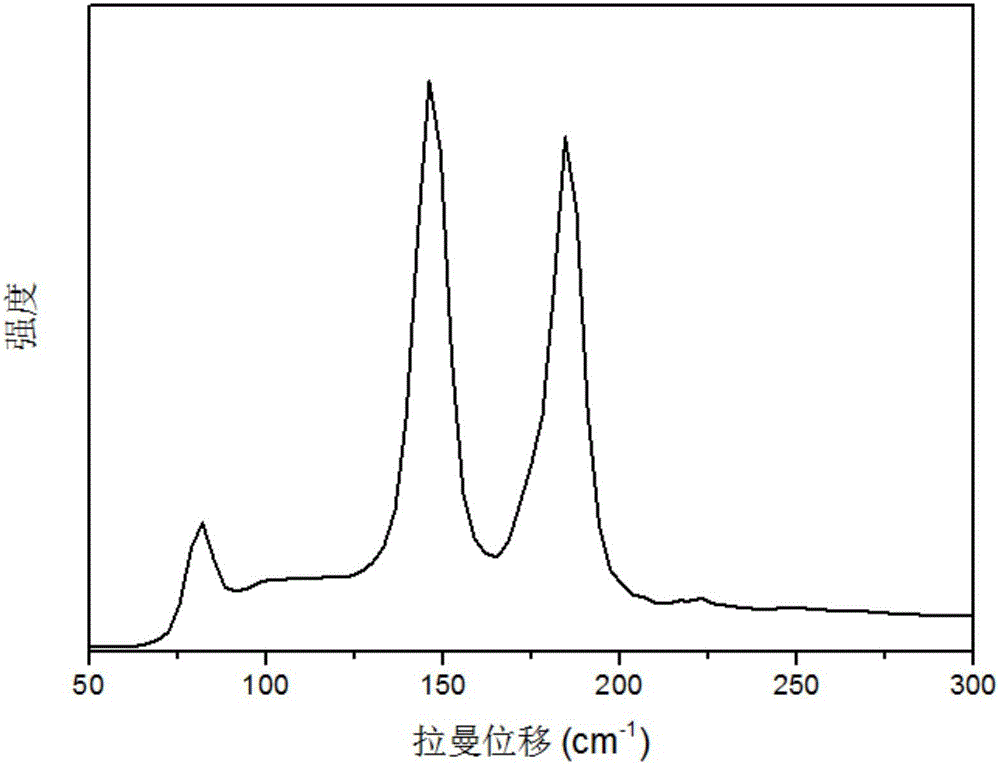
Germanium selenide polycrystal thin film and solar battery comprising thin film, and preparation methods therefor
ActiveCN106783541AFast heating rateQuality improvementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingSolar batteryLight absorption coefficient
The invention discloses a high-quality germanium selenide polycrystal thin film and a preparation method therefor, a solar battery comprising the germanium selenide polycrystal thin film and a preparation method therefor. The germanium selenide polycrystal thin film is 300-500nm in thickness; the preparation method adopts a closed space sublimation method; the preparation method is simple in process, short in reaction period and high in film forming quality; elements included in p type absorption layer material GeSe in the solar battery are all elements with relatively high content in the earth crust, so that the elements are rich in resource, free of toxins and environment friendly; the indirect energy gap is 1.12eV, the absorption edge wavelength is about 1,000nm, response to solar spectrum is in the most ideal solar spectrum band, and the light absorption coefficient is as high as 105cm<-1>; meanwhile, based on the sublimation characteristic of the thin film, the film can be formed rapidly based on the closed space sublimation method; and therefore, the formed compound thin film solar battery has excellent photovoltaic performance, environment protection and is expected to realize low-cost production.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
