Solvent casting process, polarizing plate protective film, optically functional film and polarizing plate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 3
Preparation of Optically Functional Film
[0160] Onto one surface of the triacetylcellulose film [thickness: 100 .mu.m, {(nx+ny) / 2-nz}.times.d=70 nm] prepared in Example 1, a gelatin layer (layer thickness: 0.1 .mu.m) was applied. Subsequently, a coating solution of long-chain alkyl-modified polyvinyl alcohol ("MP-203", Kuraray Co., Ltd.) was applied onto the gelatin layer and dried for 30 seconds by warm wind at 110.degree. C., followed by rubbing the coated film to form an oriented film. On the surface of the oriented film, a discotheque liquid crystal was applied. In details, a coating solution containing 20 mass % of the compound TE-8 (m=4) described in JP 8-43625A, and 0.1 mass % of photoinitiator (Ilgacure 907, produced by Ciba Geigy Japan Co., Ltd.) in methyl ethyl ketone was applied by a slide coater at a coating velocity of 20 m / minute, with a coating amount of 12 cc / m.sup.2, to form the discotheque liquid crystal layer with a thickness of 2.4 .mu.m. The discotheque liquid cr...
example 5
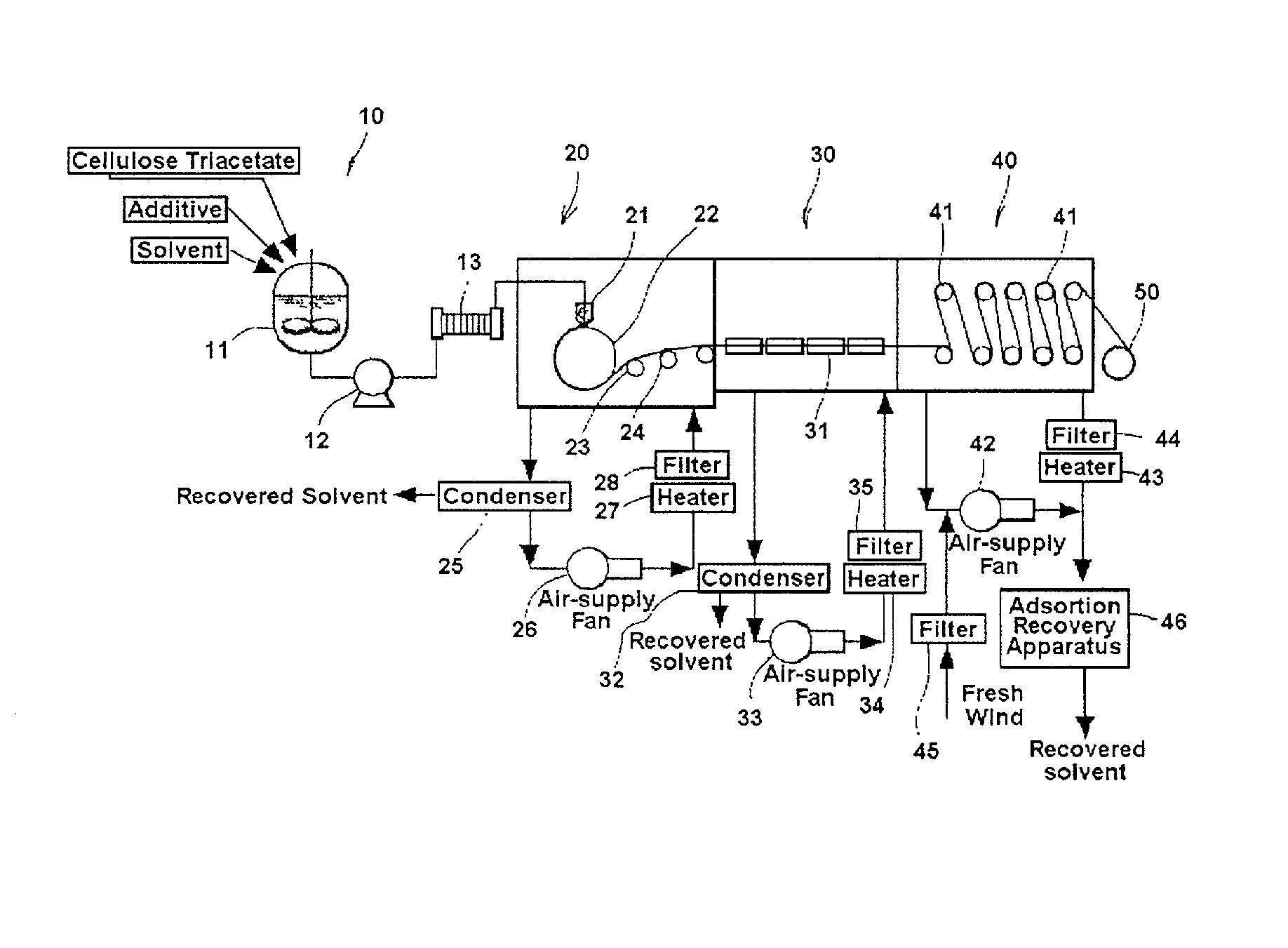
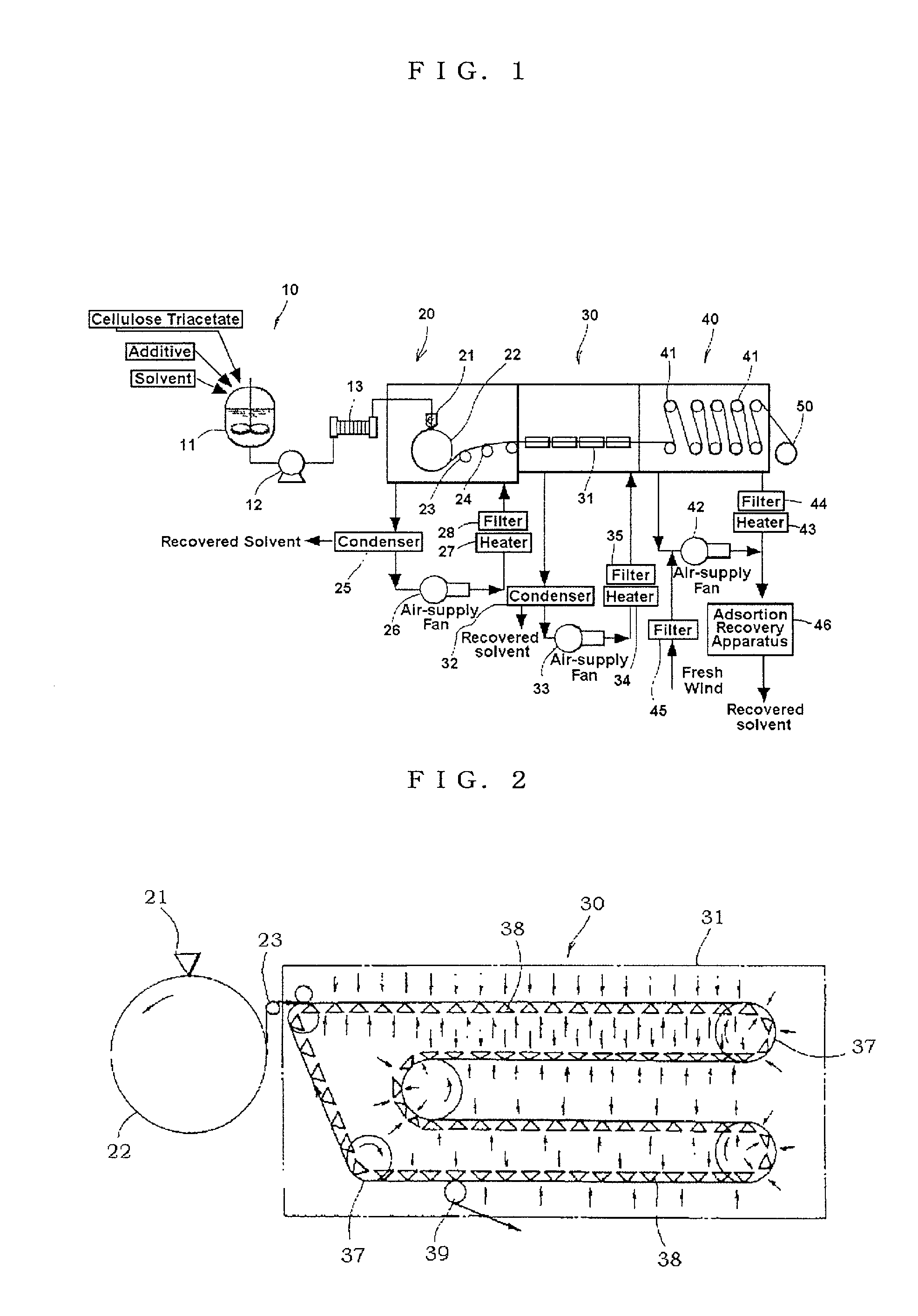
[0169] Dope E' was the same as Dope E except that matte agent was removed from Dope E in Example 4, and Dope F was the same as Dope E in Example 4. Using a multi-manifold type die, the dopes were simultaneously cast on the casting support in the same way as Example 4, while Dope E' formed the core part corresponding to the thickness of 70 .mu.m after drying, and Dope F formed outer layers on both surfaces of the core part corresponding to the thickness of 5 .mu.m after (trying. Then, the film stripped off from the casting support was carried by the pin tenter machine with the conditions of residual solvent of 280 mass % and a temperature -2.degree. C. The other conditions for casting and drying the film were the same as Example 4.
example 7
[0176] The dopes were cast and dried under the same conditions as Example 6 with the exception that the mean thickness of the film was 135 .mu.m, the residual solvent quantity of the film on stripped off from the belt being the casting support was 150%, the temperature and the thickness of the film in the area of being carried by the pin tenter was respectively 12.degree. C. and 200 .mu.m and the residual solvent quantity was 220%.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com