Separator for organic electrolyte battery, process for producing the same and organic electrolyte battery including the separator
A technology of an organic electrolyte and a manufacturing method, applied in the field of battery separators, can solve the problems of dendrite short circuit, cost reduction, battery failure rate and the like
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
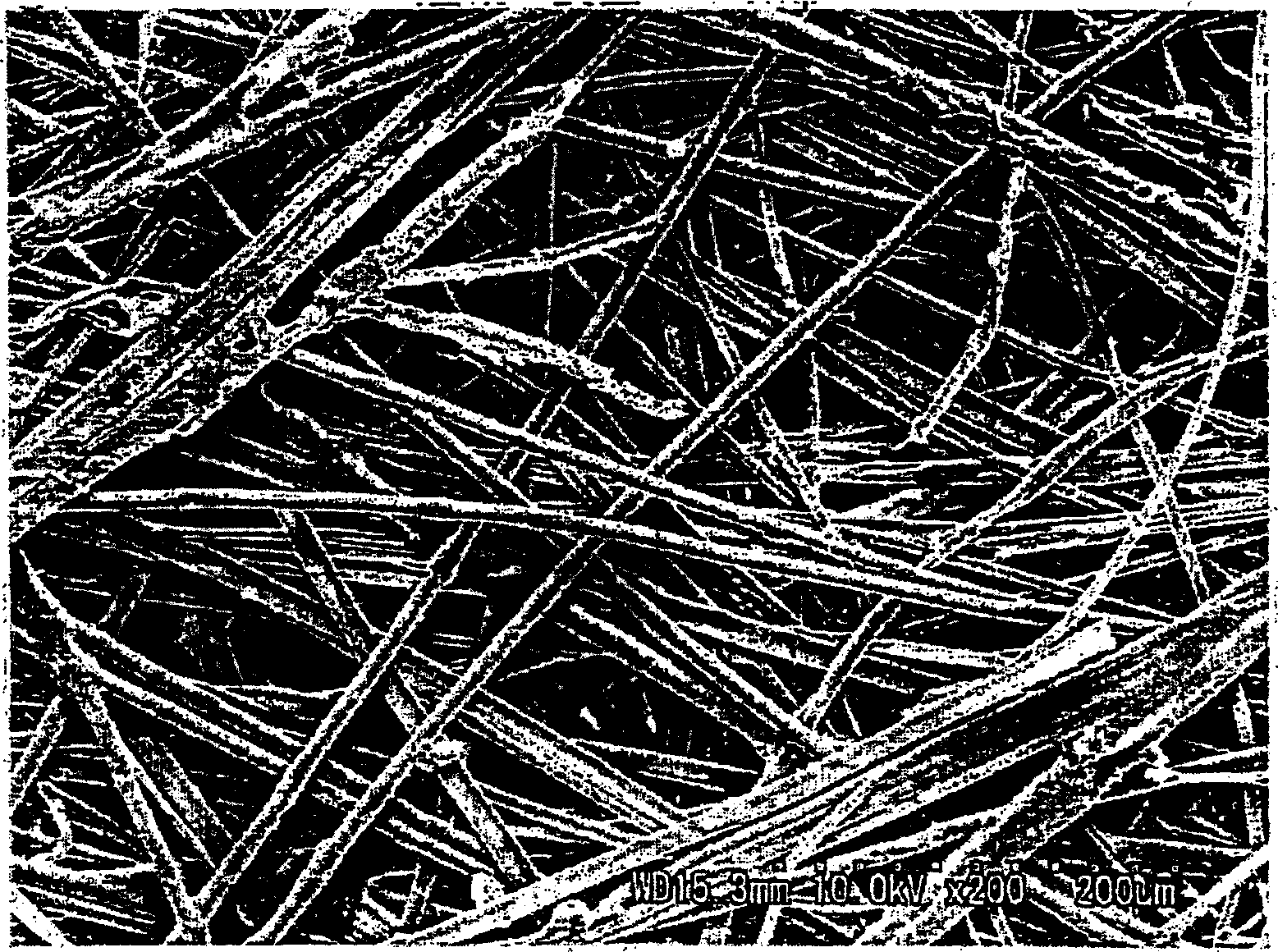
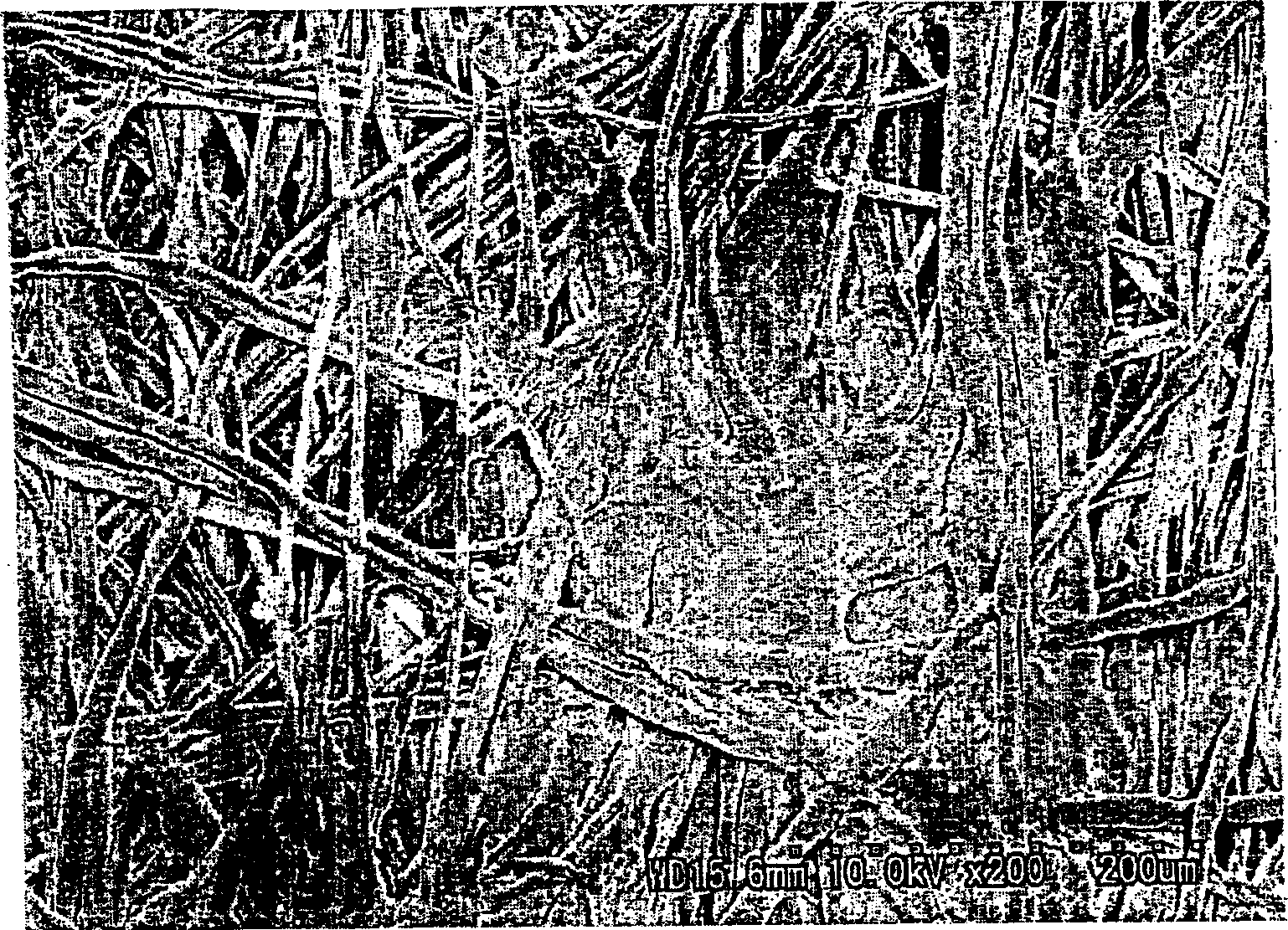
[0122] 50% by mass of fiber 1 with a fineness of 1.4dtex (short axis thickness after division: PP2.57μm, EVOH2.66μm), 30% by mass of fiber 3 of 0.8dtex (fiber diameter 10.3μm), 20% by mass of 0.6dtex Fiber 4 (fiber diameter: 8.37 μm) was mixed to prepare a water dispersion slurry having a concentration of 0.5% by mass. The obtained water-dispersed slurry is formed into a web by a cylinder-type wet-laid paper machine and a short-wire wet-laid paper machine respectively. The weight per unit area is 15g / m 2 wet-laid web. Carry out heat treatment at 135 ℃ and make it dry with tumble drier next, the wet heat gelation resin of fiber 1 and the leather sheath composition of fiber 4 are bonded together temporarily simultaneously, take up the weight of unit area with roller and be 30g / m 2 wet-laid nonwoven sheet. In the obtained wet-laid nonwoven sheet, almost 100% of the fibers 1 were divided and dispersed almost uniformly in the nonwoven fabric. In addition, the split ratio is ob...
Embodiment 2
[0126] Except that the fiber 3 was 1.2 dtex (fiber diameter 13.1 μm) and the fiber 4 was 1.2 dtex (fiber diameter 13.0 μm), it was treated in the same manner as in Example 1 to obtain a separator for an organic electrolyte battery. The obtained separator had an average fiber diameter of the nonwoven sheet before gel processing was 7.81 μm. In addition, the average fiber diameter of the other fibers was 9.52 µm except for the hydrothermally gelling resin.
Embodiment 3
[0128] A separator for an organic electrolyte battery was obtained in the same manner as in Example 1 except that the fiber 1 was set to 3.3 dtex (short axis thickness after division: PP 3.96 μm, EVOH 4.06 μm). The obtained separator had an average fiber diameter of the nonwoven sheet before gel processing was 6.78 μm. In addition, the average fiber diameter of the other fibers was 7.68 µm except for the hydrothermally gelling resin.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com