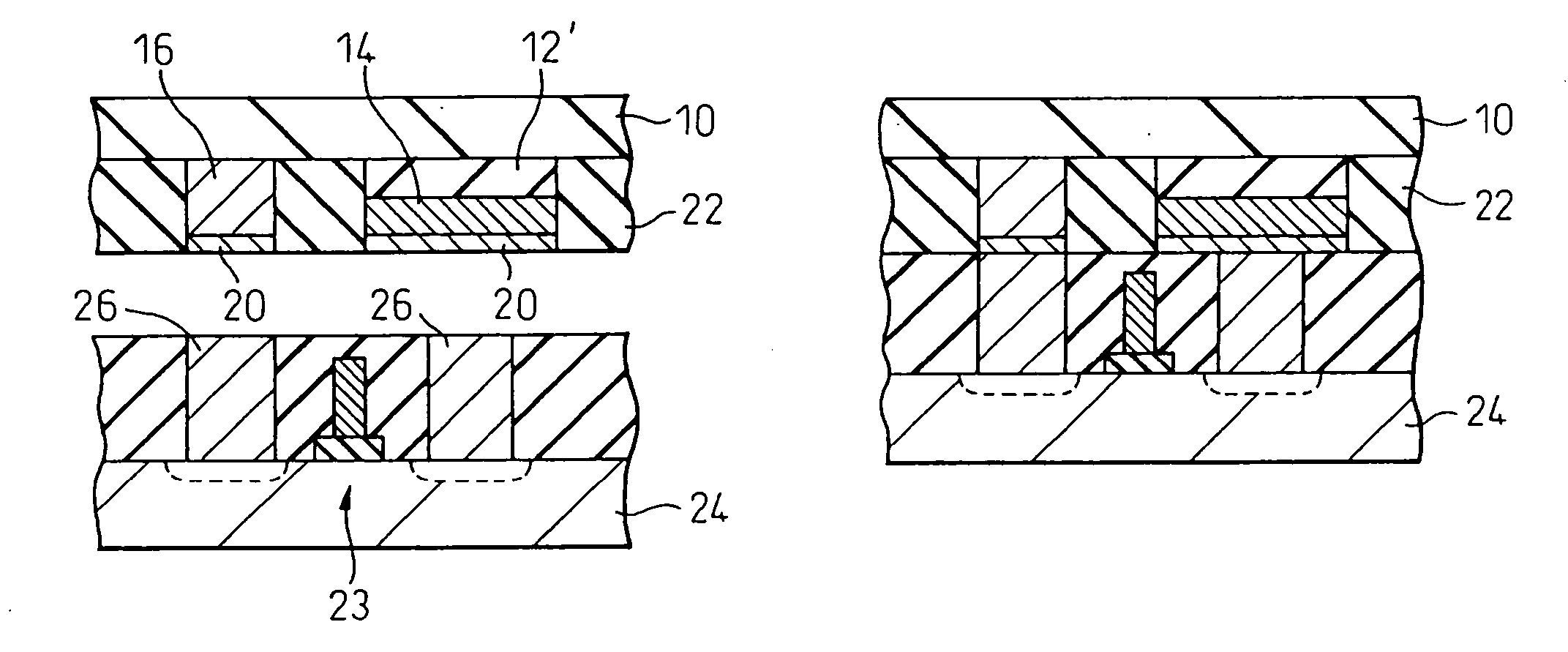
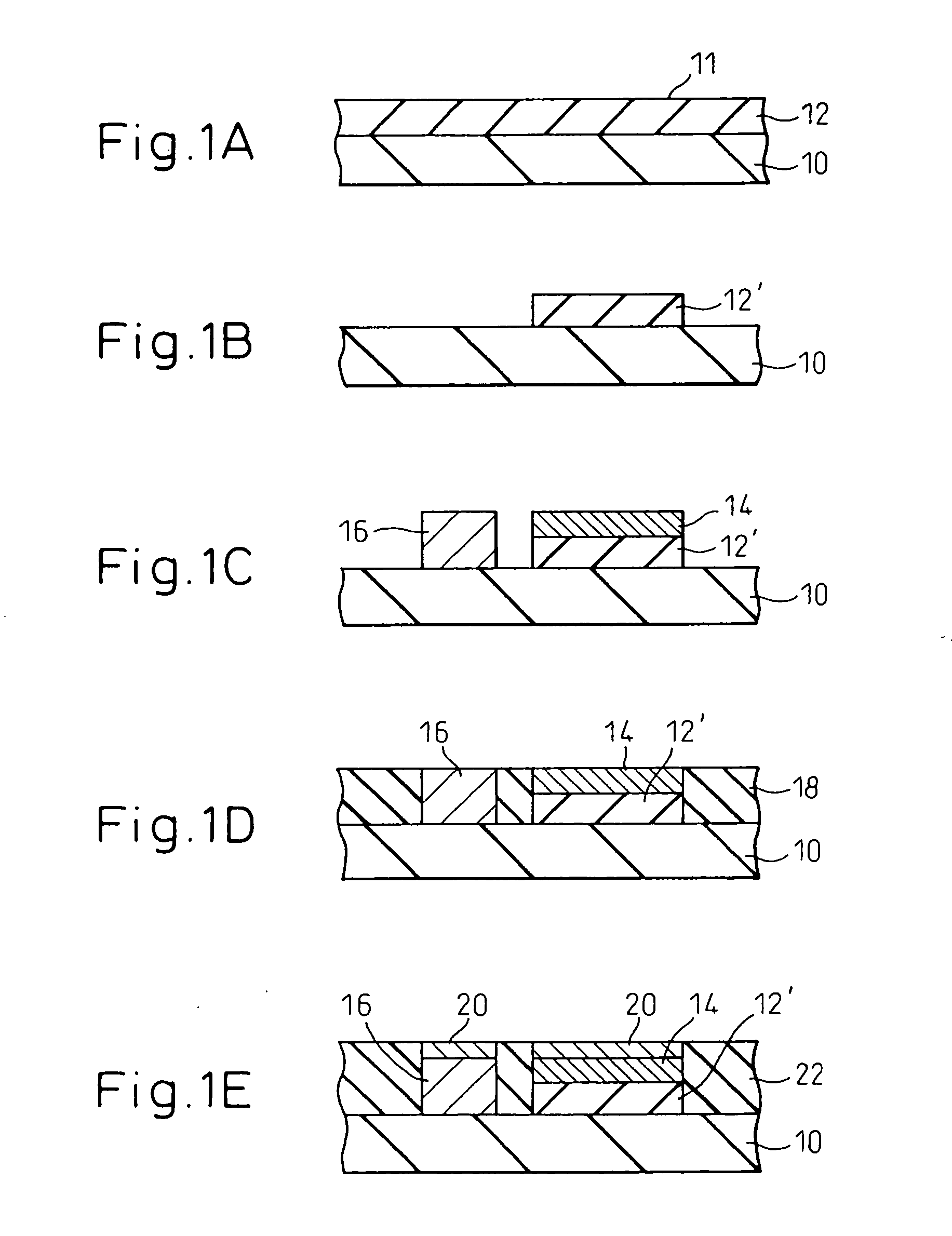
Method of producing semiconductor device
InactiveUS20060166378A1Improve reliabilityInhibition formationSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDevice materialFerroelectric thin films
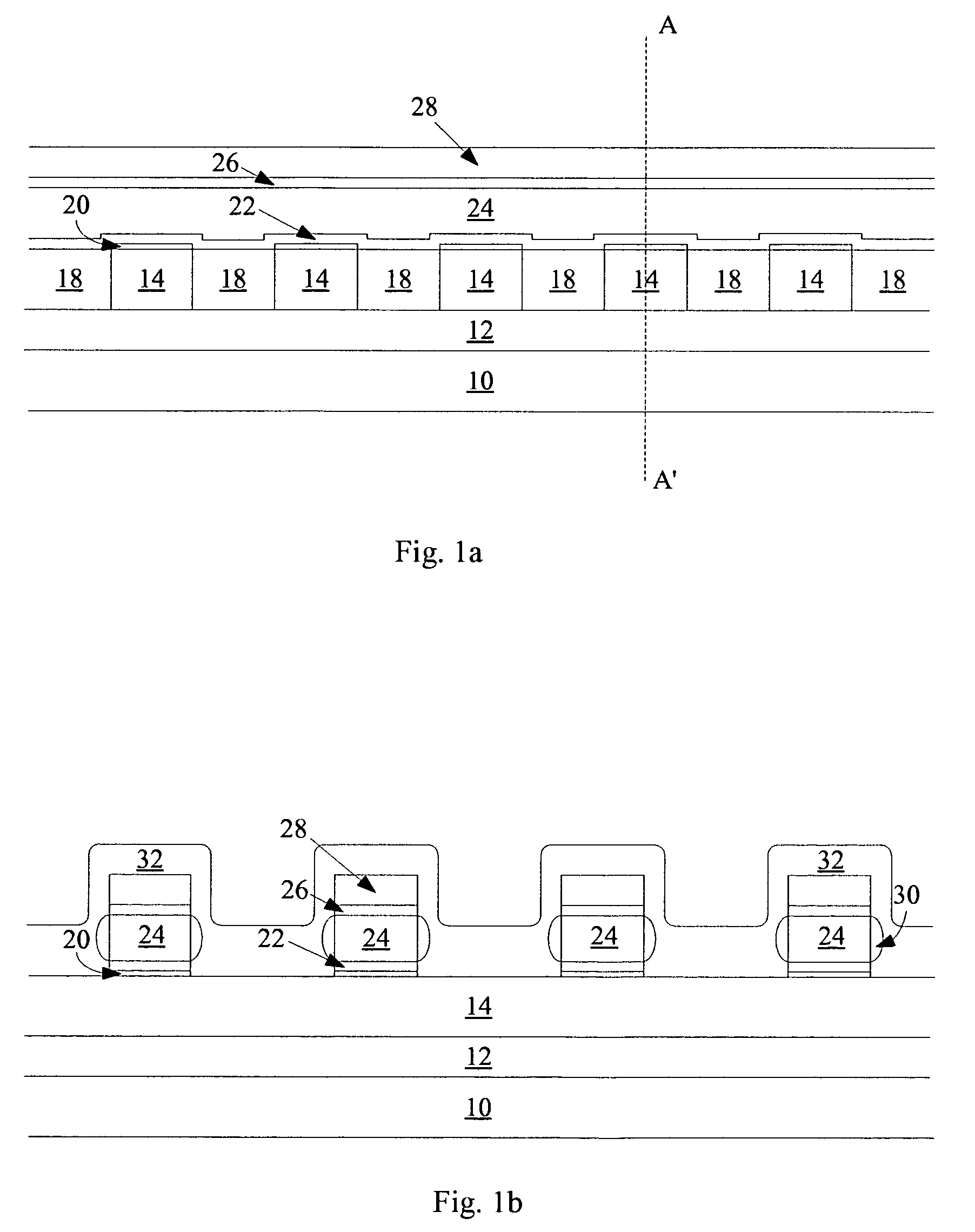
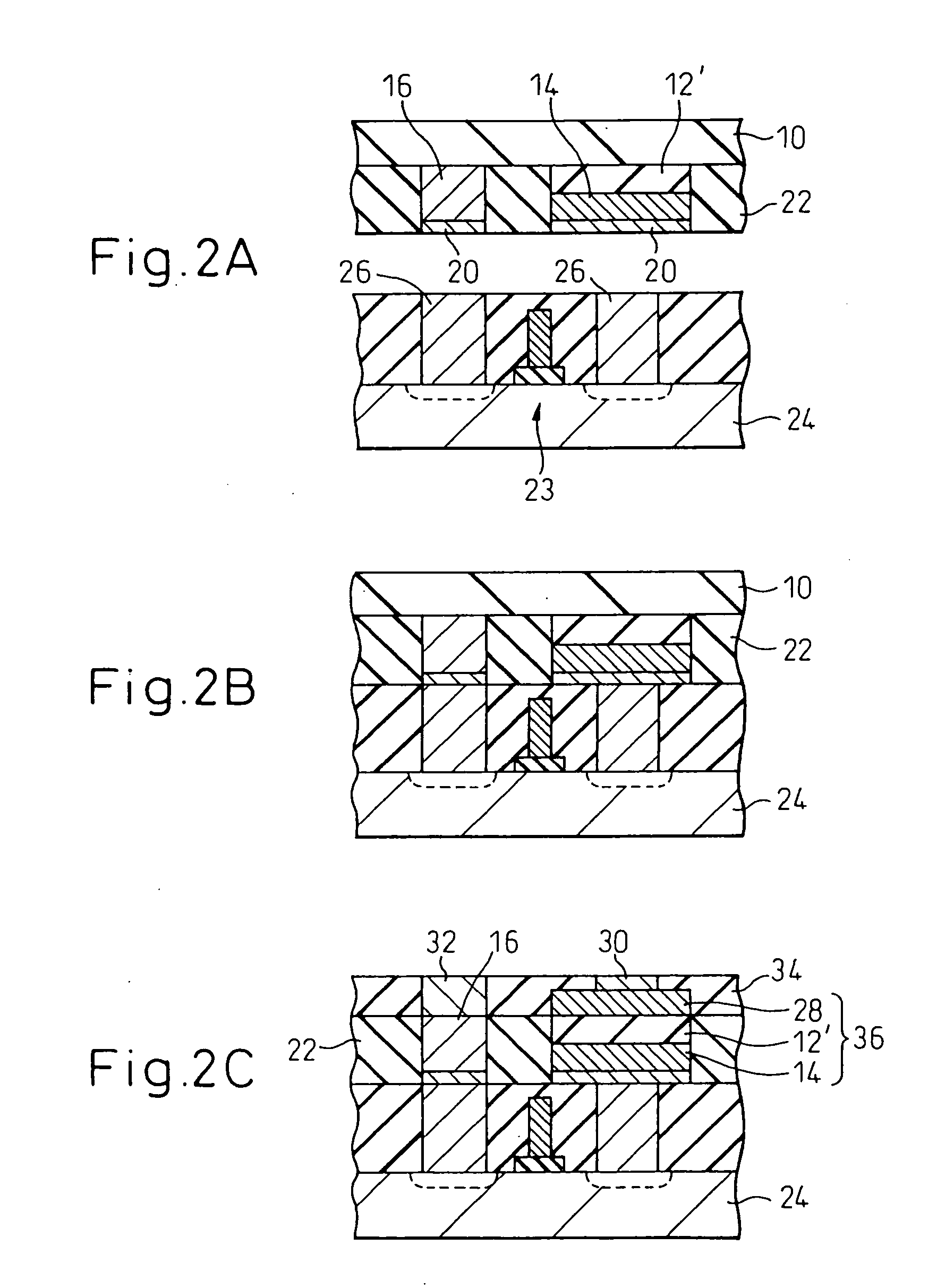
A semiconductor device incorporating a capacitor structure that includes a ferroelectric thin film is obtained by forming, on a single crystalline substrate 10 having a surface suited for growing thereon a thin film layer of ferroelectric single crystal having a plane (111), a ferroelectric single crystalline thin film 12′ containing Pb and having a plane (111) 11 in parallel with the surface of the substrate (or a ferroelectric polycrystalline thin film containing Pb and oriented parallel with the plane (111) in parallel with the surface of the substrate) and part 16 of a circuit of a semiconductor device, to thereby fabricate the single crystalline substrate 10 having said ferroelectric thin film containing Pb and said part of the circuit of the semiconductor device; and bonding said single crystalline substrate 10 to another substrate on which the other circuit of the semiconductor device has been formed in advance, to couple the two circuits together. The capacitor in the semiconductor device thus obtained includes a ferroelectric thin film having a large amount of polarizing charge. The semiconductor device can be used as a highly reliable nonvolatile memory.