Method for production of hepatic-lobule-like cell cluster from adipose-tissue-derived cell
a technology of adiposetissue and adipose tissue, which is applied in the direction of skeletal/connective tissue cells, drug compositions, peptides, etc., can solve the problems of incomplete cure medically impossible, and no report of regenerating hepatic lobule. , to achieve the effect of promoting or inhibiting the formation of hepatic lobules and promotes or inhibi
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Isolation and Culture of Adipose Tissue-Derived Cell
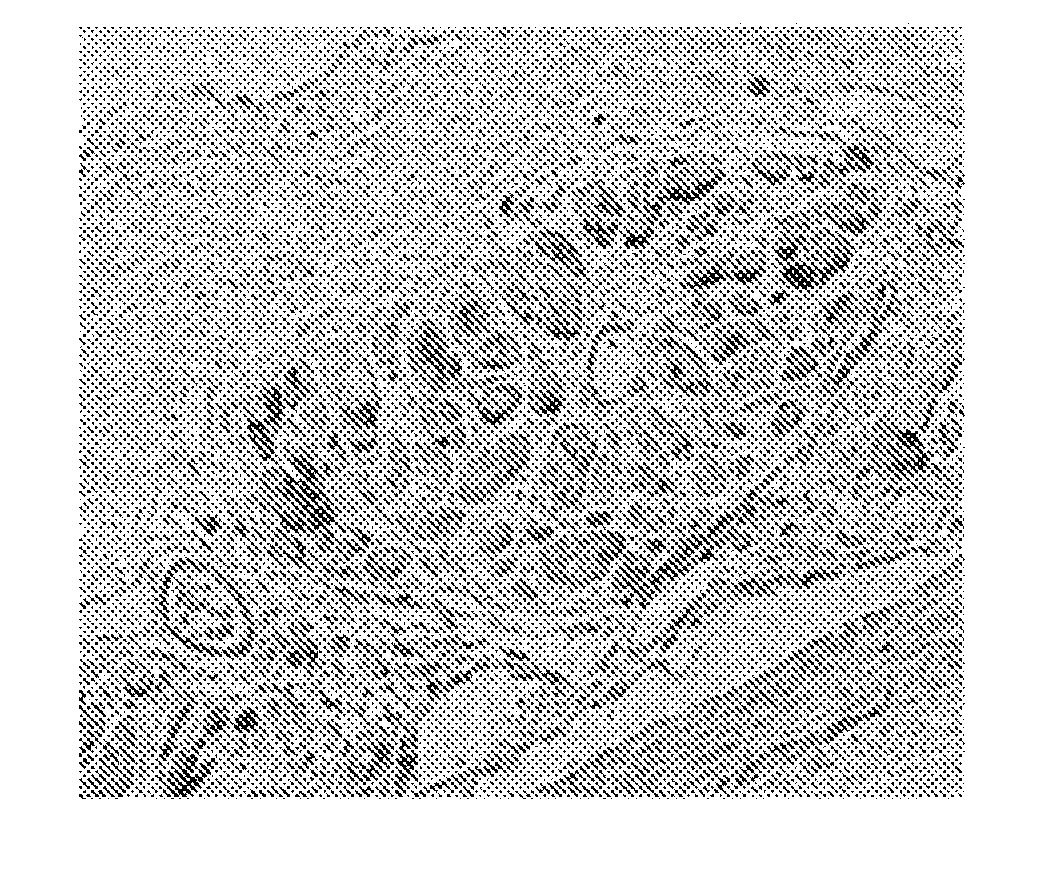
[0159]A human adipose tissue was sliced into 2 to 3 mm2-large fragments and digested using collagenase I. The digestate was cultured for 24 to 36 hours in DMEM containing 10% FBS and antibiotics and treated with 0.02% EDTA to obtain adipose tissue-derived cells. The obtained adipose tissue-derived cells were amplified by 3 to 5 passage cultures in a culture medium containing 60% DMEM (low glucose), 40% MCDB201, 1×ITS (10.0 mg / L insulin, 5.5 mg / L transferrin, 6.7 ng sodium selenite), 10 ng / mL rhEGF, 1 nM dexamethasone, 0.1 mM ascorbic acid and 5% FCS (Hyclone), in a fibronectin-coated dish. A micrograph of adipose tissue-derived cells is shown in FIG. 1.
Acquisition of Undifferentiated Cell from Adipose Tissue-Derived Cells
[0160]Cells that were singularized by treating adipose tissue-derived cells treated with 0.25% trypsin / EDTA (Nacalai Tesque) to be dissociated were cultured for 2 to 3 days in knock out DMEM (GIBCO Invitrogen) cont...
