Method for machining micro holes in ceramic matrix composite through femtosecond lasers
A technology of femtosecond laser and composite materials, which is applied in the field of micropore processing of ceramic matrix composite materials by using femtosecond laser, to achieve the effect of small thermal effect, high processing precision and small processing damage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
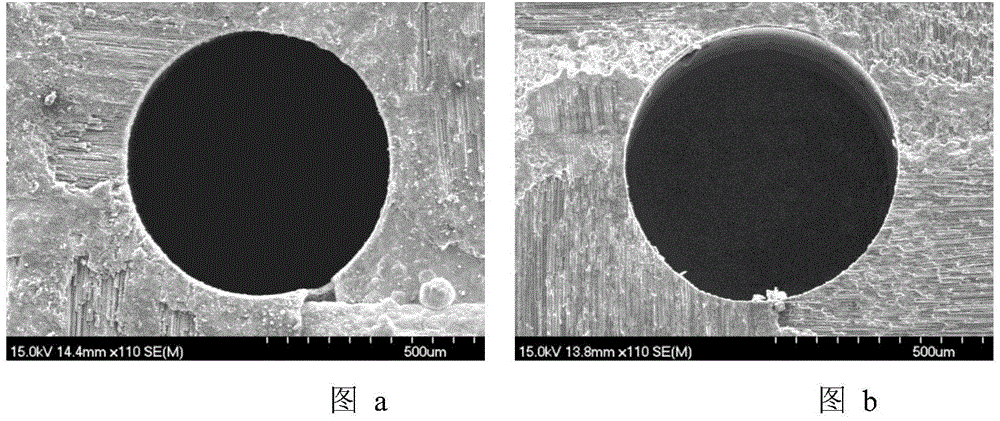
[0041] The method for forming circular holes proposed in this embodiment is applicable to CMC-SiC materials, and this embodiment only uses C / SiC composite materials as an example for illustration. The diameter of the formed hole is 600 μm (such as figure 2 ).
[0042] In this embodiment, the femtosecond laser used is the PHAROS femtosecond laser from Lithuania Light Conversion Company.
[0043] The specific process of this implementation is:
[0044] Step 1, the surface of the sample is cleaned. The 2D CVI C / SiC composite material was processed into a rectangular block sample of 20 mm × 10 mm × 3 mm, then ultrasonically cleaned for 15 minutes under alcohol immersion to remove surface dust, oil and other impurities, and finally dried in an oven to obtain the cleaned sample.
[0045] Step 2, processing micro-holes. Micromachining of 2D CVI C / SiC composite samples by femtosecond laser. . In this embodiment, the sample is processed by layer-by-layer removal, the processing h...
Embodiment 2
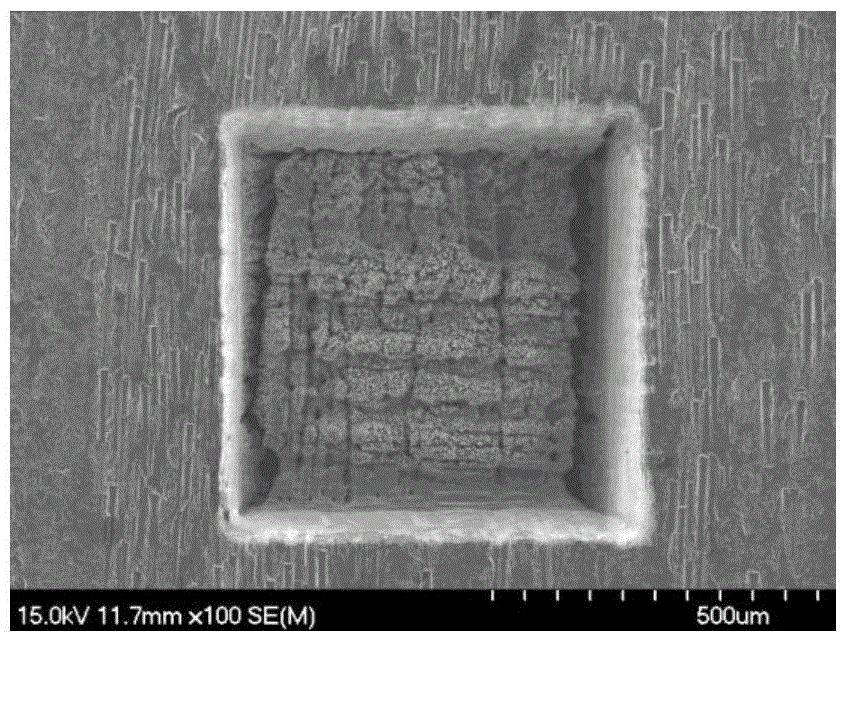
[0056] The method for forming a square hole proposed in this embodiment is suitable for silicon carbide ceramic matrix composite materials, and in this embodiment only a C / SiC composite material sample is used as an example for illustration. The plane size of the formed hole is 650μm×650μm (such as image 3 ).
[0057] In this embodiment, the femtosecond laser used is the PHAROS femtosecond laser from Lithuania Light Conversion Company.
[0058] Step 1. Clean the sample surface. The 2D CVI C / SiC composite material was processed into a rectangular block sample of 20 mm × 10 mm × 3 mm, then ultrasonically cleaned for 15 minutes under alcohol immersion to remove surface dust, oil and other impurities, and finally dried in an oven to obtain the cleaned sample.
[0059] Step 2, machining holes. Holes are machined in 2D CVI C / SiC composite samples by femtosecond laser. In this embodiment, the linear scanning square hole processing is performed on the sample by layer-by-layer rem...
Embodiment 3
[0070] The method for forming a rectangular hole proposed in this embodiment is suitable for silicon carbide ceramic matrix composite materials, and this embodiment only uses a C / SiC composite material sample as an example for illustration. The plane size of the formed rectangular hole is 1300μm×650μm (such as Figure 4 ).
[0071] In this embodiment, the femtosecond laser used is the PHAROS femtosecond laser from Lithuania Light Conversion Company.
[0072] Step 1. Clean the sample surface. The 2D CVI C / SiC composite material was processed into a rectangular block sample of 20 mm × 10 mm × 3 mm, then ultrasonically cleaned for 15 minutes under alcohol immersion to remove surface dust, oil and other impurities, and finally dried in an oven to obtain the cleaned sample.
[0073] Step 2, process the rectangular hole. A rectangular hole is machined on a 2D CVI C / SiC composite sample by a femtosecond laser. In this embodiment, the linear scanning rectangular hole processing is...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com