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Method of fabricating electroluminescent device using coordination metal compounds adducted with electron donor ligands as precursors
InactiveUS20010046558A1Electrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesSurface reactionGas phase
A method of fabricating polycrystalline thin films based on IIA-group, IIIA-group, IVA-group, transition, or inner-transition metal sulfides or selenides by surface reaction and vapor phase reaction by using coordination metal compounds, adducted with neutral ligands and H2Z (Z=S, Se) as precursors. The present invention also discloses a method of fabricating metal oxide polycrystalline thin films based on IIA-group, IIIA-group, IVA-group, transition, or inner-transition metal oxides by surface reaction and vapor phase reaction by using coordination metal compounds, adducted with neutral ligands as one of precursors. Main object of the present invention is to provide a method of fabricating high quality EL device using the above technique.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Thin film transistors and semiconductor constructions
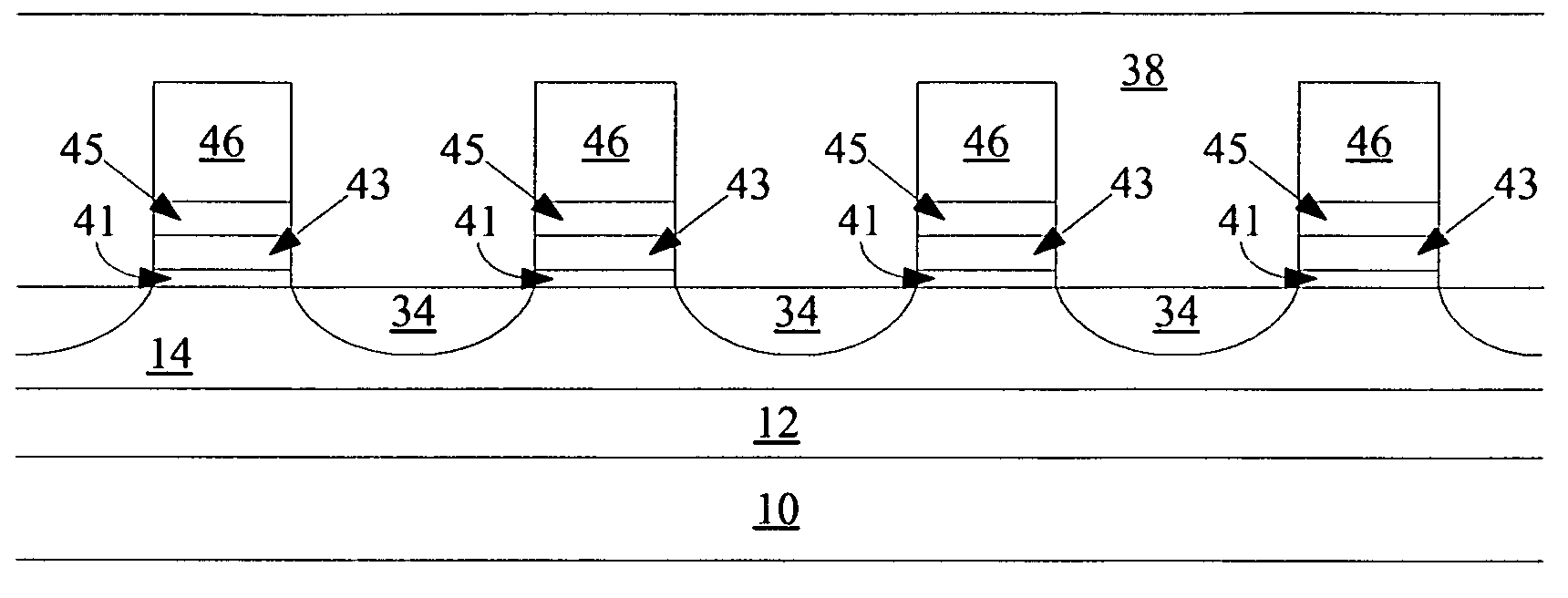
