N-pin structure semiconductor luminous diode
A technology for light-emitting diodes and light-emitting regions, which is applied to semiconductor devices, electrical components, circuits, etc., and can solve the problems of not obtaining the current spreading effect, reducing the brightness of the device by the current spreading layer, and failing to obtain current spreading.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
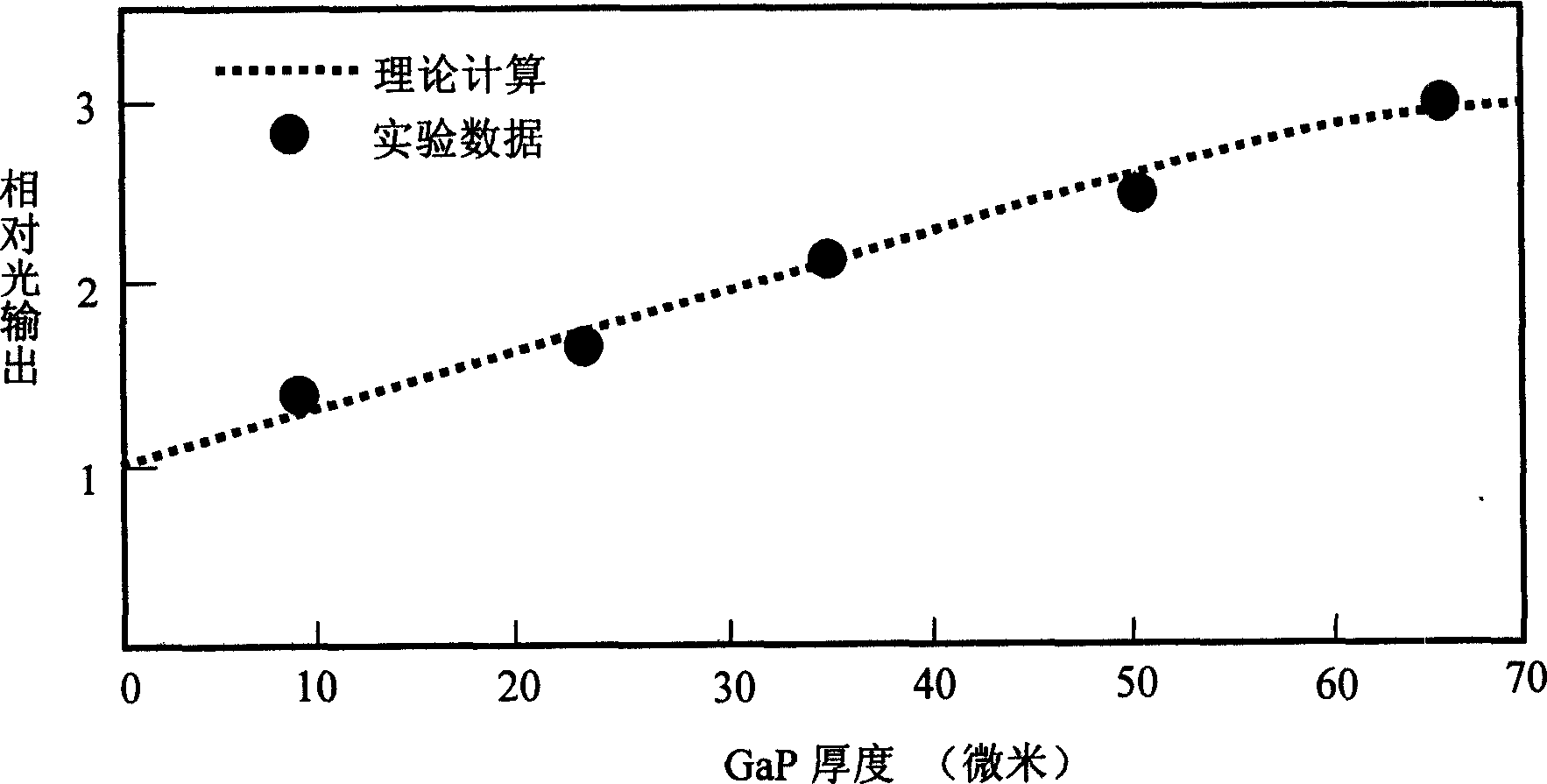
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
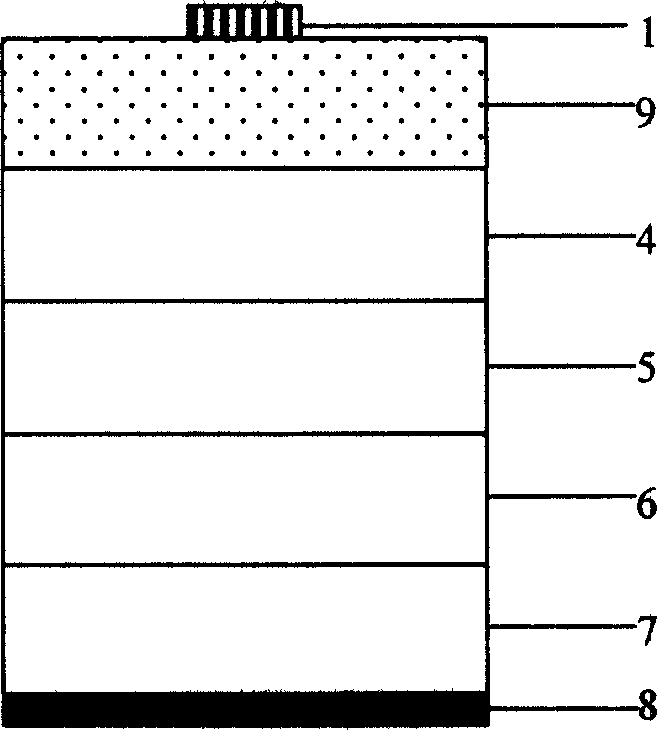
[0034] Such as Figure 5 As shown, the realization method of the n-pin structure red light-emitting diode is as follows:
[0035] 1. Using common metal-organic chemical vapor deposition (MOCVD) method in n + -GaAs substrate 7 epitaxially grows n-AlInP lower confinement layer 6, AlGaInP heterojunction light-emitting region 5, p-AlInP upper confinement layer 4, p + -GaAs / n + - GaAs tunnel junction 3 and n-GaP current spreading layer 2;
[0036] 2. Use a Karl Suss lithography machine to lithography the mask pattern.
[0037] 3. By conventional evaporation method, ohmic contact electrode 1 Au / Ge / Ni / Au is evaporated on the front side;
[0038] 4. Using the conventional stripping method, there is only metal left at the ohmic contact electrode 1;
