Sos substrate having low surface defect density
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
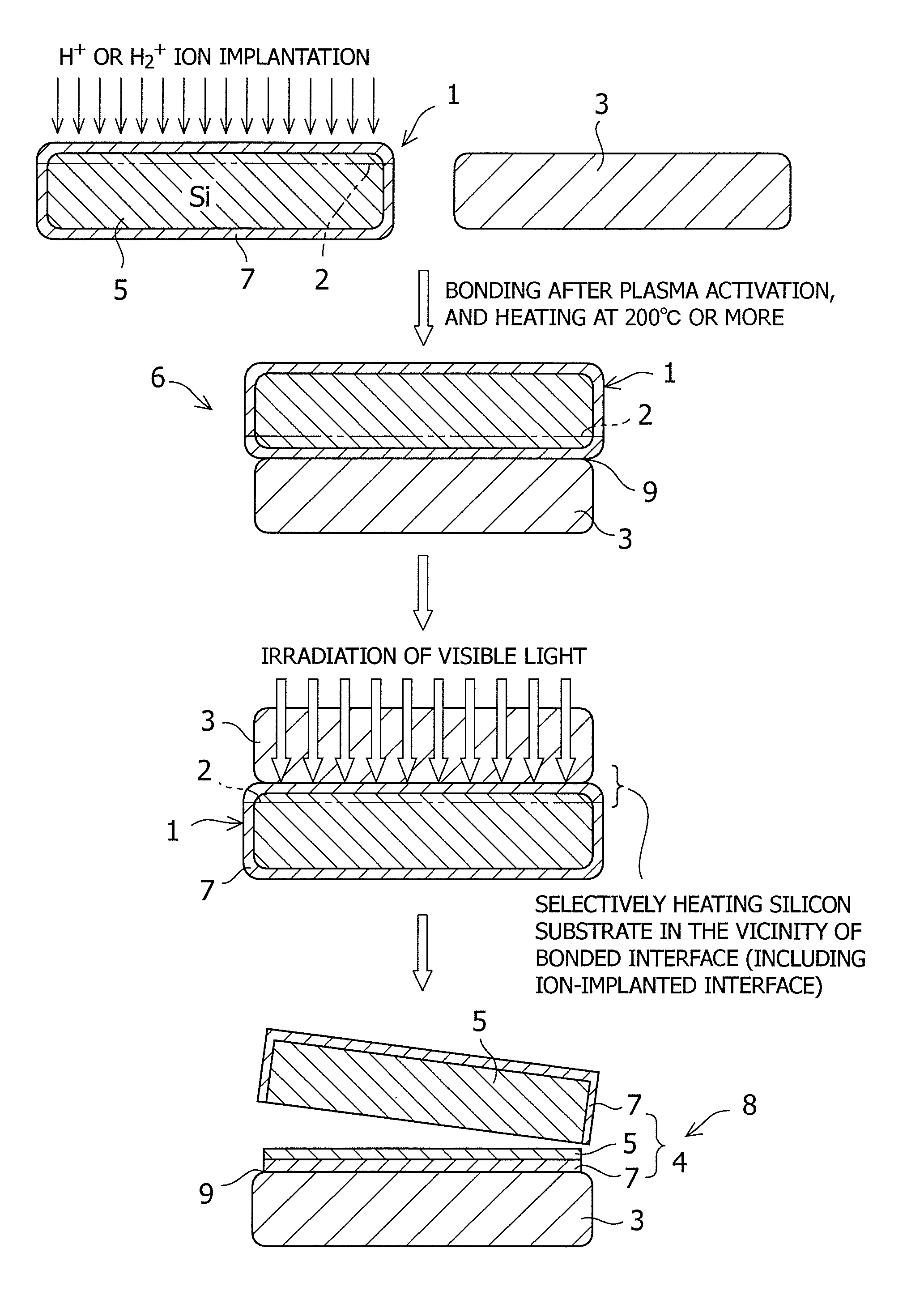
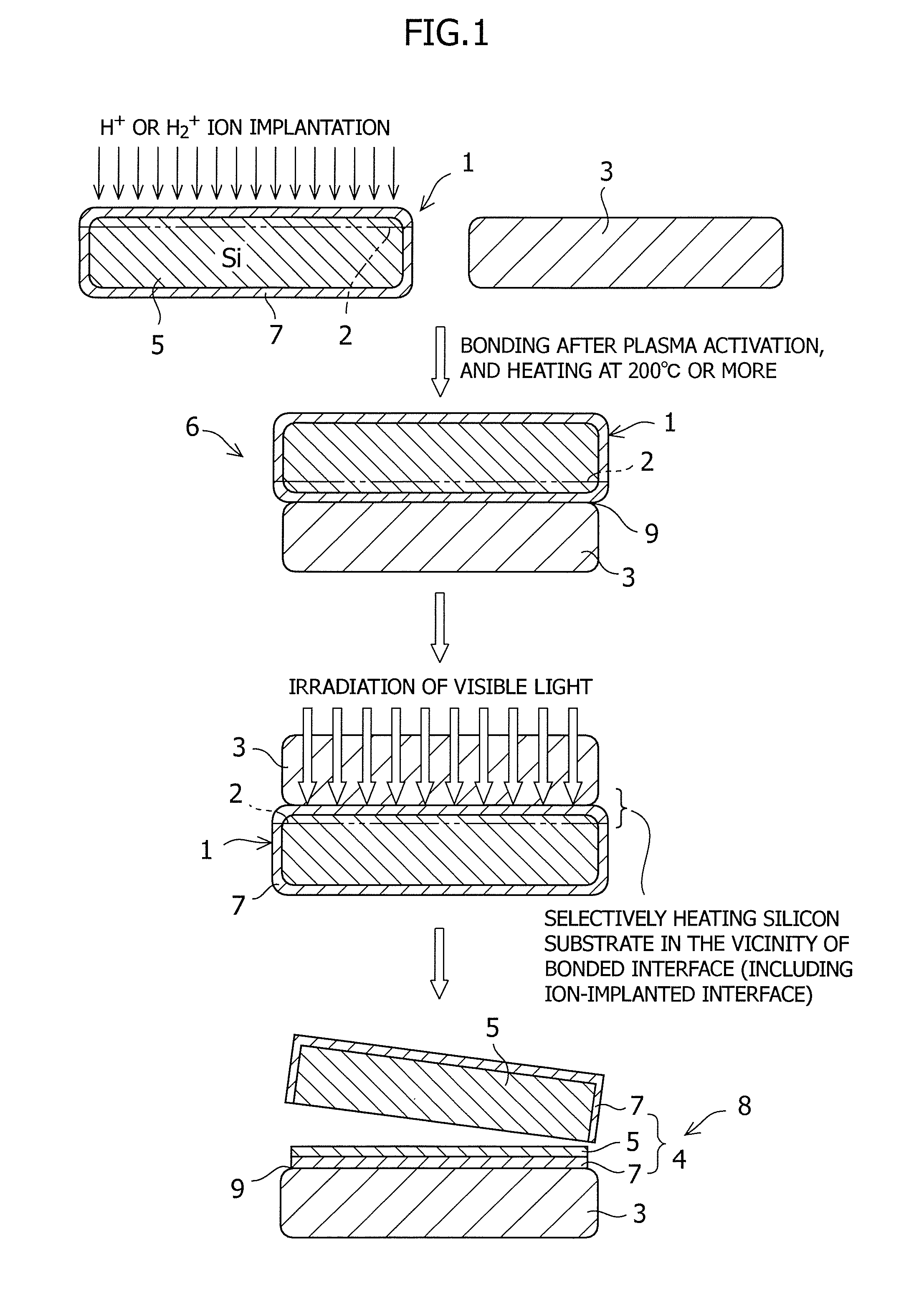
[0070]A silicon substrate (thickness 625 μm) having a diameter of 150 mm on which an oxide film had been grown to 200 nm was subjected to implantation of hydrogen ions at 57 keV and a dose amount of 6.0×1016 atoms / cm2. Both surfaces of a sapphire substrate were subjected to ion beam activation treatment. Then the silicon substrate was bonded to the sapphire substrate at 150° C. After the bonded substrates were subjected to heat treatment at 225° C. for 24 hours for primary bonding, a green laser having a wavelength of 532 nm was irradiated from the sapphire substrate side at 200° C. A laser condition at the time was 20 J / cm2. After the overall surface of the substrate was irradiated, a silicon film was transferred to the sapphire substrate by splitting along the bonded interface to which a mechanical impact was applied. The transfer of the silicon film onto the overall surface of the sapphire substrate could be confirmed. After the silicon layer of the substrate was made to a thickn...
example 2
[0071]A silicon substrate (thickness 625 μm) having a diameter of 150 mm on which an oxide film had been grown to 200 nm was subjected to implantation of hydrogen ions at 57 keV and a dose amount of 6.0×1016 atoms / cm2. Both surfaces of a sapphire substrate were subjected to plasma activation treatment. Then the silicon substrate was bonded to the sapphire substrate at 200° C. After the bonded substrates were subjected to heat treatment at 225° C. for 24 hours for primary bonding, light from a xenon plash lamp was irradiated from the sapphire substrate side at 250° C. After the overall surface of the substrate was irradiated, a silicon film was transferred to the sapphire substrate by splitting along a bonded interface to which a mechanical impact was applied. The transfer of the silicon film onto the overall surface of the sapphire substrate could be confirmed. After the silicon layer of the substrate was made to a thickness of 200 nm by etching (an ammonia hydrogen peroxide solutio...
