Crosslinking poly(organophosphazenes) microsphere and preparation method thereof
A technology for cross-linking polyphosphazene and microspheres, which is applied in chemical instruments and methods, catalyst carriers, physical/chemical process catalysts, etc. It can solve the problems that polyphosphazene microspheres have not been reported, achieve good thermal stability and simple process Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0021] Add 0.1 gram (0.29 mmol) hexachlorocyclotriphosphazene, 0.22 gram (0.86 mmol) 4,4'-dihydroxydiphenyl sulfone and 0.17 gram (1.73 mmol) triethylamine in 150 milliliter flask, again Add 90 ml of acetone, stir to dissolve, and react under magnetic stirring for 2 hours at 25°C. After the reaction, the solid is centrifuged, and the crude product is washed three times with acetone, then three times with deionized water, and finally placed in a vacuum oven After drying for 24 hours, 0.52 g of cross-linked polyphosphazene microspheres was obtained, with a yield of 47% based on hexachlorocyclotriphosphazene.
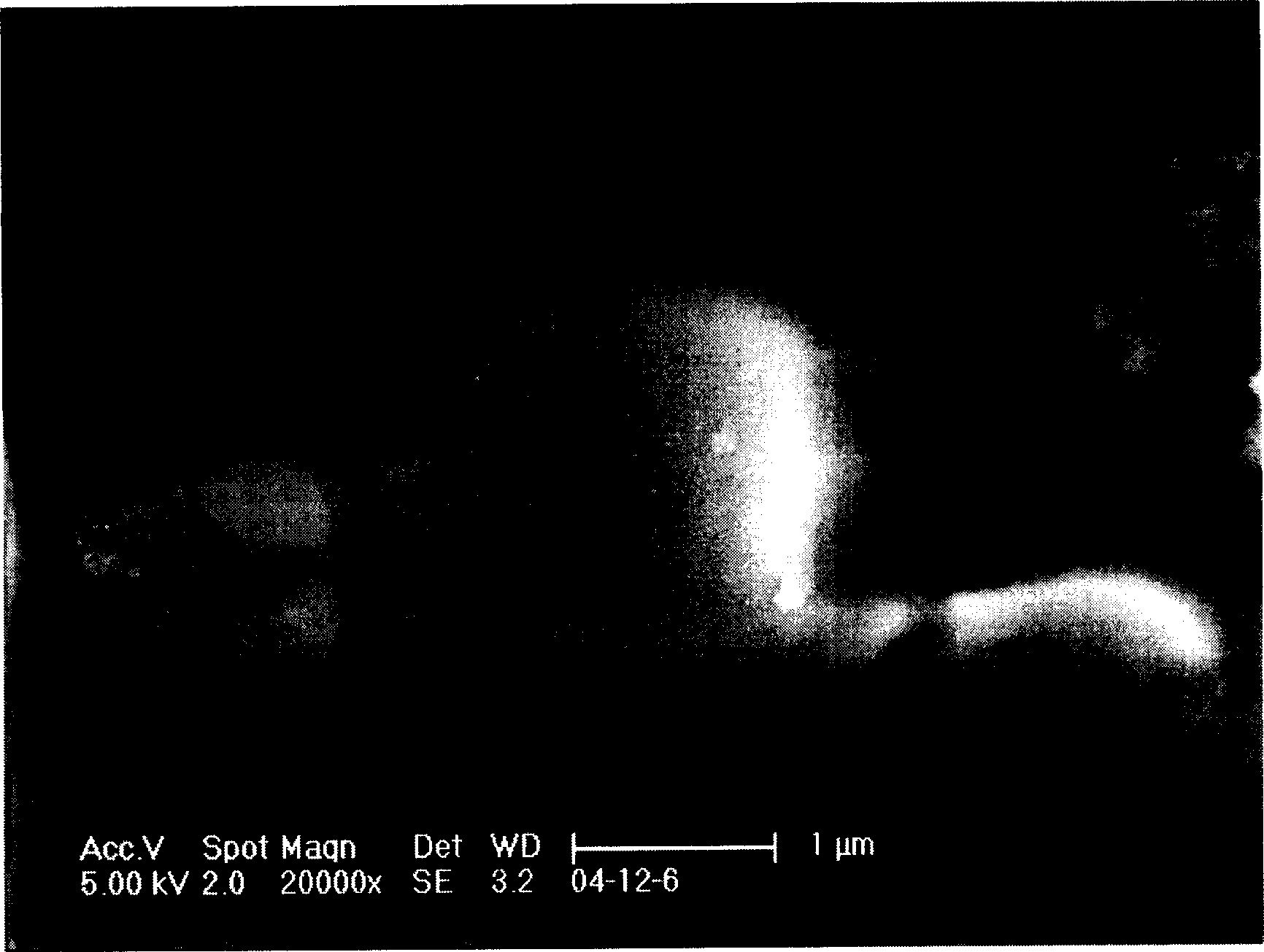
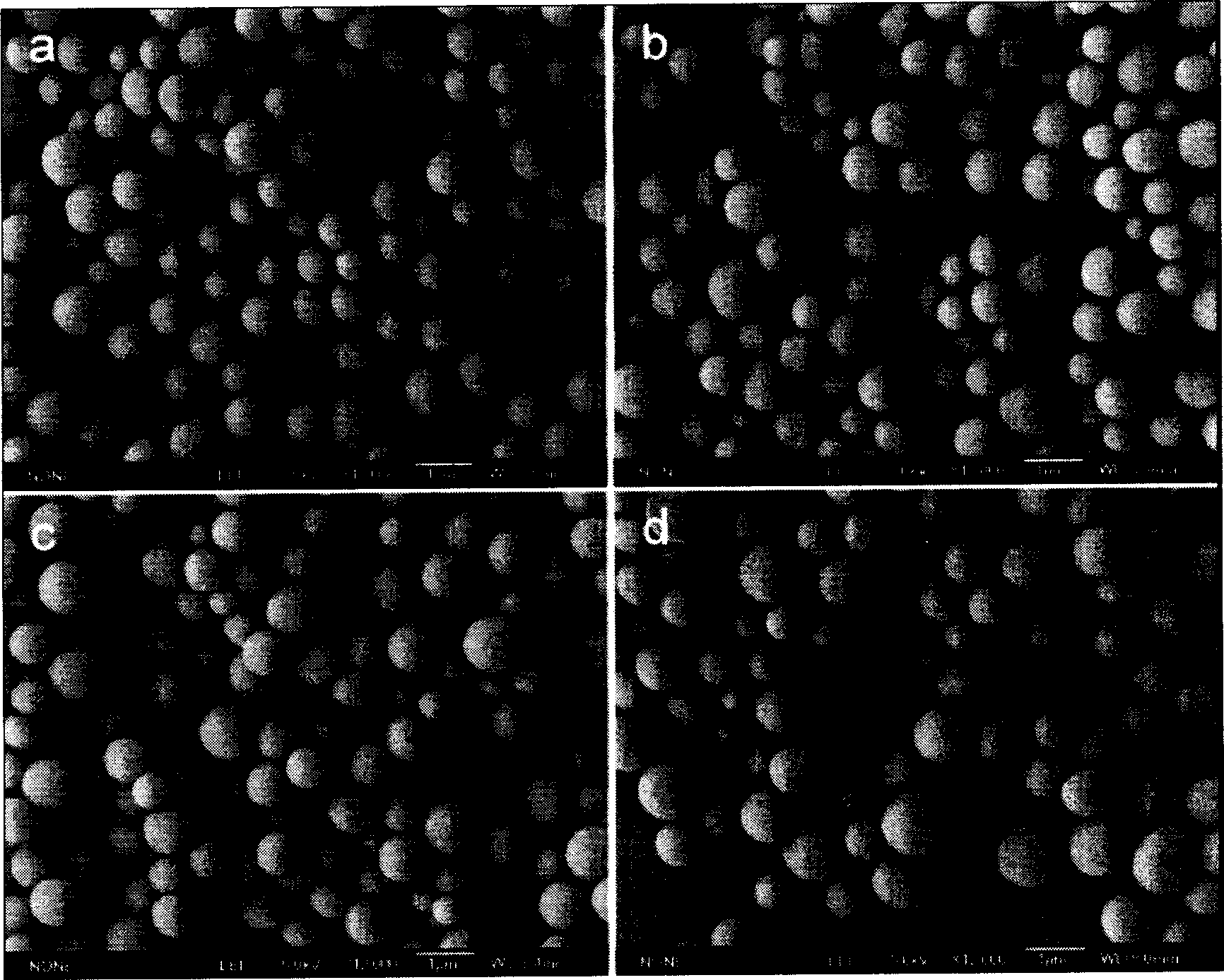
[0022] figure 1 It is the transmission electron micrograph of the obtained cross-linked polyphosphazene microspheres, figure 2 Scanning electron micrographs of cross-linked polyphosphazene microspheres, image 3 It is a field emission scanning electron micrograph of the cross-linked polyphosphazene microsphere, and it can be seen from the photograph that the diameter of...
