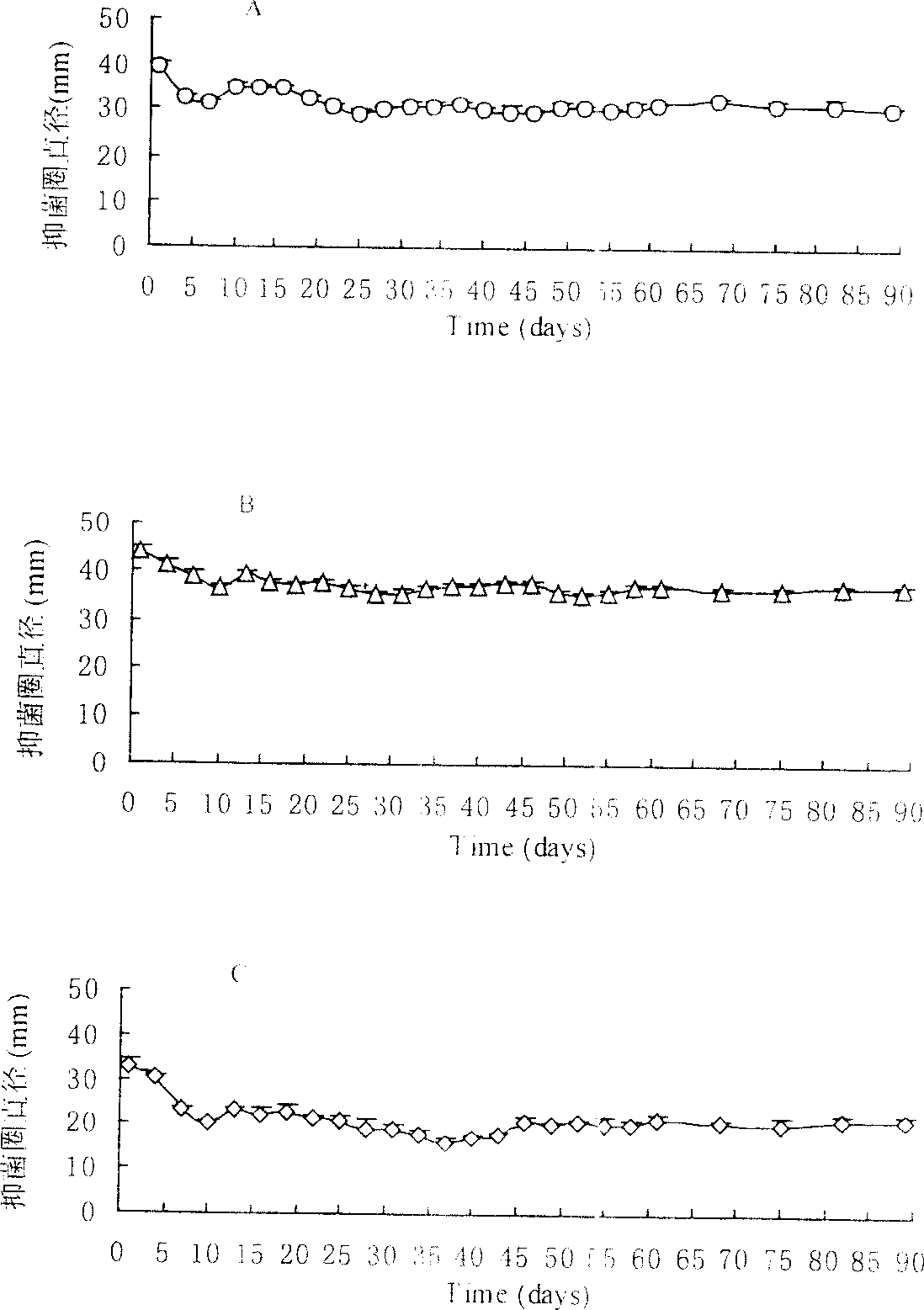Carrier of regulating medicine releasing speed and preparation thereof
A release speed and drug release technology, which is applied in the preparation of the drug carrier and the field of carriers that regulate the release rate of the drug, can solve the problems of few experimental research reports, and achieve the effects of simple production technology, prolonged drug release time, and low systemic toxicity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] Example 1 Preparation of Polysebacic Anhydride, Polylactic Acid Blend Drug Controlled Release Tablets by Solvent Suspension and Volatility Method
[0037] It is known that the preparation methods of controlled-release tablets of polymer materials mainly include melting-dispersion method and solvent evaporation method (Gao Bo, Luge, Su Tongfang. Controlled-release system of biodegradable drugs implanted into the brain for the treatment of brain tumors. Advances in pharmacy. 2000;24:274). The melting and dispersing method is to heat the polymer to the melting point to make it appear in a molten state, add solid powdered drug according to the required drug loading ratio and stir well, then pour it into a preheated mold, cool it at room temperature, and process it into the required product. size and shape. The solvent evaporation method is to dissolve the polymer material and the loading drug in a certain co-soluble solvent, pour it into the mold at a low temperature, and ...