A method of forming a thin film transistor relative to a substrate includes, a) providing a thin film transistor layer of polycrystalline material on a substrate, the polycrystalline material comprising grain boundaries; b) providing a fluorine containing layer adjacent the polycrystalline thin film layer; c) annealing the fluorine containing layer at a temperature and for a time period which in combination are effective to drive fluorine from the fluorine containing layer into the polycrystalline thin film layer and incorporate fluorine within the grain boundaries to passivate said grain boundaries; and d) providing a transistor gate operatively adjacent the thin film transistor layer. The thin film transistor can be fabricated to be bottom gated or top gated. A buffering layer can be provided intermediate the thin film transistor layer and the fluorine containing layer, with the buffering layer being transmissive of fluorine from the fluorine containing layer during the annealing. Preferably, the annealing temperature is both sufficiently high to drive fluorine from the fluorine containing layer into the polycrystalline thin film layer and incorporate fluorine within the grain boundaries to passivate said grain boundaries, but sufficiently low to prevent chemical reaction of the fluorine containing layer with the polycrystalline thin film layer.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Light emitting devices with a zinc oxide thin film structure
InactiveUS20080164466A1Increase probabilityPromote grain growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingTenebresent compositionsDeep levelLight-emitting diode
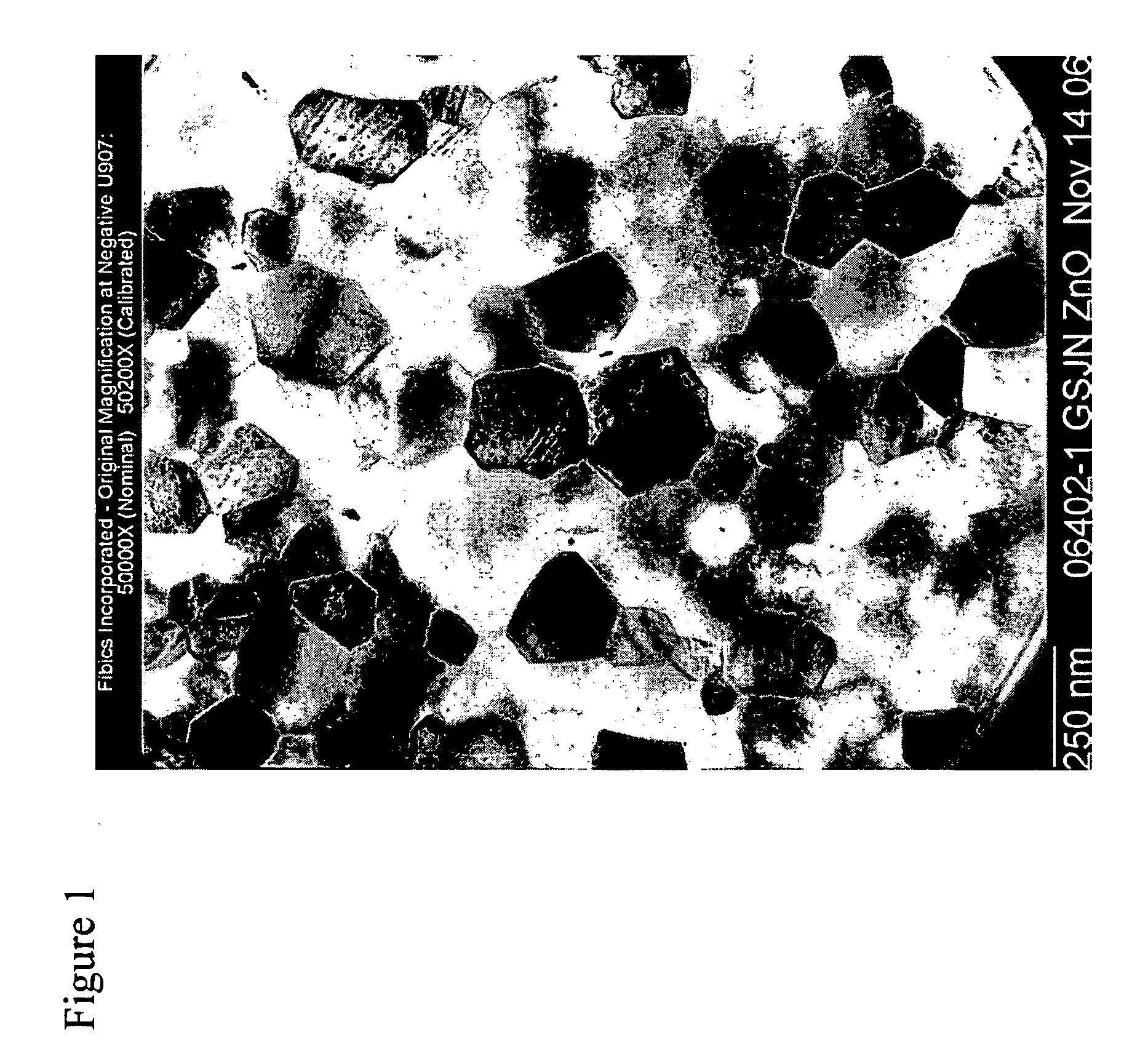
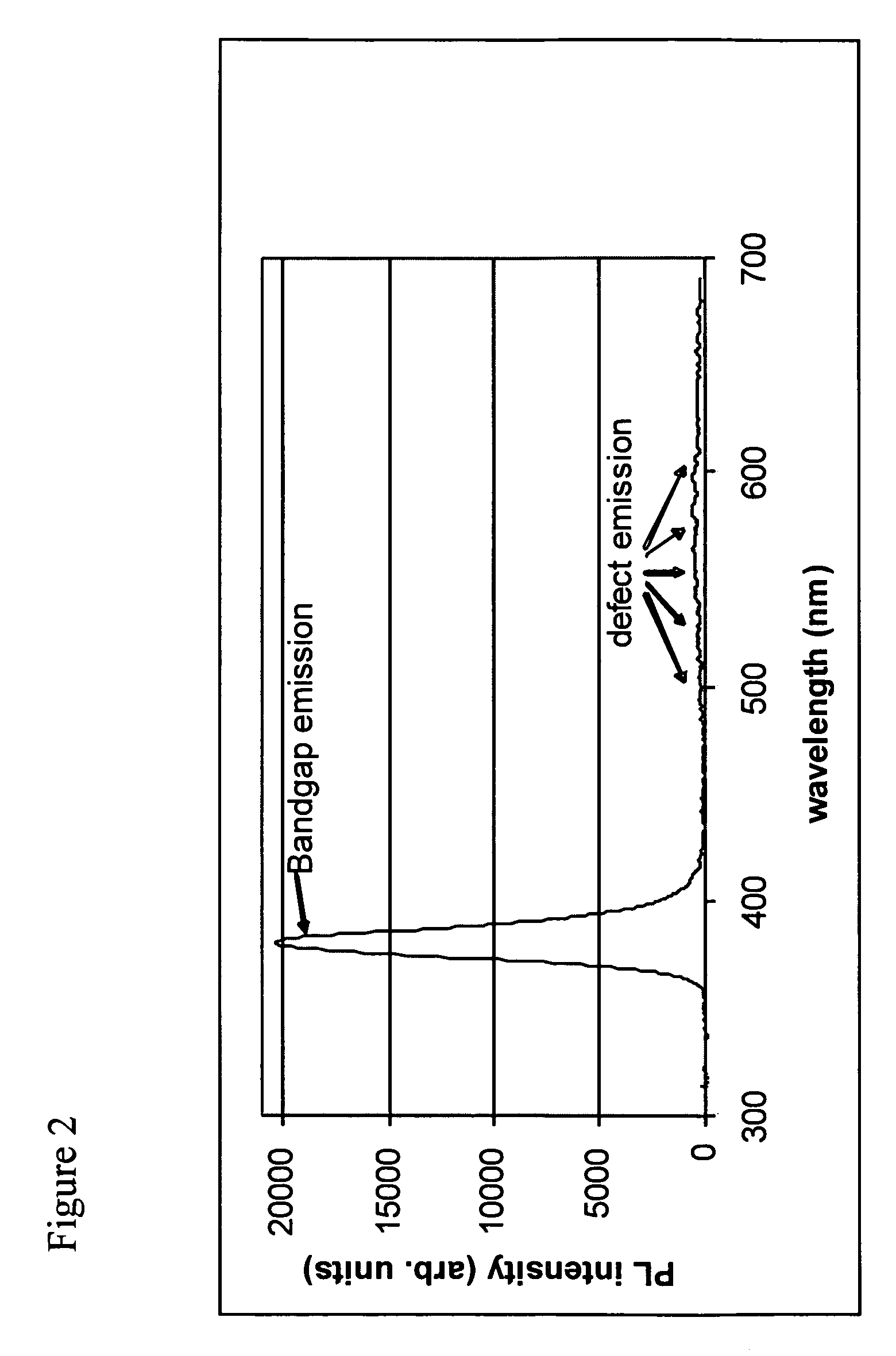
The present invention relates to a sol-gel deposition / heat treatment process, which consistently produces polycrystalline direct bandgap semiconductor, e.g. ZnO, thin films exhibiting a photo luminescent (PL) spectrum at room temperature that is dominated by a single peak, e.g. in the ultraviolet part of the spectrum, in which the PL intensity of the bandgap emission is more than approximately 40 times greater than any deep-level defect emission peak or band. The present invention incorporates such direct bandgap semiconductor, e.g. ZnO, polycrystalline thin films produced by the method of the present invention into electro-luminescent devices that exhibit similarly high ratios of bandgap / deep-level defect emission intensity.
Owner:GROUP IV SEMICON
Fabricating method of polycrystalline silicon thin film, polycrystalline silicon thin film fabricated using the same
InactiveUS20100270558A1Reduce processing timeHigh crystallinityTransistorSolid-state devicesMetal alloyAmorphous silicon
Provided are a method of fabricating a polycrystalline silicon thin film using high temperature heat generated by Joule heating induced by application of an electrical field to a conductive layer, which can ensure process stability at high temperature and thus processing time can be reduced and a polycrystalline silicon thin film having excellent crystallinity can be obtained, a