Antifungal agent and preparation and use method
An antifungal and preparation technology, which is applied in the field of treating patients with fungal or bacterial infections and manufacturing the pharmaceutical preparation, can solve the problems of dissolution rate and bioavailability reduction, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0029] Home-prepared cores usually follow the following preparation procedure:
[0030] (a) Mix polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) with isopropanol and distilled water until
[0031] PVP is completely dissolved;
[0032] (b) Put the sucrose granules into a fluid bed granulator equipped with a spray insert (e.g.:
[0033] Glatt or Huttlin);
[0034] (c) mixing together starch and talc;
[0035] (d) Spray (a) onto sucrose granules while mixing (c) with the sprayed sucrose granules
[0036] to form a wet core; and
[0037] (e) drying the wet core to form the core of the composition. (B) Drug emulsification layer:
[0038] The drug emulsification layer contains azole antimicrobial drug, emulsifier, binder and absorption aid. Typically the azole antimicrobial is first dissolved in an organic solvent. Examples of organic solvents include, but are not limited to, dichloromethane, ethanol, and isopropanol. A preferred organic solvent is to use a combination of dichloromethan...
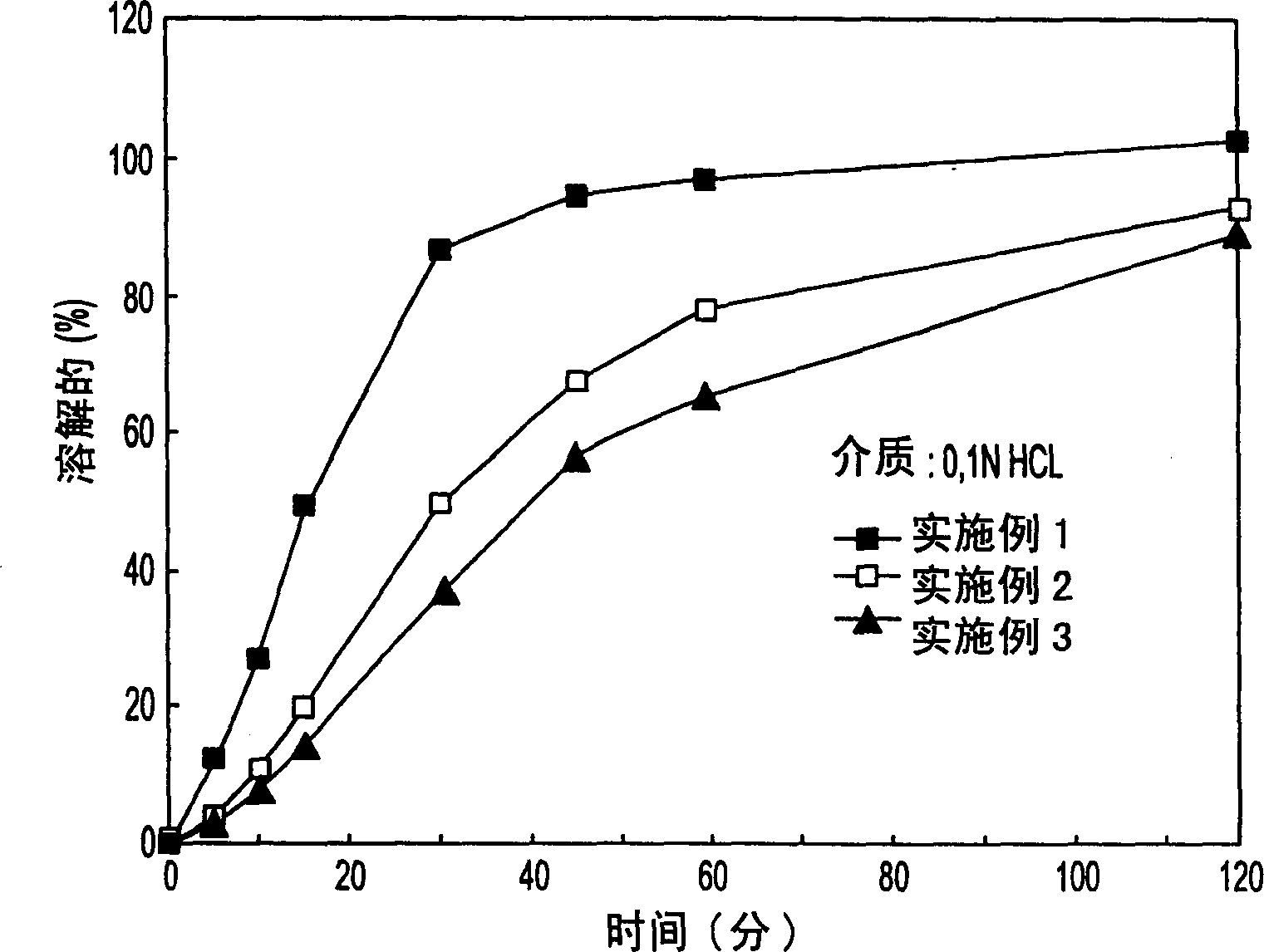
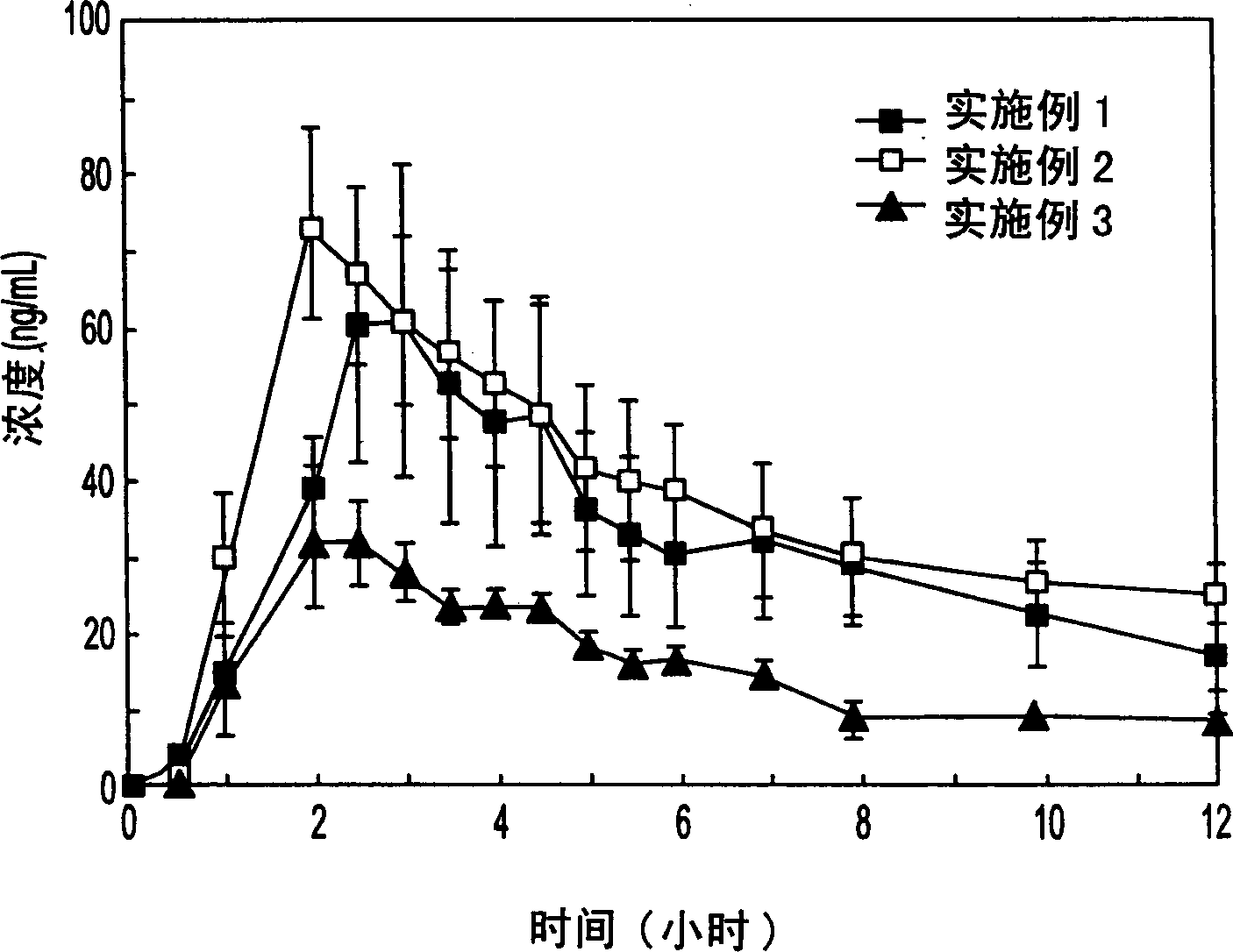
Embodiment 1
[0054] Embodiment 1 (A) prepares core material and method:
[0055] Element
quantity
Polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP K-30)
40g
Isopropanol
300ml
200ml
sucrose
400g
800g
900g
[0056] The core was prepared by a three-step method. The first step involved dissolving 40 g of PVP K-30 in 300 ml of isopropanol with stirring and subsequently mixing it with 200 ml of purified water to form an emulsion. The second step involves mixing together 800g of starch and 900g of talc. The final step involves placing the sucrose in a fluid bed granulator (e.g. Glatt or Huttlin) and spraying the PVP K-30 emulsion produced in the first step onto the sucrose while adding the starch-talc mixture to the sucrose to form the core of the description. The core is further dried in warm air. (B) Materials and methods for preparing the drug emulsification layer:
[0057]...
Embodiment 2
[0063] Element
[0064] In the pharmaceutical composition of Example 2, the weight ratio between the core and itraconazole is about 1:0.59. The weight percentages of the core, itraconazole, vitamin E polyethylene glycol succinate, DL-malic acid and HPMC are 40.4%, 23.7%, 0.01%, 0.01%, and 35.9%, respectively. It should be noted that two solvents, dichloromethane and ethanol, were used to help dissolve itraconazole. The volume ratio of dichloromethane and ethanol used to dissolve itraconazole was about 1:1.07. In addition, the protective layer contained 11.5% by weight of polyethylene glycol 20,000, also dissolved in methylene chloride and ethanol. The volume ratio of dichloromethane and ethanol is about 1:1.05.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com