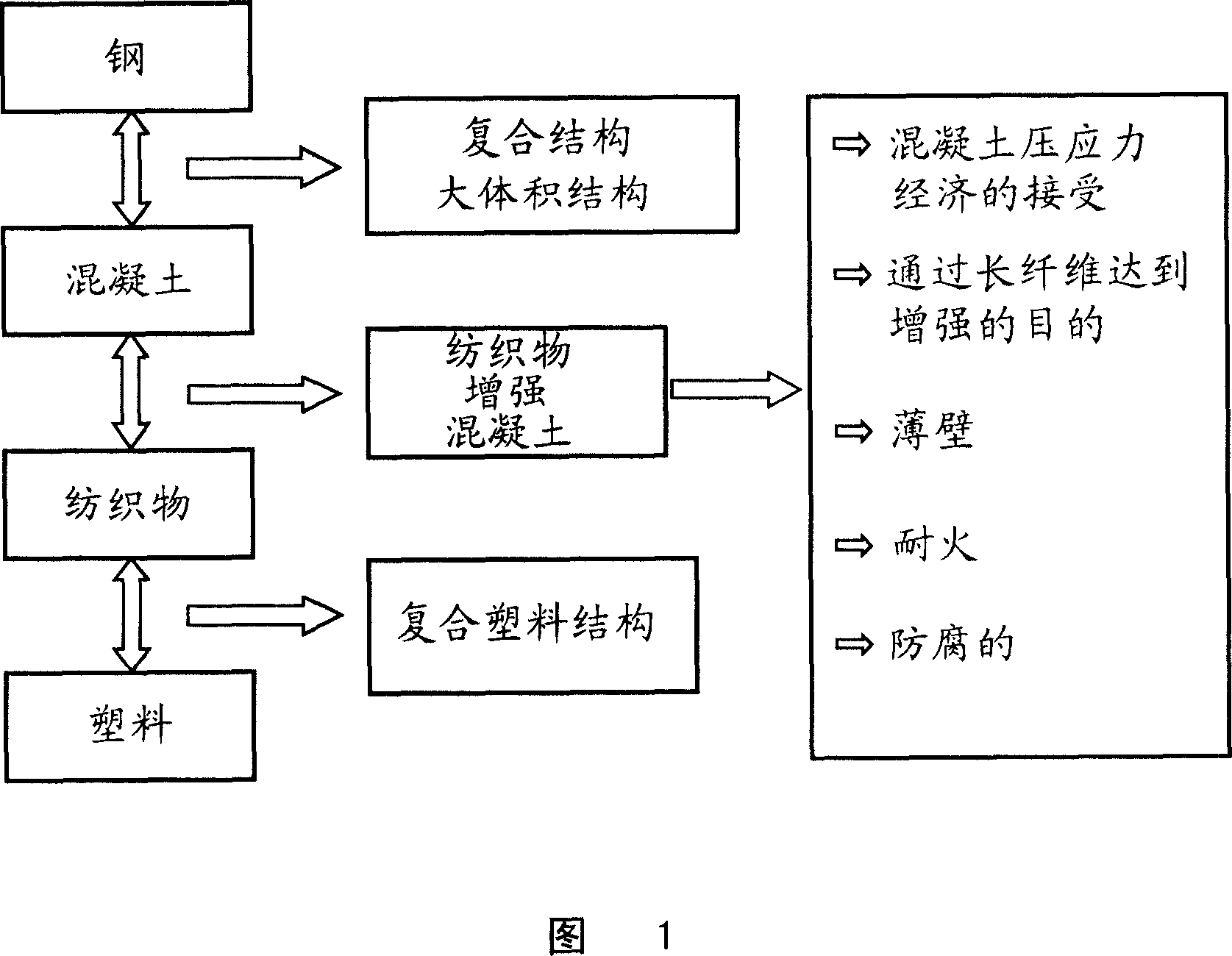
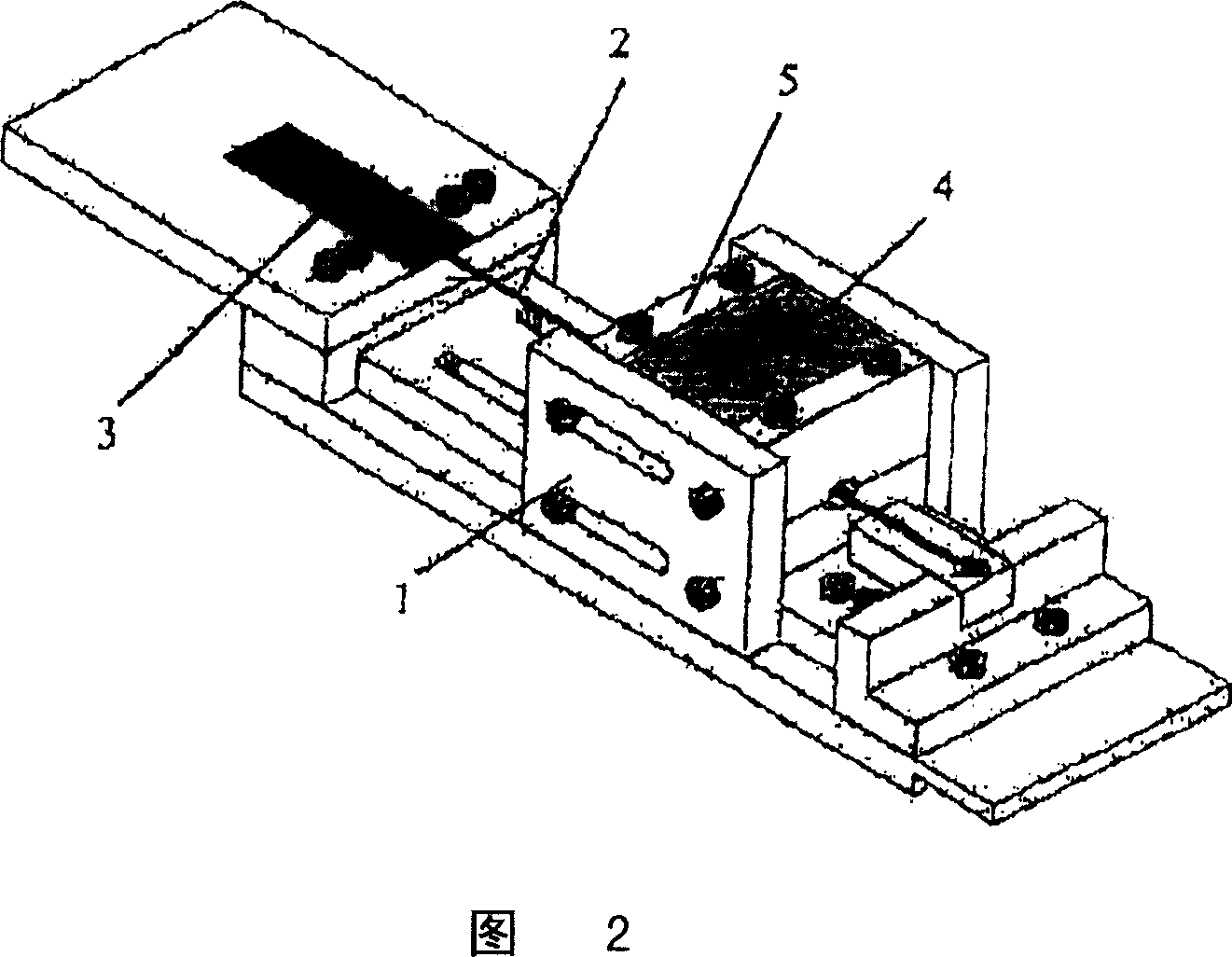
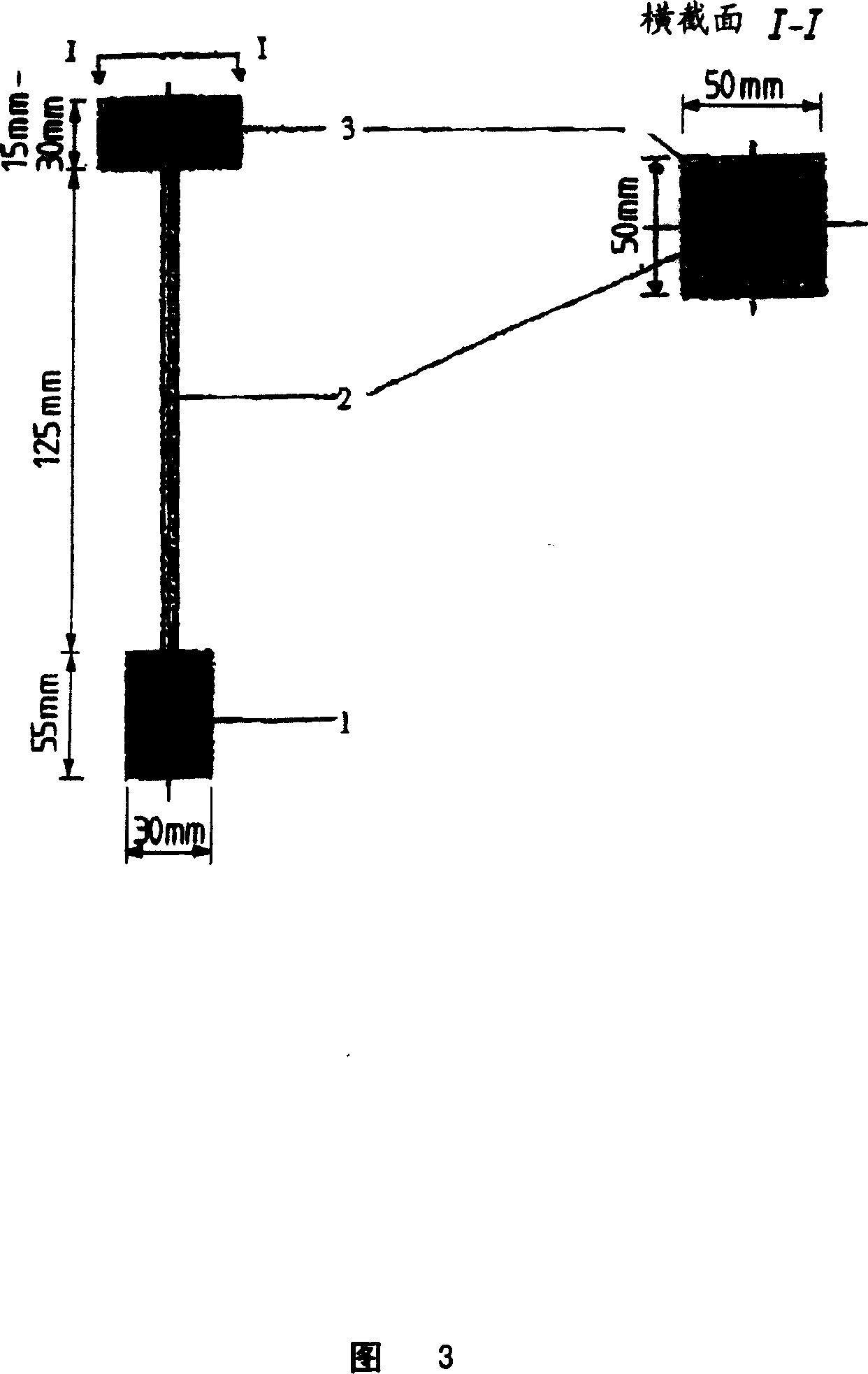
Compositions for use in concrete
A technology for strengthening concrete and formulations, applied in coating, transportation and packaging, thin material handling, etc., can solve the problems of calculating spun tensile strength/loading performance of reinforced fabrics, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0051] The preparation of polychloroprene has been known for a long time and is preferably carried out by emulsion polymerization in alkaline aqueous medium: see "Ullmanns Encyclopdie der technischen Chemie", Vol. 9, p. 366, Verlag Urban und Schwarzenberg, Munich - Berlin, 1957; "Encyclopedia of Polymer Science and Technology", Vol. 3, pp. 705-730, John Wiley, New York, 1965; "Methodender Organischen Chemie" (Houben-Weyl) XIV / 1, 738ff. Georg Thieme Verlag Stuttgart 1961.
[0052] Suitable emulsifiers include all compounds and mixtures thereof which stabilize emulsions to a sufficient extent, such as water-soluble salts, especially sodium, potassium and ammonium salts of