polycrystalline thin film using the method and a thin film transistor including the polycrystalline thin film. The method includes providing a substrate, forming a metal or metal alloy layer having a melting point of 13000 C or more on the substrate, forming an insulating layer on the metal or metal alloy layer, forming an amorphous silicon (a-Si) thin film, an amorphous / polycrystalline composite silicon thin film, or a poly-Si thin film on the insulating layer, and applying an electrical filed to the metal or metal alloy layer to induce Joule heating and generate high temperature heat, and crystallizing and annealing the amorphous silicon (a-Si) thin film, the amorphous / polycrystalline composite silicon thin film, or the poly-Si thin film using the high temperature heat.
Owner:ENSIL TECH CO LTD
Method of Manufacturing a Semiconductor Device
ActiveUS20180240809A1Reduced stateImprove equipment reliabilitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGate dielectricSemiconductor
A method of manufacturing a semiconductor device, comprising the steps of: forming a gate dielectric layer and a first amorphous channel layer on a substrate; thinning the first amorphous channel layer; etching the first amorphous channel layer and the gate dielectric layer until the substrate is exposed; forming a second amorphous channel layer on the first amorphous channel layer and the substrate; annealing such that the first amorphous channel layer and the second amorphous channel layer are converted into a polycrystalline channel layer; and thinning the polycrystalline channel layer. According to the method of manufacturing semiconductor device of the present invention, the grain size of the polycrystalline thin film is increased by depositing a thick amorphous film and then annealing and thinning it. An additional protective layer is used to avoid etching damage on the sidewalls, effectively reducing the interface state and damage defects of the polycrystalline channel layer, thereby enhancing the reliability of the device.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
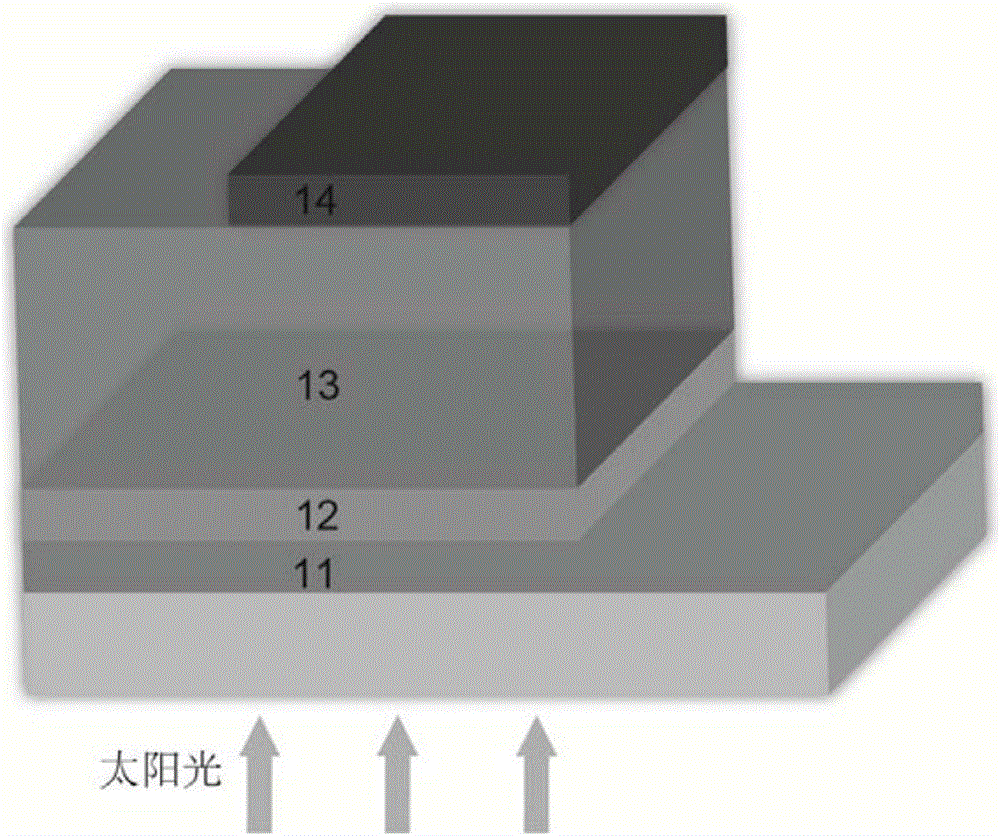
Flexible-substrate iron silicide (beta-FeSi2) thin-film solar battery and preparation method thereof
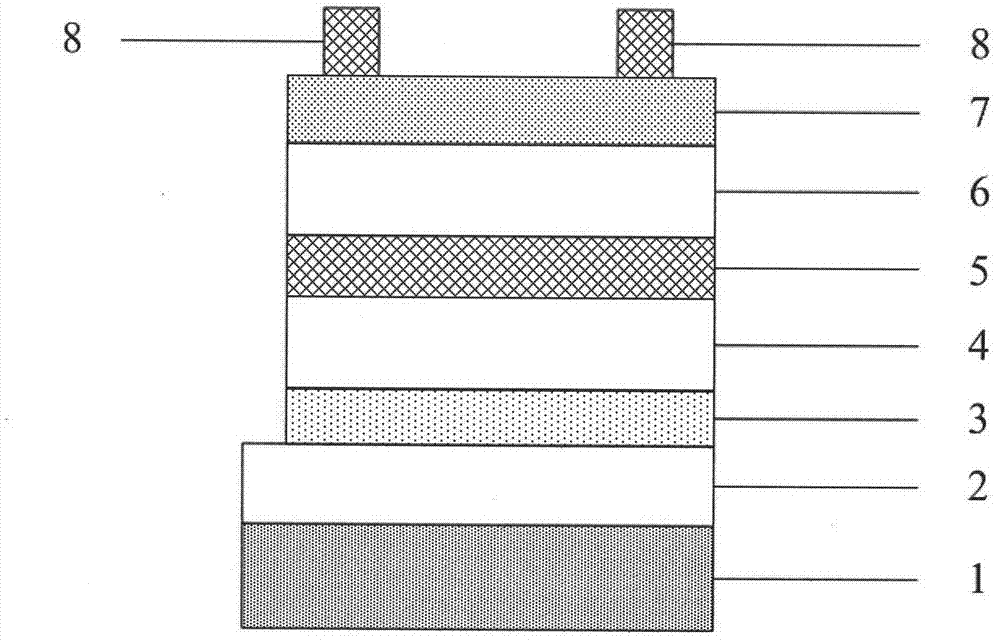
InactiveCN102760776AImprove adhesionQuality improvementFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor materialsElectrical battery
The invention discloses a flexible-substrate iron silicide (beta-FeSi2) thin-film solar battery and a preparation method thereof, and relates to a structural design of a polycrystalline beta-FeSi2 thin-film solar battery device and a preparation method of a thin-film semiconductor material. The flexible-substrate iron silicide (beta-FeSi2) thin-film solar battery is characterized in that a flexible metal foil is used as a substrate material (1), a bottom electrode is metal molybdenum (Mo) film (2), an n-p node is formed by an N-type polycrystalline