[0039] 5. The sample is thinned to 100 μm by conventional mechanochemical corrosion method;
[0040] 6. Evaporate the upper and lower ohmic contact electrodes 8 Au / Ge / Ni / Au on the substrate 7 according to the conventional process;
...
Embodiment 2
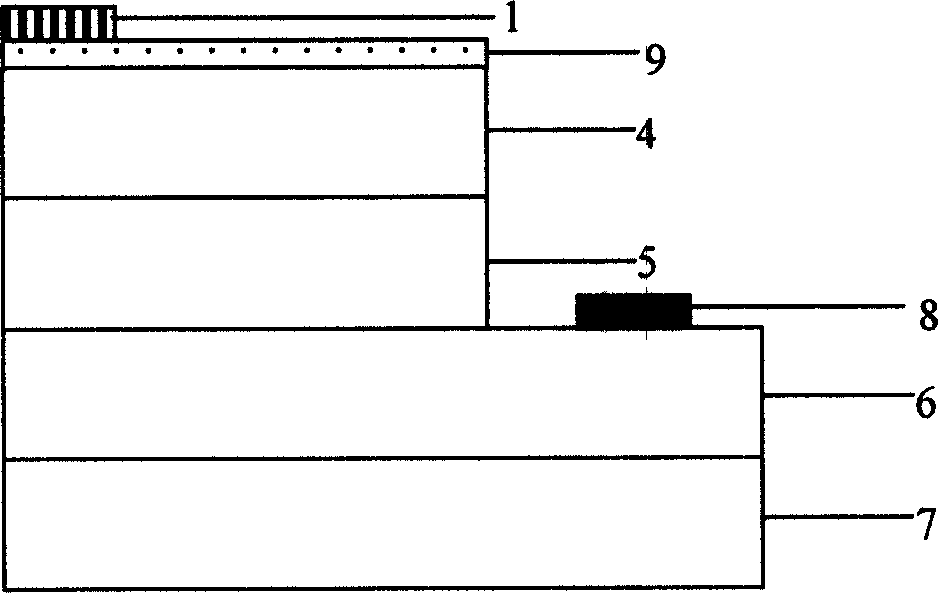
[0044] Such as Figure 7 As shown, the realization method of n-pin structure blue light-emitting diode is as follows
[0045] 1. Epitaxially grow the n-GaN lower confinement layer 6, the InGaN / GaN quantum well light-emitting region 5, and the p-GaN upper confinement layer 4 on the sapphire substrate 7 sequentially by ordinary metal-organic chemical vapor deposition (MOCVD). + -InGaN / n + - InGaN tunnel junction 3, and n-GaN current spreading layer 2;
[0046] 2. Use a conventional Karl Suss lithography machine to photoetch mask patterns for dry etching;
[0047] 3. Use Oxford (Oxford) ICP-100 to etch the sample out of the mesa structure to 6 places of the n-GaN lower confinement layer, the etching gas is chlorine and argon, the etching time is 10 minutes, and the etching depth is 600 nanometers;
[0048] 4. Obtain the shapes of the upper and lower ohmic contact electrodes 1 and 8 by photolithography according to the conventional process;
[0049] 5. The upper and lower ohmi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com