Embodiment 2
[0028] Add 1 gram (2.9 mmoles) of hexachlorocyclotriphosphazene, 2.2 grams (8.6 mmoles) of 4,4'-dihydroxydiphenyl sulfone and 34 grams (346 mmoles) of triethylamine in a 500 ml flask, and then Add 250 ml of acetone, stir to dissolve, and react under magnetic stirring for 1 hour at 25°C. After the reaction, the solid is centrifuged, and the crude product is washed three times with acetone, then three times with deionized water, and finally placed in a vacuum oven After drying for 24 hours, 1.17 g of cross-linked polyphosphazene microspheres were obtained, with a yield of 64% based on hexachlorocyclotriphosphazene. Electron microscope photos show that the diameter of the microspheres is 0.4-4.5 microns, and the surface of the microspheres is flat and solid. Spectral analysis shows that the structure is a cross-linked condensation structure of hexachlorocyclotriphosphazene and 4,4'-dihydroxydiphenylsulfone .
Embodiment 3
[0030] The equipment and preparation process described in Example 1 were adopted, except that the reaction temperature was carried out at the reflux temperature of acetone, and the yield based on hexachlorocyclotriphosphazene was 55%. The analysis of the experimental results shows that the diameter of the microsphere is 0.5-4.5 microns, the surface of the microsphere is flat and solid, and its structure is a cross-linked condensation structure of hexachlorocyclotriphosphazene and 4,4'-dihydroxydiphenylsulfone.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com