example 3
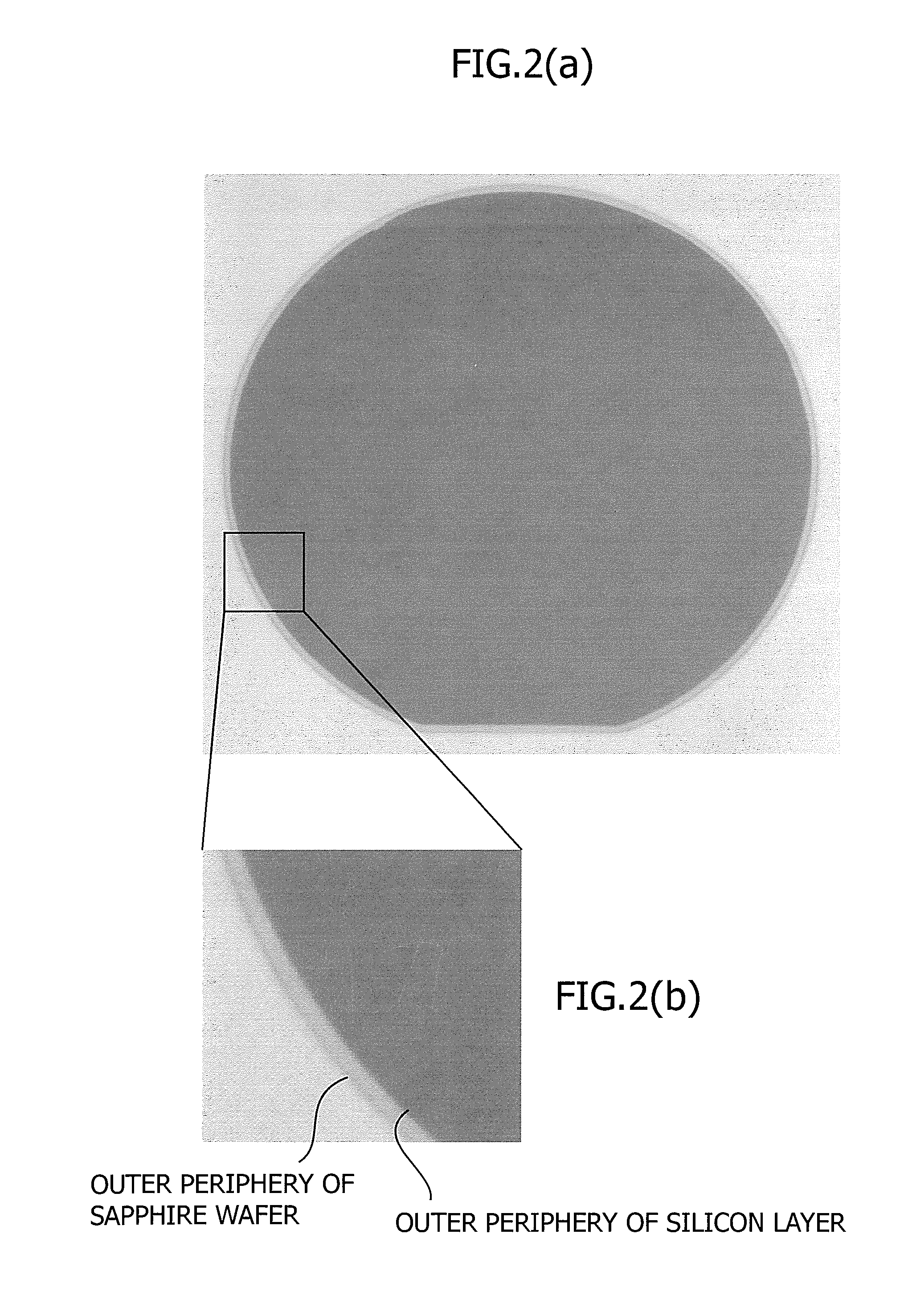
[0073]A silicon substrate (thickness 625 μm) having a diameter of 150 mm on which an oxide film had been grown to 200 nm was subjected to implantation of hydrogen ions at 57 keV and a dose amount of 6.0×1016 atoms / cm2. Both surfaces of a sapphire substrate were subjected to UV ozone activation treatment. Then, the silicon substrate was bonded to the sapphire substrate at 100° C. After the bonded substrates were subjected to heat treatment at 225° C. for 24 hours for primary bonding, light from a xenon flash lamp were irradiated from the sapphire substrate side at 175° C. After the overall surface of the substrate was irradiated, a silicon film was transferred to the sapphire substrate by splitting along a bonded interface to which a mechanical impact is applied. The film thickness was made to about 250 nm by EDP polishing and CMP polishing. Since splitting and transferring were regulated by an ion implanted interface, the film thickness variation after the transfer was suppressed to...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com