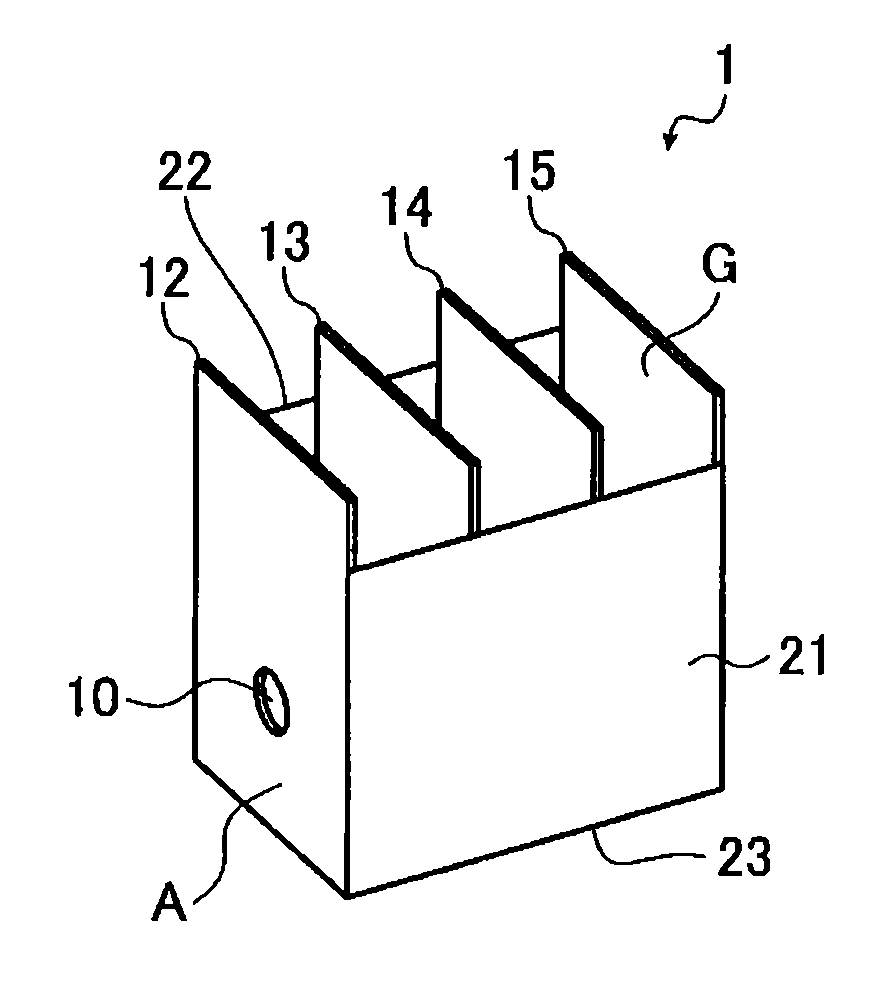
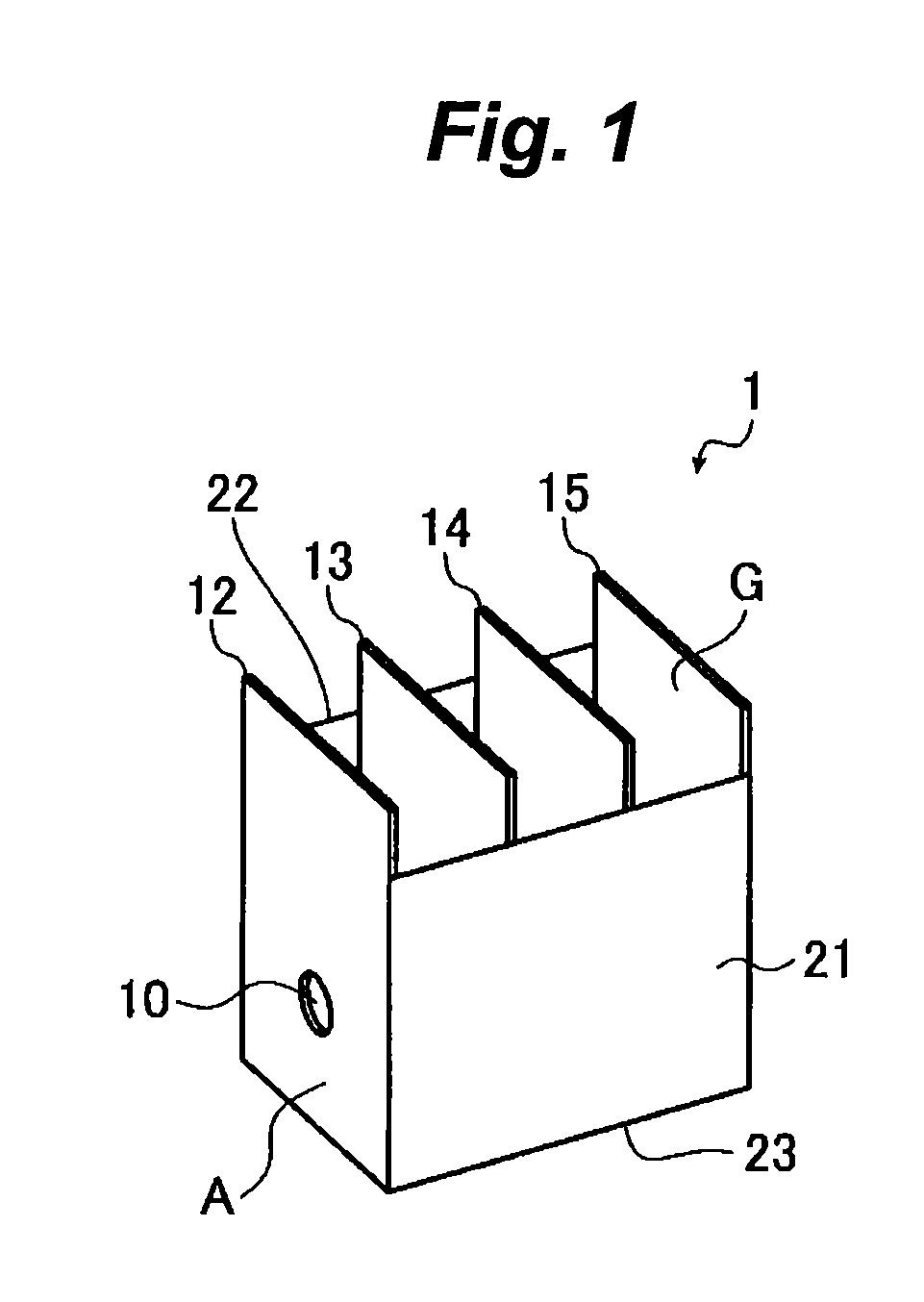
Chemical conversion solution for metal structure and surface treating method
a chemical conversion solution and metal structure technology, applied in electrophoretic coatings, solid-state diffusion coatings, coatings, etc., can solve the problems of insufficient throwing power during electrodeposition, insufficient environmental point of view, and damage to human body, etc., to achieve high coating adhesion of metal surfaces, high throwing power, and corrosion resistance.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0157]Chemical conversion solution 1 having the following composition was prepared, and surface treatment of the three types of the metal plate and the box as described below was conducted by the surface treating method (1) to form a chemical conversion film. The chemical conversion solution 1 was prepared by adding the following components (A) to (F) to 80% of the total content of water in the order of (F), (A), (B), (D), and (E), finally adding water to the predetermined volume, and stirring at room temperature for 20 minutes. The solution was heated to the predetermined temperature, and pH was adjusted. The surface treated metal plate was rinsed with water, and then with deionized water, and without drying, the metal plate was subjected to the electrodeposition by using the procedure and conditions as described above to thereby form the coating.
[0158]Chemical Conversion Solution 1
[0159](A): tin fluoride, 0.2 mmol / L
[0160](B): fluorotitanic acid, 3 mmol / L
[0161](C): nitrate radical ...
example 2
[0174]Chemical conversion solution 2 having the following composition was prepared, and surface treatment of the three types of the metal plate and the box was conducted by the surface treating method (3). The chemical conversion solution was prepared by adding the following components (A) to (F) to 80% of the total content of