Compounds with large magnetic entropy changes and their preparation
A compound, magnetic entropy change technology, applied in magnetic objects, magnetic materials, electrical components and other directions, can solve the problems of restricting magnetic refrigeration, insoluble, insufficient magnetic entropy change, etc., achieving simple manufacturing process, adjustable Curie temperature, The effect of increasing magnetic entropy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] Raw materials such as nickel, manganese, gallium, etc. are classified into chemical components Ni 51.5 mn 22.7 Ga 25.8 Proportion (electron concentration is 7.513), put into vacuum electric arc furnace, induction furnace or other smelting furnace, vacuumize to 10 -1 or above, pass in argon gas, and obtain a compound with uniform composition after repeated melting and cooling. The compound obtained by smelting was homogenized at 900°C for 72 hours, and then annealed at 700°C for 60 hours. In order to prevent sample oxidation, the homogenization treatment and annealing process can be carried out under vacuum or argon protection. The sample was proved by X-ray diffraction to be a non-modulated square structure, belonging to the martensitic phase. SQUID was used to measure the magnetization curve as a function of temperature. The compound obtained through the above steps has a Curie temperature of -77°C. The calculation results show that the magnetic entropy becomes 4...
Embodiment 2
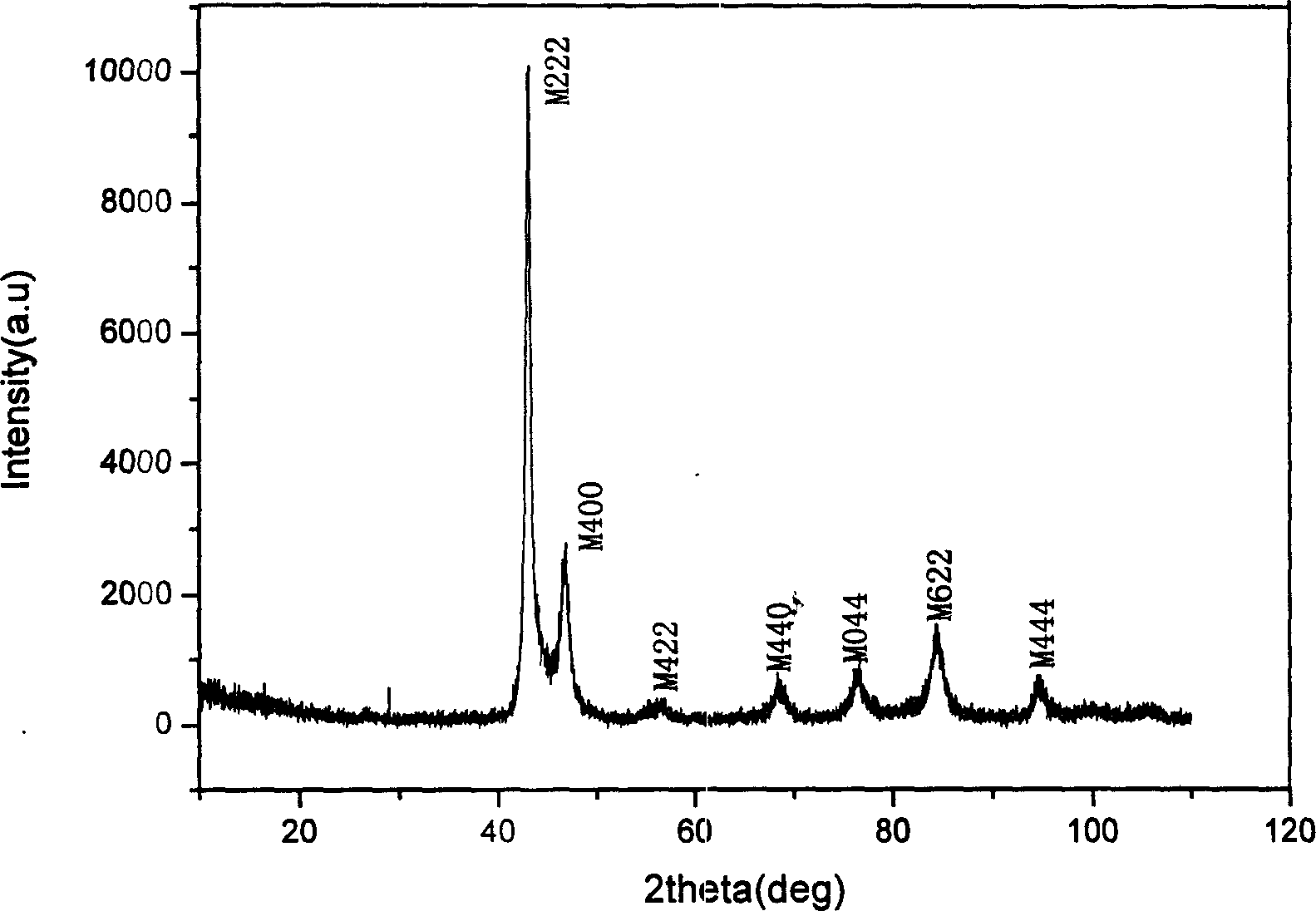
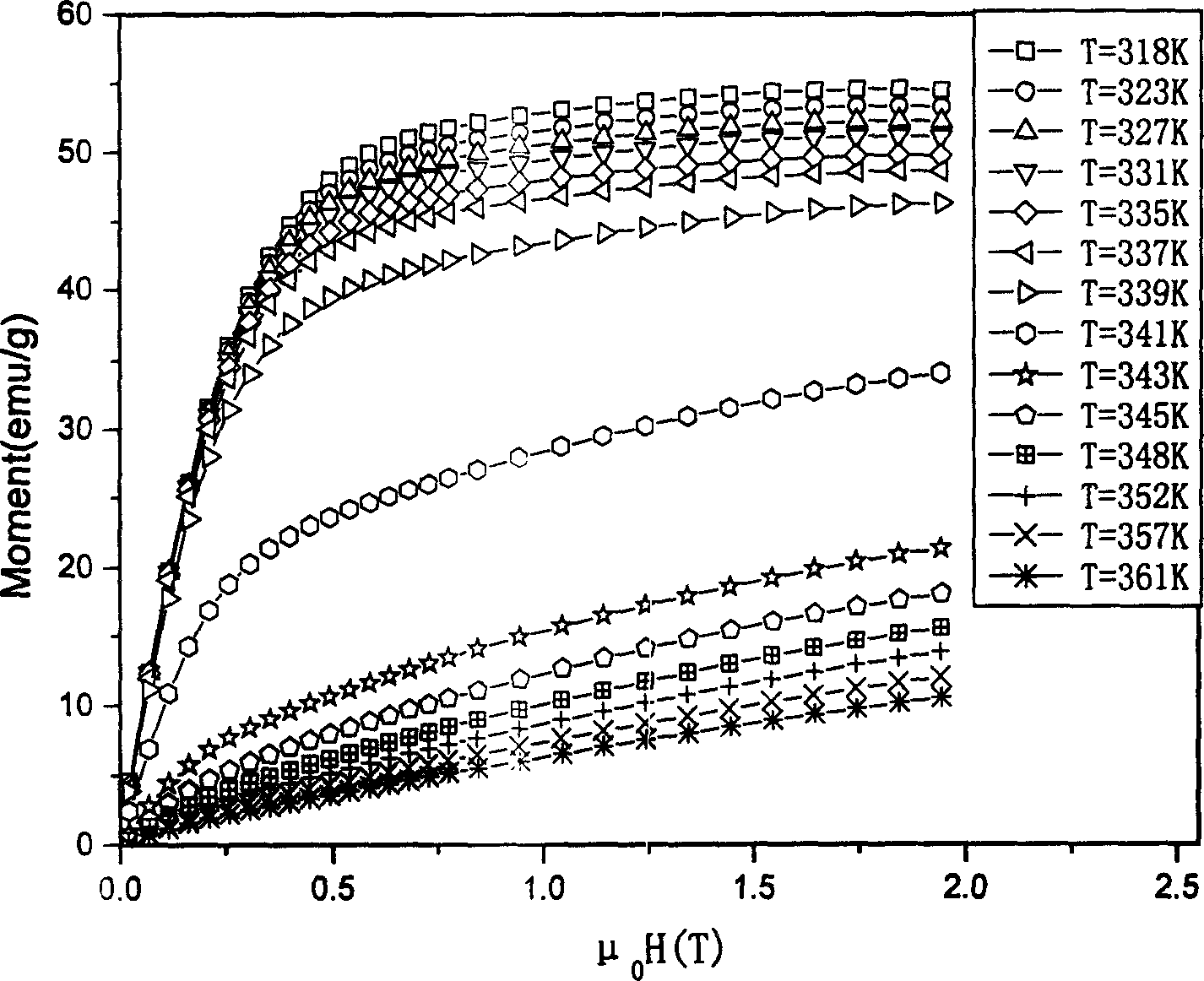
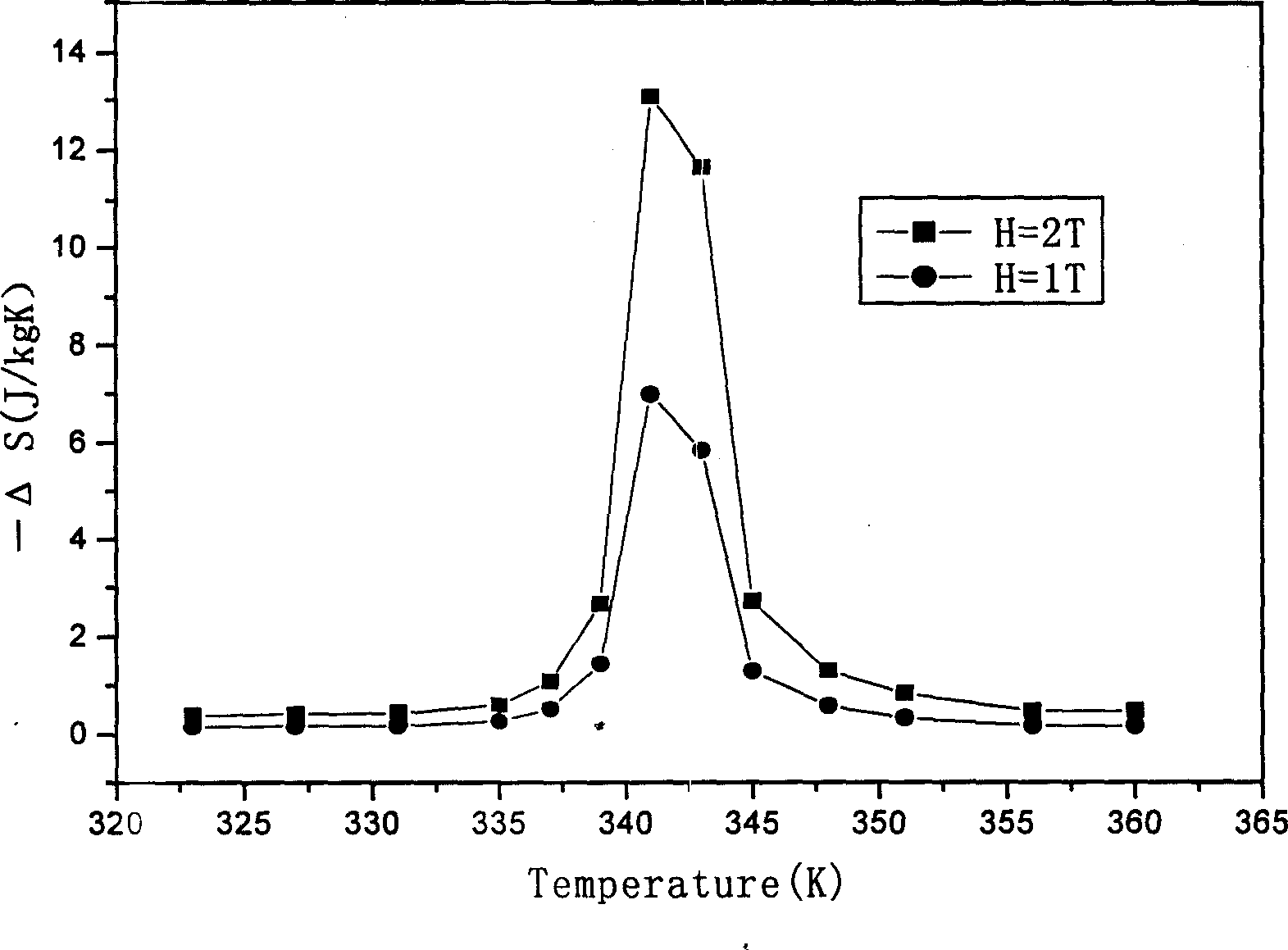
[0022] Raw materials such as nickel, manganese, gallium, etc. are classified into chemical components Ni 54.9 mn 20.5 Ga 24.6 Proportion (electron concentration is 7.663), put into vacuum electric arc furnace, induction furnace or other smelting furnace, vacuumize to 10 -1 or above, pass in argon gas, and obtain a compound with uniform composition after repeated melting and cooling. The compound obtained by smelting was homogenized at 1050°C for 48 hours, and then annealed at 650°C for 72 hours. In order to prevent sample oxidation, the homogenization treatment and annealing process can be carried out under vacuum or argon protection. The sample prepared in this way proves to be non-modulated square structure through X-ray diffraction, belongs to martensitic phase (see figure 1 ). Vibrating sample magnetometer LakeShore-7410 was used to measure the isothermal magnetization curve near the phase transition temperature (see figure 2 ). The compound obtained through the ab...
Embodiment 3
[0024] Raw materials such as nickel, manganese, gallium, etc. are classified into chemical components Ni 55.5 mn 19.8 Ga 24.7 Proportion (electron concentration is 7.677), put it into a vacuum electric arc furnace, induction furnace or other smelting furnace, vacuumize to 10-1 or above, pass in argon gas, and obtain a compound with uniform composition after repeated melting and cooling. The compound obtained by smelting was homogenized at 950°C for 72 hours, and then annealed at 750°C for 48 hours. In order to prevent sample oxidation, the homogenization treatment and annealing process can be carried out under vacuum or argon protection. The sample prepared in this way proves to be non-modulated square structure through X-ray diffraction, belongs to martensitic phase (see Figure 4 ). Vibrating sample magnetometer LakeShore-7410 was used to measure the isothermal magnetization curve near the phase transition temperature (see Figure 5 ). The compound obtained through the...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Curie temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Magnetic entropy change | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Curie temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com