long-chain fatty acids, rosin and rosin derivatives, high molecular weight alcohol sulfates, Arylsulfonic acids, formaldehyde polycondensates of aromaticylsulfonic acids, nonionic emulsifiers based on polyethylene oxide and polypropylene oxide, and polymers as emulsifiers, such as polyvinyl alcohol (DE-A 2 307 ...
Embodiment 1
[0079]The aqueous phase (W) and the monomeric phase (M) are discharged into 7 identical reactors with a capacity of 50 liters together with the catalyst phase (A) in a constant weight ratio through a measuring and controlling device Composition of the polymerization grid (cascade) of the first reactor. The average residence time per can was 25 minutes. The autoclave corresponds to that described in DE-A 2 650 714 (data are expressed in parts by weight per 100 parts by weight of monomers used).
[0080] (M) = monomer phase:
[0081] Chloroprene 100.0 parts by weight
[0082] 0.11 parts by weight of n-dodecylmercaptan
[0083] Thiodiphenylamine 0.005 parts by weight
[0084] (W) = water phase:
[0085] 115.0 parts by weight of deionized water
[0086] Disproportionated abietic acid sodium salt 2.6 parts by weight
[0087] Potassium hydroxide 1.0 parts by weight
[0088] (A) = catalyst phase:
[0089] 1% formamidine sulfinic acid solution 0.05 parts by weight
[0090] P...
Embodiment 2
[0097] The same procedure as in Example 1 was used, but the concentration of regulator in the monomer phase was reduced to 0.03 wt.%.
[0098] The solid content is 33wt.%, the colloid content is 1.2wt.%, and the pH value is 12.9.
[0099] After steam distillation, the dispersion was adapted to an adiabatic storage tank at a temperature of 80 °C for 3 days, where the temperature was post-adjusted by input of heat, if necessary, while the sample was used to measure the increase in colloidal content in the latex.
[0100] The dispersion was also emulsified as described in Example 1.
[0101]
Example 1
Polychloroprene Dispersion
Colloid: 0%
Solids: 58%
pH: 12.9
Example 2
Polychloroprene Dispersion
Colloids: 16%
Solids: 56%
pH: 127
Silica Dispersion
DISPERCOLL S 5005
Bayer Material Science AG
Solid: 50%
Particle size: 50nm
Surface area:...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| softening point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com