thin film beta-FeSi2 (4), a weak N-type polycrystalline thin film beta-FeSi2 (5) and a P-type polycrystalline thin film beta-FeSi2 (6); and a transparent conducting layer is made of aluminium zinc oxide (ZnO: Al) (7). The flexible-substrate iron silicide (beta-FeSi2) thin-film solar battery is characterized in that pn nodes of the solar battery are made of betal-FeSi2 polycrystalline thin film material. The preparation method comprises the step of preparing the bottom electrode (2), a transition layer (3), the N-type thin film layer (4), the weak N-type thin film layer (5) and the P-type thin film layer (6), the transparent conducting layer (7) and an upper electrode metal film (8). The flexible-substrate iron silicide (beta-FeSi2) thin-film solar battery and the preparation method of the flexible-substrate iron silicide (beta-FeSi2) thin-film solar battery have the advantages that the materials of all layers of the battery can be obtained by adopting magnetron sputtering deposition under the vacuum environment, the structure is simple, the weight is light, the bendability is achieved, the cost performance is high, the cost of the raw materials of the battery is low, the preparation method is simple and pollution-free, large-area and large-scale production of battery products is easily carried out by adopting a roll-to-roll continuous mode, and the application field of the battery is wide.
Owner:江苏天孚太阳能有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com