Embodiment 2
[0048] Example 2 In vitro drug release experiment of polysebacic anhydride, polylactic acid blended ofloxacin controlled release tablet
[0049] Sampling: Take polysebacic anhydride and polylactic acid at a ratio of 5:95 or 10:90 or 15:85 or 20:80 or 25:75 or 30:70 or 40:60 or 60:40 or 80:20% Three ofloxacin tablets were placed in test tubes respectively, 10 ml of 0.1M phosphate buffer solution (pH7.4) was added to each, and a constant temperature water bath was placed at 37°C. The buffer solution was changed at 2 hours, 5 hours, and 10 hours after the start of the experiment; the buffer solution was changed every day from the 1st to 14th day of the experiment, and every 2 days on the 15th to 28th day; The buffer was changed every 3 days; thereafter every 7 days until 3 months after release. After the liquid was taken out and centrifuged, the supernatant liquid was taken and sealed in a test tube, and stored at -20°C until testing.
[0050] Preparation of standard curve: Acc...
Embodiment 3
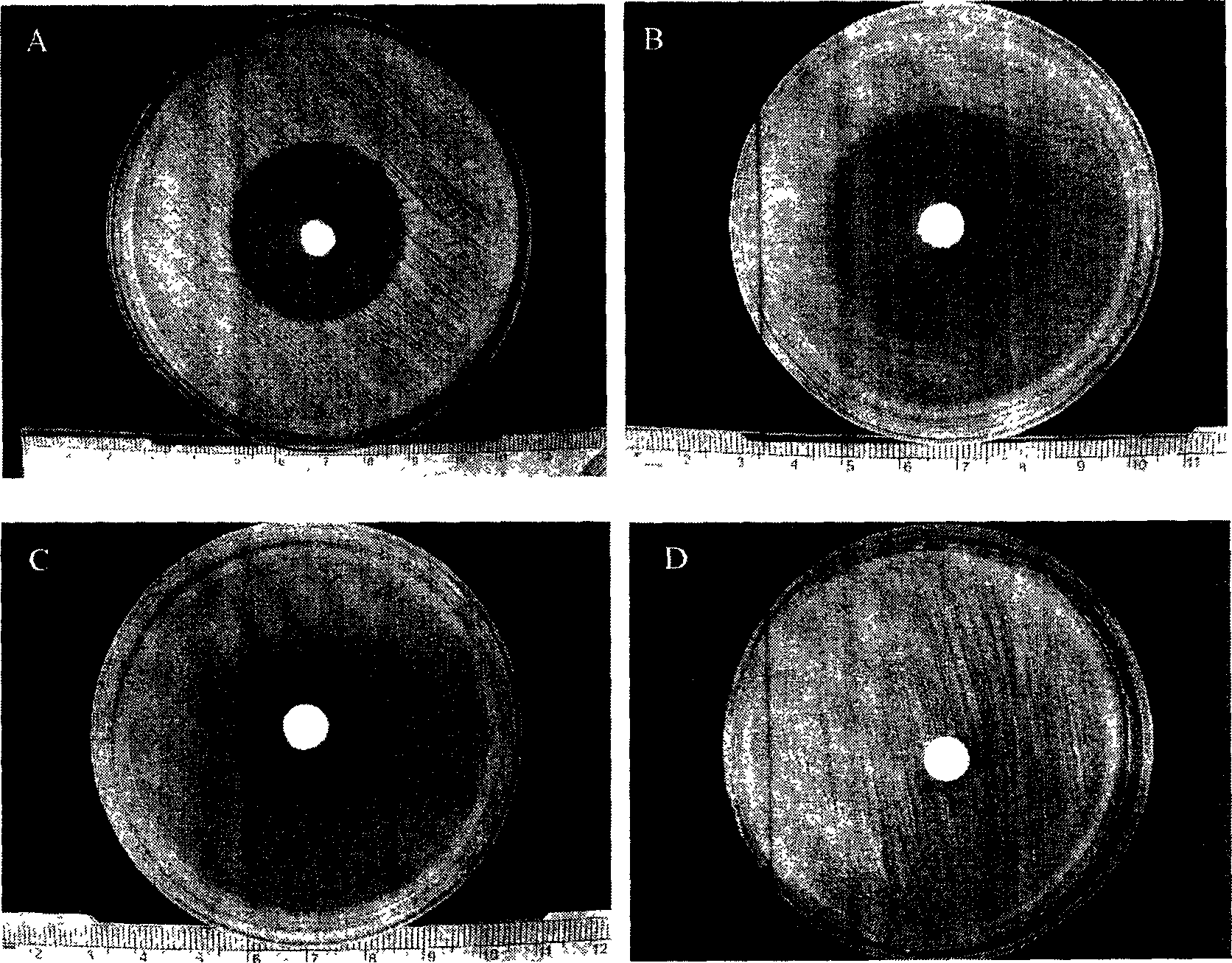
[0057] Example 3 In vitro bacteriostatic experiment of polysebacic anhydride, polylactic acid blended ofloxacin sustained-release tablets
[0058] Take 9 tablets of ofloxacin sustained-release tablets blended with polysebacic anhydride and polylactic acid, each 3 tablets as a group, and place them in the agarose inoculated with Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa respectively. In the center of the culture medium (only one piece is placed in a petri dish), measure the size of the inhibition zone after culturing at 37°C for 24 hours. Then transfer the tablet into a new medium to measure the inhibition zone every 3 days, and replace the new medium, repeating this until 2 months after the experiment, and then replace the new medium every week until 3 months after the experiment. Another tablet of polysebacic anhydride and polylactic acid blend without ofloxacin and of the same size, shape and blending ratio was placed in the above bacterial culture ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com