Polycarbonate copolymer and method of producing the same
a polycarbonate and copolymer technology, applied in the field of polycarbonate copolymer and method of production, can solve the problems of insufficient heat resistance and transparency of polycarbonates described in patent documents 1 to 5 and achieve the effects of low refractive index, high thermal stability, and large abbe number
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
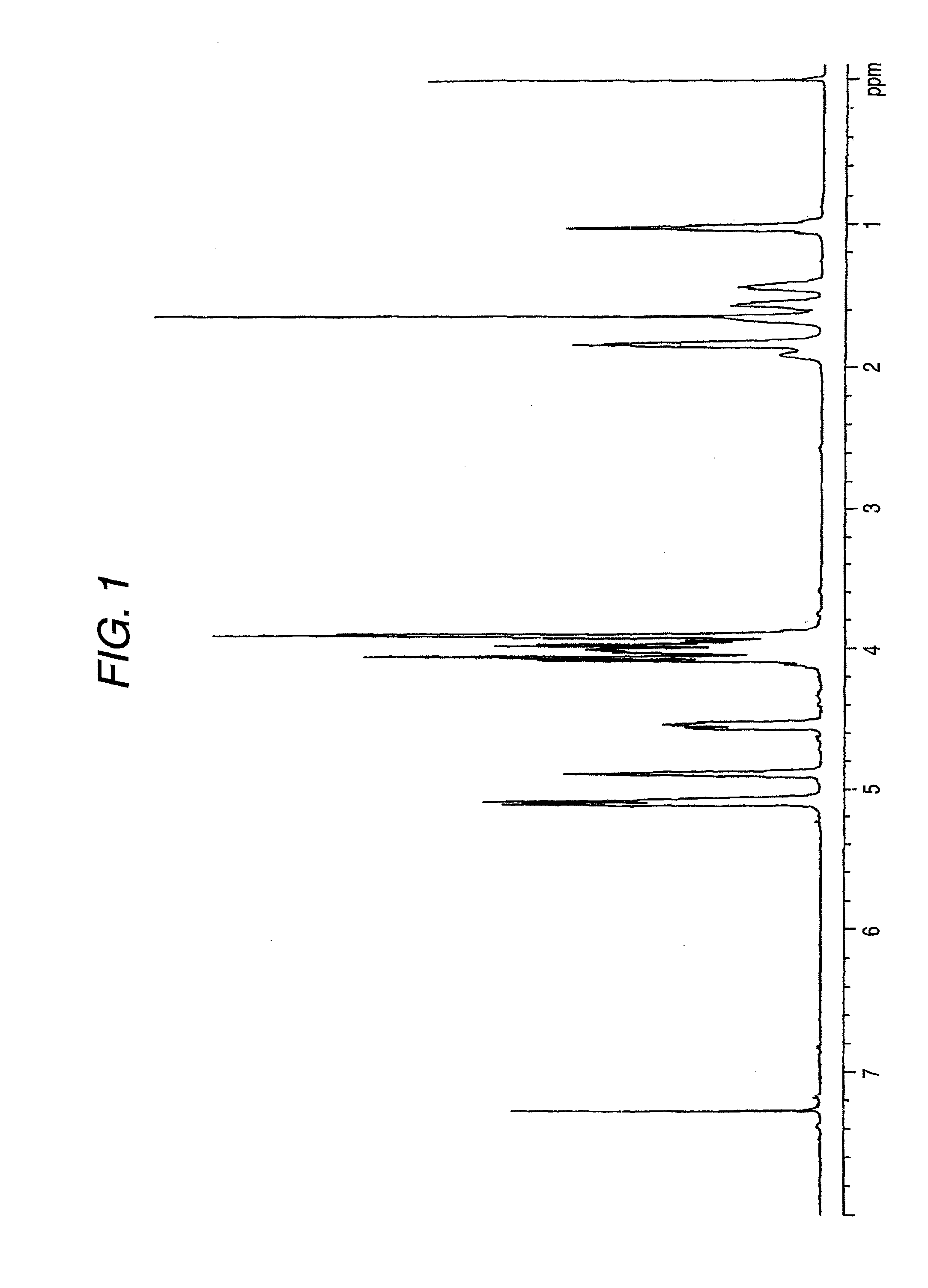
example 1
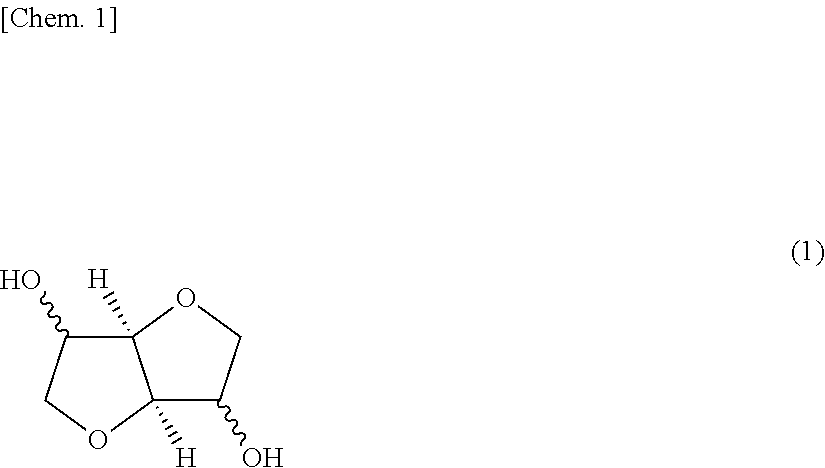
[0175]Into a reaction vessel, 13.0 parts by weight (0.246 mol) of 1,4-cyclohexanedimethanol (hereinafter simply referred to as “1,4-CHDM”), 59.2 parts by weight (0.752 mol) of diphenyl carbonate (hereinafter simply referred to as “DPC”) and 2.21×10−4 parts by weight (1.84×10−6 mol) of cesium carbonate as a catalyst were charged per 27.7 parts by weight (0.516 mol) of isosorbide. As a first step of the reaction, these raw materials were dissolved under heating at a heating bath temperature of 150° C. while stirring, if desired, in a nitrogen atmosphere (about 15 minutes).