water in the order of (F), (A), (B), (D), and (E), finally adding water to the predetermined volume, and stirring at room temperature for 20 minutes. The solution was heated to the predetermined temperature, and pH was adjusted. The surface treated metal plate was rinsed with water, and then with deionized water, and without drying, the metal plate was subjected to the electrodeposition by using the procedure and conditions as described above to thereby form the coating.
[0175]Chemical Conversion Solution 2
[0176](A): tin fluoride, 1 mmol / L
[0177](B): fluorotitanic acid, 5 mmol / L
[0178](C): nitrate radical from (D) and (E), 40 mmol / L
[0179](D): aluminum nitrate, 10...
example 3
[0184]Chemical conversion solution 3 having the following composition was prepared, and surface treatment of the three types of the metal plate and the box was conducted by the surface treating method (2). The chemical conversion solution was prepared by adding the following components (A) to (F) to 80% of the total content of water in the order of (F), (A), (B), (D), and (E), finally adding water to the predetermined volume, and stirring at room temperature for 20 minutes. The solution was heated to the predetermined temperature, and pH was adjusted. The surface treated metal plate was rinsed with water, and then with deionized water, and without drying, the metal plate was subjected to the electrodeposition by using the procedure and conditions as described above to thereby form the coating.
[0185]Chemical Conversion Solution 3
[0186](A): germanium fluoride, 0.5 mmol / L
[0187](B): fluorotitanic acid, 0.1 mmol / L; fluorozirconic acid, 0.5 mmol / L
[0188](C): nitrate radical from (D) and (E...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Molar density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Molar density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Molar density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com