example 2
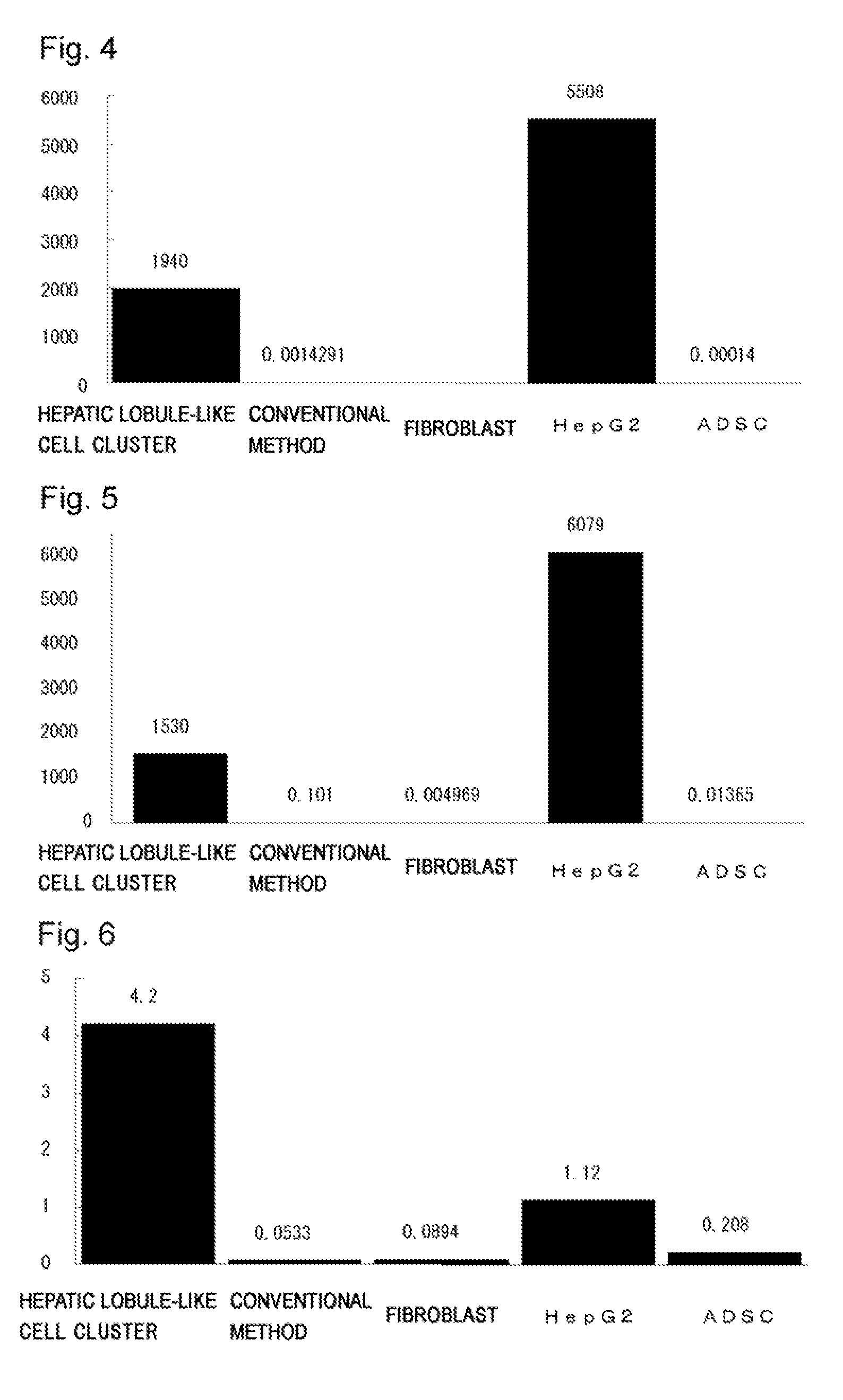
Hepatocyte Gene Expression Characteristics of Hepatic-Lobule-Like Cell Cluster
1. Extraction of RNA
[0162]Extraction of RNA from the hepatic-lobule-like cell cluster was carried out using RNeasy Protect Mini Kit (QIAGEN), as follows. The hepatic-lobule-like cell cluster was recovered, and the buffer RLT containing 10 μl / ml 2-mercaptoethanol (Naacalai Tesqu[13]) was added at a proportion of 600 μl / 107 cell. Cells were homogenized by pipetting with a 20G needle and then 600 μl of 70% ethanol was added. Transferred onto an RNeay[14] Mini column inside a 2 ml collection tube were 700 μl of the obtained mixed solution, which was centrifuged at 1000 rpm for 15 seconds. Next, 350 μl of buffer RW1 was added onto the column and centrifuged at 1000 rpm for 15 seconds. Added to 70 μl of buffer RDD were 10 μl of DNase I stock solution (QIAGEN), which were tumble-mixed, added to the RNeasy silica gel membrane inside the RNeasy Mini column, and incubated at room temperature for 15 minutes. Added wa...
example 3
Production of Hepatic Protein by Hepatic-Lobule-Like Cell Cluster
A. Western Blot Analysis
[0165]Hepatic-lobule-like cell cluster was washed three times with PBS (Nacalai Tesque), and then M-PER (PIERCE) was added. Cells were lysed by ultrasonication, centrifuged at 14000 g for 15 minutes to eliminate insoluble cell constituents. Sample buffer (Nacalai Tesque) was added in the same amounts as the sample, boiled at 100° C. for 5 minutes and ice-cooled. The protein concentration in the obtained sample was measured using BCA Protein Assay Reagent (PIERCE).
2. SDS-PAGE
[0166]Gel mini plate for electrophoresis (PAG mini “Daiichi”; Daiichi Pure Chemicals Co.) and running buffer were used to perform SDS-PAGE. The amount of protein used was 5 μg. The electrophoresis conditions were 10 mA in the stacking gel and 40 mA in the running gel.
3. Western Blot
[0167]The electrophoresed gel above was washed in blotting buffer for 10 minutes. Next, the proteins in the gel were copied o...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com