[0176]Subsequently, the pressure was adjusted from normal pressure to 13.3 kPa and while elevating the heating bath temperature to 190° C. over 1 hour, the generated phenol was extracted outside of the reaction vessel.
[0177]After keeping the entire reaction vessel at 190° C. for 15 minutes, as a second step, the pressure in the reaction vessel was adjusted to 6.67 kPa, the heating bath temperature was elevated to 230...
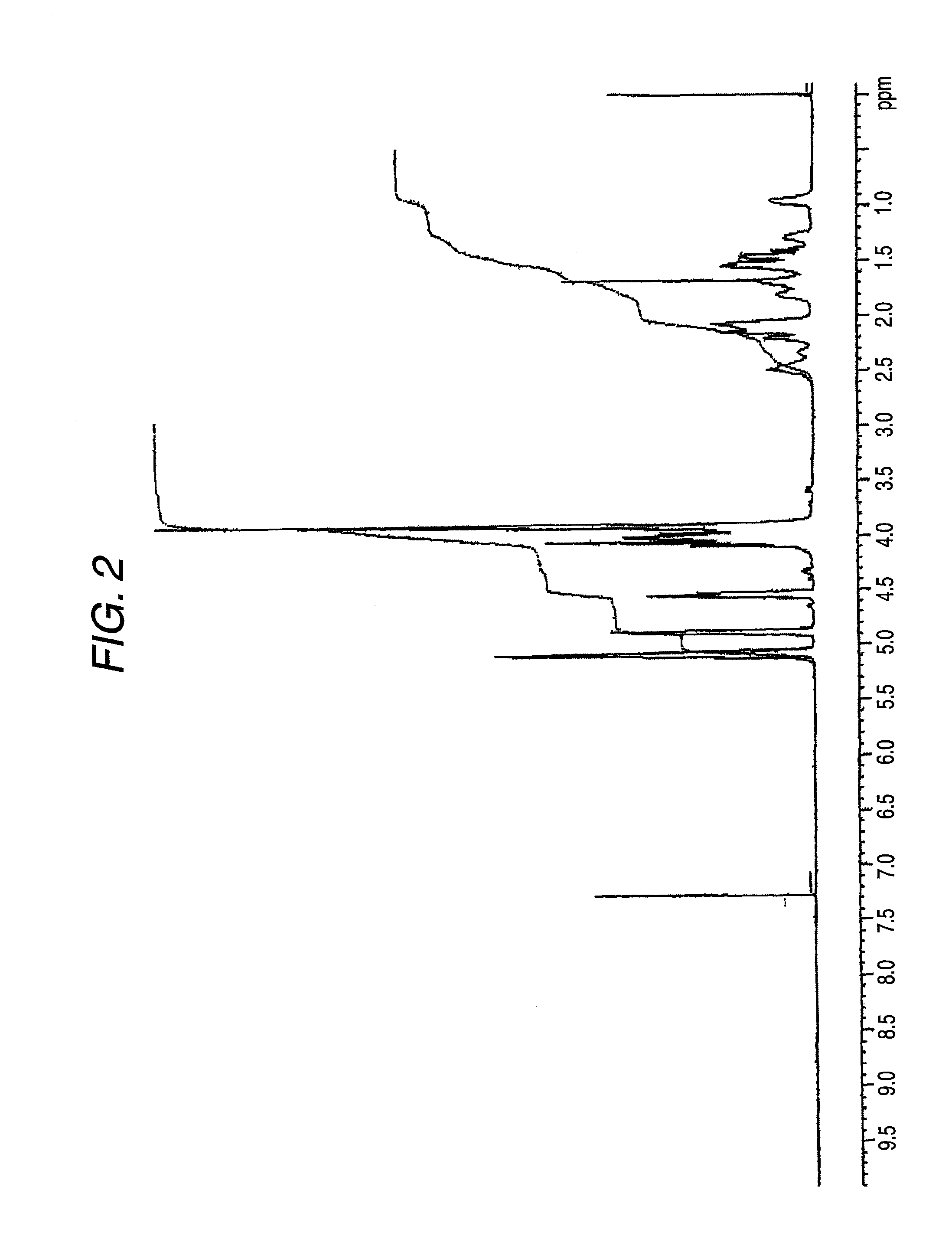
example 2
[0184]Into a reaction vessel, 31.8 parts by weight (0.458 mol) of isosorbide, 8.7 parts by weight (0.127 mol) of 1,4-CHDM, 59.5 parts by weight (0.583 mol) of DPC and 2.22×10−4 parts by weight (1.43×10−6 mol) of cesium carbonate as a catalyst were charged. As a first step of the reaction, these raw materials were dissolved under heating at a heating bath temperature of 150° C. while stirring, if desired, in a nitrogen atmosphere (about 15 minutes).
[0185]Subsequently, the pressure was adjusted from normal pressure to 13.3 kPa and while elevating the heating bath temperature to 190° C. over 1 hour, the generated phenol was extracted outside of the reaction vessel.
[0186]After keeping the entire reaction vessel at 190° C. for 15 minutes, as a second step, the pressure in the reaction vessel was adjusted to 6.67 kPa, the heating bath temperature was elevated to 240° C. over 20 minutes, and the generated phenol was extracted outside of the reaction vessel. With an increase in the stirring...
example 3
[0191]The reaction was performed in the same manner as in Example 2 except for changing the raw materials to 35.9 parts by weight (0.674 mol) of isosorbide, 4.4 parts by weight (0.083 mol) of 1,4-CHDM, 59.7 parts by weight (0.764 mol) of DPC and 2.22×10−4 parts by weight (1.87×10−6 mol) of cesium carbonate as a catalyst.
[0192]The reduced viscosity of the obtained polycarbonate copolymer was 0.712 dl / g, the glass transition temperature Tig was 148° C., and the color b value was 9.1. These results are shown in Table 1.
[0193]Also, when this polycarbonate copolymer was pressed at 200° C. and formed into a film having a thickness of about 200 μm, the refractive index for d line was 1.5014 and the Abbe number was 57. These results are shown in Table 3.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thermal reduction temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Abbe number | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Izod impact strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com