Water soluble anti-cancer medicine slow-release fiber preparation and preparing method therefor
A water-soluble, fiber-based technology, applied in drug combination, drug delivery, anti-tumor drugs, etc., can solve the problems of limiting drug loading performance, and achieve stable release, good body structure compatibility, and strong adaptability to implantation structures Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
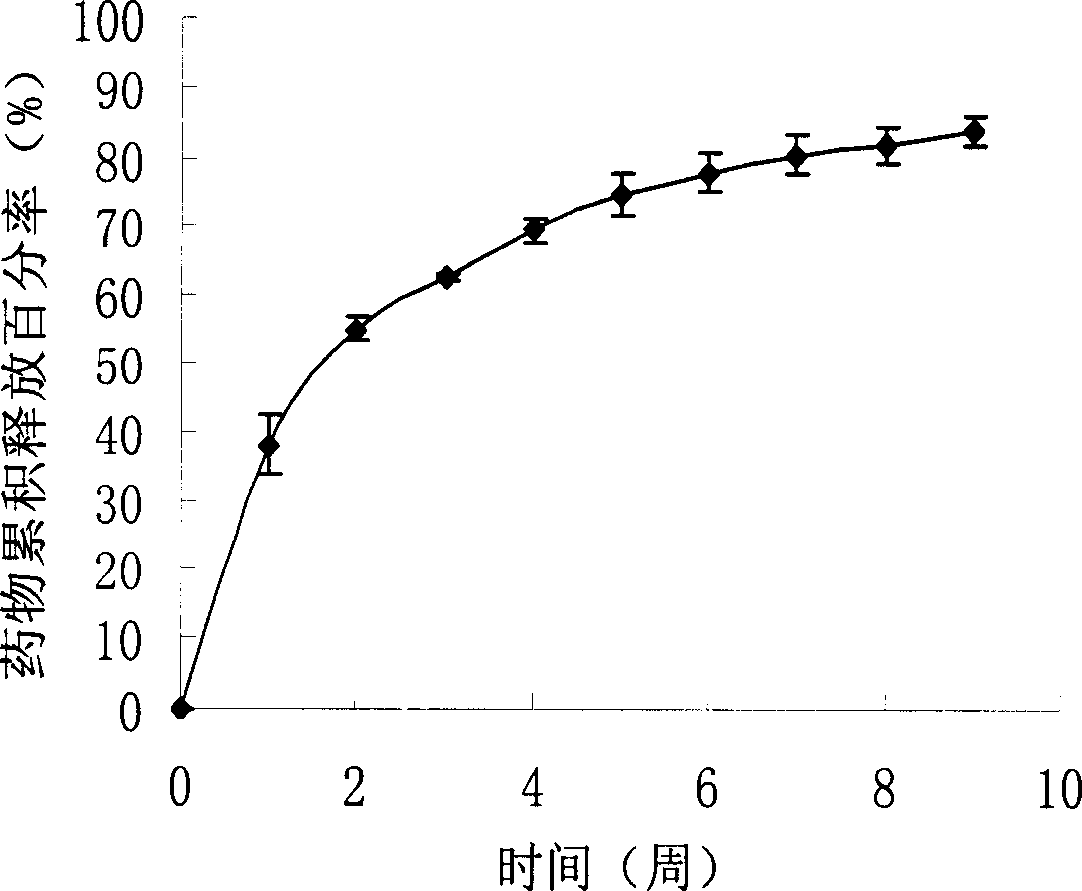
[0028] Add 0.32g of fluorouracil powder into 5ml of chloroform, and ultrasonically suspend; then add 0.75g of PLLA (L-lactic acid, viscosity-average molecular weight: 100,000), dissolve and stir evenly; then pass the mixed solution at a speed of 0.05ml / min through A 16-gauge flat-tipped needle is injected into the isopropanol curing agent, and the curing distance is 20cm. The solvent of the mixed solution diffuses in the curing agent, and the polymer and the drug are precipitated to form drug-loaded fibers; finally, the fibers are collected at the bottom of the curing agent container and removed by vacuum drying. Organic solvents, ie, see figure 1 . The resulting fiber diameter is 79.4 μm, the drug loading yield is 92.2%, and the drug can be released for 9 weeks, see figure 2 In vitro drug release profile, the release medium is NaN containing 0.1mg / ml 3 Phosphate buffer solution of pH 7.4, the release temperature is 37°C.
Embodiment 2
[0030] Add 0.125g of cisplatin powder into 5ml of chloroform, and ultrasonically suspend; then add 0.35g of PLLA (viscosity average molecular weight: 200,000), dissolve and stir evenly; then pass the mixed solution through a No. 16 flat head at a speed of 0.05ml / min Needle, injected into the isopropanol curing agent, the curing distance is 20cm, the solvent of the mixed solution diffuses in the curing agent, the polymer and the drug are precipitated to form drug-loaded fibers; finally, the fibers are collected at the bottom of the curing agent container, and the organic solvent is removed by vacuum drying. see image 3 . The resulting fiber diameter is 65.2 μm, the drug loading yield is 75.3%, and the drug can be released for 4 weeks, see Figure 4 In vitro release profile, the release medium is NaN containing 0.1mg / ml 3 Phosphate buffer solution of pH 7.4, the release temperature is 37°C.
Embodiment 3
[0032] Add 0.22g of nitrogen mustard powder into 5ml of dichloromethane, and ultrasonically suspend; then add 0.75g of PLA (polylactic acid, containing 3% D-type, with a viscosity average molecular weight of 50,000), dissolve and stir evenly; then mix the solution with At a speed of 0.07ml / min, through a No. 16 flat-tipped needle, inject into the petroleum ether curing agent, the curing distance is 20cm, the solvent of the mixed solution diffuses in the curing agent, and the polymer and the drug are precipitated to form drug-loaded fibers; The fibers are collected at the bottom, dried in vacuum to remove the organic solvent, and obtained. The diameter of the obtained fiber is 53.4 μm, the drug loading yield is 89.3%, and the drug can be released slowly for 20 days.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com